The text is presented for informational purposes only. We strongly urge you not to self-medicate. When the first symptoms appear, consult a doctor. We recommend reading: “Why you can’t self-medicate?”
Symptoms of diabetes mellitus are a set of clinical manifestations specific to a given disease, which indicate to doctors and patients the emergence or progression of a pathological process.
Diabetes mellitus is recognized as one of the most common diseases in the world; today it affects 347 million people worldwide. According to statistics, in just two decades the number of cases has increased more than 10 times. Approximately 90% of these people have type 2 diabetes. If pathology is detected in the initial stages, a huge number of serious complications can be avoided. That is why it is so important to know what indicates the onset of the disease, and how a person needs to be examined in order to be able to control this severe endocrinological pathology. The manifestations of diabetes do not depend on its type. The human body is able to understand when a sufficient level of energy stops coming from the glucose necessary in this case, as a result of a violation of its metabolism, and it remains in excess in the bloodstream, causing colossal irreversible damage to systems and organs. Disturbed metabolic processes in the body are caused by a lack of insulin, which is responsible for the process of glucose metabolism. But the features of the pathogenesis of diabetes mellitus of the first and second types have significant differences, so it is necessary to know exactly the symptoms of each of them.
Causes of female diabetes mellitus
The main reason for the development of the disease is genetic predisposition.
If the parents suffered from high blood sugar, the child will inherit this unpleasant pathology. You can identify the presence of genes with a deviation marker using DNA analysis. A test conducted in our laboratory will help determine whether you are at risk of insulin deficiency. This will make it possible to start therapy as early as possible and stop the development of the disease. There are other factors that provoke diabetes:
- Having excess weight. Excessive fat mass disrupts metabolism and acts as a guardian of possible pathologies.
- Infectious pathologies.
- Stress and overwork. This factor is especially dangerous for women over 30.
- Bad habits, especially smoking. Resins contaminate blood vessels and interfere with the normal functioning of the circulatory system.
Why do we need glucose
The term “blood sugar,” used in everyday life, was coined by medieval doctors who believed that complaints of frequent pustules on the skin, thirst and frequent trips to the toilet were associated with excess sugar in the body.
In this case, we are talking about glucose - ultimately, all carbohydrates are broken down into it. Its amount must be adjusted so that all cells, and first of all, the brain, freely receive a valuable source of energy, and are not excreted by the kidneys in the urine.
If the body experiences a deficiency of glucose, for normal functioning it will consume fats, the breakdown of which produces ketone bodies - toxins dangerous to the brain, and the body as a whole.
Remember a sick child: an acetonemic state can be recognized by convulsions, vomiting, weakness, and drowsiness. With a carbohydrate deficiency, the child’s body takes energy from fats.
Part of the glucose coming from outside is stored by the liver in the form of glycogen. When there is a lack of glucose, special hormones convert complex carbohydrates into glucose. The concentration of glucose in the bloodstream is regulated by the hormone insulin, synthesized by beta cells of the pancreas.
Other hormones also affect its level:
- Adrenaline, norepinephrine, glucocorticoids are hormones synthesized in different parts of the adrenal glands;
- Glucagon – activated when sugar levels drop below normal;
- “Command hormones” of the hypothalamus and pituitary gland in the head are responsible for the synthesis of adrenaline and the possibility of glucocorticoids.
Other hormone-like compounds also increase sugar levels, but the reverse processes are regulated only by insulin. The autonomic nervous system stimulates their performance: the decrease is controlled by the parasympathetic department, the increase is controlled by the sympathetic department.
Is there a circadian rhythm for glucose? The minimum readings on the glucometer can be observed at 3-6 am. Metabolic disorders are expressed in increased plasma glucose levels (hyperglycemia) and decreased levels (hypoglycemia). Both conditions are extremely undesirable for the body.
Why is high sugar dangerous?
Glucose serves as a source of energy only after entering the cell. In this case, its conductor is endogenous insulin produced by the pancreas. If there is not enough of it or, for various reasons, it loses its ability to work, glucose accumulates in the blood, and the cells continue to starve, requiring a new portion of food from us.
Excess unprocessed glucose is transformed into visceral fat, which is deposited on internal organs. Part of the reserve is stored by the liver, producing glucose when its intake from food is insufficient.
If your blood sugar rises during the day, what to do will depend on the time of measurement: before or after meals. In order for food to be converted into life energy and not stored in the “fat depot”, creating the preconditions for new health problems, it is important to maintain glycemic balance.
Excess glucose, as well as lack of it, is detrimental to the human body. Sugars in it act as oxidizing agents, forming various protein and acid compounds.
The inflammatory process in cells is called glycation. Its result is the synthesis of toxins that can persist in the body for up to one year. It is clear that with increasing glucose concentration, poisoning by toxins occurs more actively.
There is another risk factor that increases the concentration of free radicals. This is oxidative stress, which provokes the development of serious diseases:
- Retinopathy, visual impairment;
- Pathologies of the heart and blood vessels;
- Kidney failure;
- Degenerative changes in the brain;
- Increased aging of the body as a whole.
At a minimum, high glucose levels contribute to decreased performance, weight gain, and increased blood pressure.
Hyperglycemia
What to do if your blood sugar has risen? High sugar in the bloodstream can be an adaptive reaction that guarantees the supply of energy to tissues during high energy consumption (during muscle strain, severe pain, overexcitation, panic). Such changes are usually short-lived and do not give cause for concern.
If the glucometer constantly shows elevated sugar readings, it means that it accumulates in the blood faster than the body can process it. In such a situation, a malfunction of the endocrine system is possible: dysfunction of the pancreas, intoxication of the body, and the appearance of sugar in urine tests.
Manifestation of diabetes in the early stages
The peculiarity of this disease is that external signs may not appear for several years after the onset of development. This leads to the fact that the pathology manages to cause significant harm to the body before treatment begins. It is important for women to be able to identify subtle signals of distress in the body.
You should definitely consult a doctor if you notice the following signs:
- Decreased performance and fatigue. Moreover, this condition does not go away even after proper rest.
- Attacks of drowsiness and lethargy that regularly occur after eating.
- Persistent dry mouth. This is the main and practically the first sign of diabetes in women. Can't quench your thirst no matter how much you drink? You need to see a doctor urgently.
- Rapid weight loss, in which you constantly feel hungry and can eat quite a lot.
- Itching and ulcers on the skin, wounds whose origin you cannot explain.
What sugar levels are considered normal?
Normal glucose levels in the bloodstream are those numbers that are considered optimal for the normal functioning of the body and the course of vital processes. There are numbers approved by the Ministry of Health that are considered normal. Indicators depend on the following points:
- venous blood is used for testing or capillary;
- age group;
- the presence of concomitant pathological processes.
From the moment of birth and during the first 28 days of the child’s life, the maximum allowed is 4.4 mmol/l. If glucose is below 2.8 mmol/l, you can think about its critical reduction. From 1 month of life to 5-6 years, the permissible maximum rises to 5 mmol/l, then to 5.55 mmol/l, which corresponds to the glycemic levels of an adult.
Important! The minimum threshold is 3.33 mmol/l; if the numbers decrease, we are talking about hypoglycemia. Both conditions (hyperglycemia, hypoglycemia) are considered dangerous for the human body.
During pregnancy, the sugar norm remains the same as for an adult, however, during this time, the development of gestational diabetes is possible. This is a condition in which a woman's body cells lose sensitivity to insulin (similar to non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus). The pathology disappears after the baby is born.
You can read more about the increase in sugar during pregnancy in this article.
With increasing age, the sensitivity of tissues that have insulin receptors gradually decreases, which is associated with a decrease in the number of receptors themselves and an increase in body weight. Accordingly, acceptable glycemic levels in older people shift slightly upward.
Symptoms of diabetes in women
Pathology is divided into two types. The first is called the insulin-dependent stage. It is typical for people over 30 years old. At this age, the disease develops very quickly and symptoms appear almost instantly. The presence of elevated glucose levels indicates:
- Sudden weight loss and associated weakness.
- A constant desire to drink, leading to an increased urge to urinate.
- Feeling of a metallic taste in the mouth and dry mucous membranes.
- Frequent headaches, nervousness.
- Muscle pain and spasms.
The second type is more severe.
It is difficult to treat, especially if there is a tendency to form the disease. This stage is characterized by symptoms such as:
- Serious decrease in immunity. Severe colds.
- Increased appetite leading to weight gain. Compulsive overeating.
- Increased hair loss.
The main ways to stabilize glycemia
If diabetes mellitus is diagnosed after additional examination, treatment is prescribed by an endocrinologist. When choosing a therapeutic course and a specific medication, the type of diabetes, the stage of hyperglycemia, the presence of chronic diseases, age, BMI (body mass index) and other individual characteristics are taken into account.
By strictly following the recommendations of your doctor, the disease can be kept under control and the development of complications can be delayed as much as possible. What to do if a prediabetic condition is confirmed? Most often, to normalize glucose levels, it is enough to adjust the diet.
It is necessary to adhere to the therapeutic diet “Table No. 9” (according to V. Pevzner’s classification). Proper nutrition consists of a clear distinction between foods that are healthy and harmful when you have high sugar levels. The basis of the menu should be fresh vegetables, cereals and legumes, lean meats and fish.
You can bring your glucose level back to normal using traditional medicine recipes. Popular plants with diabetics that have hypoglycemic properties are ginger, cinnamon, galega herb, bay leaf, etc. Regular exercise and walks in the fresh air help reduce sugar.
Important! To correctly create a menu and select folk remedies to lower glucose, you need to contact an endocrinologist.
Symptoms in pregnant women
It is very difficult to track how diabetes mellitus begins in pregnant women. Hormonal changes in the body make it difficult to determine the presence of abnormalities using tests. Glucose and insulin levels fluctuate within normal limits at this time. But already from the second trimester it becomes clear whether there is pathology. It is during this period that the level of danger is determined. The main external sign indicating the development of the problem is a sharp deterioration in vision.
During the development of this pathology, the condition of the genitourinary system worsens. Exacerbation of infectious diseases of this type occurs even with absolute hygiene. High blood pressure that does not return to normal for a long time will also indicate the presence of problems. Impaired protein synthesis leads to the formation of these elements in the urine. If a girl is registered with a gynecologist, she undergoes tests regularly. This helps to identify abnormalities in time and begin therapy. But for those who neglect going to the doctor, there is a high probability of not recognizing the onset of trouble.
Diet for high blood sugar
Doctors in Russian-speaking countries traditionally prescribe diet No. 9 for high blood sugar. However, it does not help, despite the fact that it causes a chronic feeling of hunger. That's why Endocrin-Patient.Com promotes the low-carbohydrate diet that Dr. Bernstein developed. It is suitable for adults, children and even pregnant women to bring sugar back to normal and keep it consistently normal. Diet is the main treatment for impaired glucose metabolism. Study carefully both options presented above.
What foods are recommended to eat?
Read and use the list of approved and recommended products. It is advisable to print it out, hang it in the kitchen, and take it with you to the store and to the market. You will also need a sample menu for the week and a list of prohibited foods.
Find out in what quantities you can eat cherries, strawberries, apricots, apples, and other fruits and berries. As for cereal products, patients are interested in semolina, pearl barley, buckwheat, barley, millet, corn porridge, as well as white and brown rice dishes.
Read more about the products:
- Bee honey - buckwheat, white acacia, instead of sugar
- Porridge - buckwheat, rice, millet, barley and others
- Oil - butter, olive, flaxseed, coconut
- Nuts - walnuts, hazelnuts, almonds, cashews, pistachios and others
- Fruits and berries
Alcoholic drinks that do not contain sugar or other dietary carbohydrates do not increase blood glucose levels. These are vodka and other 40-proof drinks, as well as red and white dry wine. The listed alcoholic beverages can be consumed if you are able to maintain moderation. Sweet and semi-sweet wines, liqueurs, and beer, especially dark ones, are prohibited. At the same time, you can keep your blood sugar within normal limits without becoming an absolute teetotaler. Read the article “Alcohol for Diabetes” for more details.
Diet for high sugar in pregnant women
Pregnant women who have high blood sugar are advised to follow a low-carbohydrate diet. Thanks to this diet, you can keep your glucose levels normal without any insulin injections or using minimal doses. Let us remind you that you cannot take any diabetes pills during pregnancy. A low-carb diet can lead to ketones (acetone) in the blood and urine. Doctors scare pregnant women that this can cause miscarriage or developmental disorders in the offspring. They are wrong. The appearance of acetone is normal and not harmful. For more details, watch the video below.
Hundreds of American women have already carried and given birth to healthy children, eating no more than 20-25 g of carbohydrates per day throughout pregnancy. Such nutrition normalizes not only blood sugar, but also blood pressure, eliminates edema, and reduces the risk of preeclampsia. Drink plenty of fluids and stay hydrated. Talk to your doctor about whether you should take magnesium-B6 tablets. Read the articles “Diabetes in Pregnancy” and “Gestational Diabetes” for more information.
Is it worth switching to diet No. 9?
Read the detailed article “Table No. 9: diet for diabetes.” This diet is very popular in Russian-speaking countries.
Diet for high sugar in a child
As a rule, the cause of high sugar in a child is type 1 diabetes. This is not a disaster; there are much worse diseases. It is important to switch not only the sick child to a low-carbohydrate diet, but also all other family members, so that there are no prohibited foods at home. Adults who are overweight will benefit from this diet. It will not bring much benefit to slender and thin family members, but it will not harm either; it can be followed for company.
Such food is not cheap, but tasty and healthy. Everyone likes it except vegetarians. A strict low-carbohydrate diet prolongs the honeymoon period for type 1 diabetes in children. Theoretically, this wonderful period can last indefinitely. In practice, some families have been keeping it for several years and have no plans to stop. However, attempts to change a child’s diet in isolation from all other family members are obviously doomed to failure. Read the article “Diabetes in Children” for more information.
Below are answers to some more frequently asked questions from patients.
Can high blood sugar raise blood pressure?
Elevated sugar gradually destroys blood vessels. Over time, this can cause hypertension, heart attack or stroke. But usually, blood glucose levels and blood pressure are not related in any way. In a patient, both of these indicators can be simultaneously increased, decreased, or one of them is increased and the other is decreased. Impaired glucose metabolism and arterial hypertension must be controlled separately. In people who are overweight, a low-carb diet brings blood sugar and blood pressure back to normal in just a few days. Doses of antihypertensive drugs can and should be significantly reduced, usually to the point of complete failure. Hypertension in thin people is a more serious disease. Read about its causes and treatment options here.
Increased insulin and blood sugar at the same time
In people who are overweight in the early stages of type 2 diabetes, insulin and blood sugar are often elevated at the same time. First, tissues lose sensitivity to insulin due to overeating carbohydrates and a sedentary lifestyle. The pancreas tries to produce more insulin in order to push glucose into the cells and reduce its concentration in the blood.
However, this increased load depletes beta cells over time. After a few years, they still produce insulin in excess, but not enough to keep their sugar levels normal. Without treatment and lifestyle changes, insulin levels in the blood will begin to fall and glucose levels will begin to rise. The disease will eventually progress to severe type 1 diabetes unless the patient dies sooner from complications.
What time of day is blood sugar highest?
For most patients, sugar levels are highest in the morning on an empty stomach. Around 4-6 am, adrenaline, cortisol and other stress hormones begin to enter the bloodstream. They force the body to wake up, and at the same time greatly increase the level of glucose in the blood. Their effect ceases around 8-10 am.
This is a common problem called dawn phenomenon. Diabetics have to make a lot of efforts to fight it. Read more about how to normalize your blood sugar in the morning on an empty stomach. After breakfast, glucose levels may paradoxically decrease, despite the fact that eating should increase them.
In some patients, sugar in the morning on an empty stomach remains normal, but regularly rises towards lunch or in the evening. It is important to establish this individual feature of the course of diabetes, and then adapt to it. Test your glucose levels frequently to find out how they typically behave at different times of the day. After this, make the necessary changes to your diet, schedule of taking pills and insulin injections.
Why is sugar elevated in the morning on an empty stomach, but normal the rest of the day?
Sugar in the morning on an empty stomach is higher than in the afternoon and evening - this is a problem for most diabetics. Don't consider yourself an exception in this sense. The reason is called the dawn phenomenon. In the morning, a few hours before waking up from sleep, the hormonal levels in the blood change so that the liver intensively takes and breaks down insulin. There is not enough of it to keep your sugar normal. When a diabetic measures his glucose level after waking up, it is elevated. Read the article “Sugar in the morning on an empty stomach: how to bring it back to normal.” Achieving normal levels may be difficult. However, don't be lazy to do this. Otherwise, chronic complications of diabetes will gradually develop.
Cause of high blood sugar in the morning on an empty stomach
Diabetes pills taken before bed wear off in the middle of the night. He's missing until the morning. Unfortunately, the same problem often occurs with an evening injection of extended-release insulin. As a result, the weakened pancreas does not have enough funds to compensate for the effect of the dawn phenomenon.
The worst thing is if a diabetic is used to having dinner late. This is absolutely impossible to do. Find out in detail on this site how to normalize your sugar in the morning on an empty stomach. Don't even dream of achieving this until you give up the bad habit of having dinner late.
Features of the course in girls
Statistics show that women are much more likely to suffer from the manifestations of pathology.
This especially applies to the second type of disease. This is due to the fact that the weaker sex has more adipose tissue, and, on the contrary, less muscle mass than men. The fact is that adipose tissue does not absorb insulin and does not utilize glucose well. Girls are also more susceptible to stress, which provokes the release of steroid hormones and increased glucose levels. A particular danger in the development of pathology is the love of sweets. Frequently eating cakes and pastries leads to an increase in fat. This leads to activation of the disease in women. Girls also develop another type of pathology - gestational. But we'll talk about it later.
What will help resist the disease?
If you receive a conclusion from the laboratory: “Blood test: increased glucose,” what does this mean? The fact that it is necessary to take a number of specific measures as soon as possible, depending on the neglect of the situation, which the “2hGP” analysis will help to clarify.
- If diabetes is not confirmed, but glucose levels are significantly elevated, it is necessary to eliminate carbohydrates almost completely.
- If you have diabetes, the diet should be accompanied by taking medications prescribed by the doctor, and monitoring of sugar levels is also required.
Skin manifestations
The course of the disease rarely affects the condition of the skin. However, sometimes changes are observed that indicate problems with glucose production. It is worth paying attention to:
- Peeling and dry skin that were not noticed before.
- Darkening of folds. This is typical for type 2 diabetes.
- Premature aging of the skin. This is due to the fact that pathology can cause aging of the entire organism. This is reflected very strongly on the skin.
Such changes occur very slowly and most people simply do not pay attention to them. It's also worth remembering that these signs may indicate other health problems. It is worth getting tested if you find yourself with similar symptoms. This will help determine the source of the symptoms and eliminate it.
Classification
There are several degrees of the condition, which are divided depending on sugar levels:
- Mild degree - glucose does not exceed 8.3 mmol/l. Signs may be mild or almost invisible.
- Medium level - sugar does not cross the line of 11 mmol/l. Symptoms of the pathology are well expressed.
- Severe degree – above 11.1 mmol/l. Most people are already showing signs of ketoacidosis.
If glucose crosses the threshold of 16 mmol/l, we are talking about a critical increase, the development of a precoma state. Above 50 mmol/l – hyperglycemic hyperosmolar coma.
Signs in women over 30
At this age, as a rule, type 1 develops, a rather severe autoimmune disease.
The development and manifestation of the disease occurs rapidly and most often does not depend on the lifestyle of the sick person. This type is considered hereditary. Its development is almost impossible to prevent. Acute symptoms and early signs for this type of disease:
- nausea and vomiting,
- numbness of the limbs,
- smell of acetone from the mouth,
- thirst and hunger.
If you have these signs, you should not hesitate to get tested in the laboratory. However, you can check your sugar level with a home glucometer. However, do not forget that such a check will not give you the complete picture.
Once you are diagnosed with diabetes, do not delay consulting your doctor. You will be prescribed a special diet and treatment that will help eliminate the severe course of the disease and protect you from disability.
Signs of complications
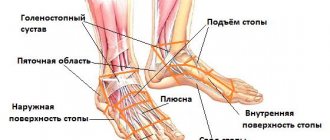
Diabetic foot
In medicine, the diabetic foot is understood as a complex anatomical and functional change in the tissues of the distal parts of the lower extremities in patients suffering from diabetes. This is the most serious complication of the pathology in question, often leading to gangrene, amputation of limbs and disability.
If you have a history of diabetes, the health of your legs should be monitored very carefully. There are three main forms of diabetic foot: neuropathic (predominant damage to nerves), ischemic (predominant damage to blood vessels and impaired blood flow), mixed.
Among the complaints of patients preceding diabetic foot, experts identify unpleasant feelings, burning and stabbing sensations in the legs, goosebumps, and a feeling of electric shock. If these troubles disappear when walking, this indicates the beginning of the development of the neuropathic form of diabetic foot. It is also important to pay attention if your feet periodically lose sensitivity. If painful sensations occur directly when walking or at night (can be calmed only by hanging the limbs from the edge of the bed), then this means the beginning of the development of an ischemic form of diabetic foot called “ischemic foot”.
Among the signs indicating the start of development of a diabetic foot, experts identify pale skin on the legs or the appearance of pigment spots on them, peeling and dry skin in this area, the appearance of different-sized blisters on the skin with clear liquid, frequent calluses, cracks between the toes, deformation of the nails. plates on the legs, thickening of keratinization of the skin of the feet, spontaneous fractures of small bones on the legs. If a person notices at least a few of these signs, he should urgently seek medical help.
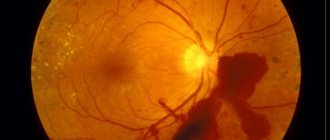
Signs of retinopathy
Diabetic ophthalmology is manifested by changes in the blood vessels in the retina of the eye, leading to disruption of microcirculation in it. This disorder leads to diabetic retinopathy. This complication develops gradually and even in the later stages it can be almost invisible to a person.
The main signs of diabetic retinopathy are:
- the appearance of “floaters” before the eyes;
- blurred vision;
- decreased visual acuity in later stages;
- hemorrhages in the vitreous body and retina.
In this case, diabetic ophthalmology can manifest itself in two main forms - non-proliferative (background) or proliferative retinopathy of the retina. With background retinopathy, the pathology primarily affects the retina itself. If there are disturbances in the capillary vessels of the retina, hemorrhages, retinal edema, and deposits of metabolic products occur. Background retinopathy is common in elderly patients with diabetes. It provokes a gradual decrease in visual acuity.
Based on the background, proliferative retinopathy develops if the deficiency of oxygen supply to the retina continues to grow. In this case, there is a pathological formation of new blood vessels growing from the retina into the vitreous body. This process leads to hemorrhages in the vitreous body and a sharp increase in the progression of vision loss in humans and irreversible blindness. In adolescence, such a transition of the complication from one form to another can occur in a couple of months, followed by retinal detachment and complete loss of vision.
Signs of encephalopathy
Diabetic encephalopathy occurs as a complication of diabetes mellitus, due to diffuse degenerative damage to the brain. The prevalence of encephalopathy directly depends on the type of diabetes, and its symptoms depend on the duration of the disease and its severity. It is a late complication and appears 10-15 years after the onset of diabetes.
Its immediate cause is metabolic disorders typical of diabetes, leading to damage to brain tissue and blood vessels. The above processes lead to impaired brain activity and decreased cognitive functions. The development of encephalopathy occurs very slowly, which makes it difficult to identify its symptoms in the early stages.
The main symptoms of diabetic encephalopathy are:
- headaches and dizziness;
- emotional instability, high fatigue, sleep disturbances and other neurasthenic disorders;
- instability of a person's gait;
- doubling of objects when looking at them, blurred vision, flashing “spots” before the eyes;
- mental, depressive disorders;
- confusion;
- deterioration of mental activity, memory, ability to concentrate;
- strokes, transient ischemic attacks, other pathologies of cerebral circulation;
- the occurrence of seizures.
At the initial stages, there are practically no clinical complications, but with the development of encephalopathy, the symptoms begin to appear more clearly. Symptoms are identical for both types of diabetes.
Frequent accompaniments of diabetes are atherosclerosis, arterial hypertension and obesity. Due to the obliteration of blood vessels when atherosclerosis occurs, the risk of ischemic strokes and heart attacks increases. When microcirculation in the renal vessels is disrupted, irreversible renal failure occurs, which over time leads to the complete cessation of renal function. This in turn leads to the need for replacement therapy for renal failure using lifelong dialysis.
Diabetic coma
A diabetic coma is understood as a serious disturbance of metabolic processes in the body of a patient suffering from diabetes. Coma can occur either with a strong increase or with a strong decrease in the level of sugar in a person’s blood.
This condition requires urgent medical attention, since in its absence serious complications and even death are possible.
Therefore, daily monitoring of glucose levels is important for type II diabetes in children and adults. At home, such an examination can be performed independently using a glucometer - a device for measuring blood sugar levels. Accuracy of measurement and ease of use are important in a glucometer.
OneTouch Select Plus Flex® is suitable even for inexperienced users and retirees who find it difficult to understand new gadgets. It is no coincidence that this glucometer has become the best-selling in Russia. What makes this device different? It is convenient - color hints help you understand at a glance what the number on the screen means. This is a simple glucometer - easy to learn how to use and easy to measure blood sugar. OneTouch Select Plus Flex® delivers accurate results, proven through years of clinical research.
The coma develops in stages, but quite rapidly. The first sign of falling into a coma may be a fainting state, a rapid increase in blood sugar, nausea and vomiting, drowsiness, pain in the abdomen a day or more before the immediate coma. Another symptom of a diabetic coma may be the strong smell of acetone from the patient’s mouth. Cramps, thirst, and decreased sensitivity may also occur.
During a hypoglycemic coma, the concentration of sugar in the blood decreases sharply. The indicator can reach 2.5 mmol per liter and below. Among the obvious symptoms of such a coma are causeless anxiety, fear of the patient, a feeling of weakness, convulsions, drop in blood pressure, and loss of consciousness. Precursors of hypoglycemic coma may include:
- general malaise;
- lack of appetite;
- diarrhea or constipation;
- dizziness, headaches, tachycardia.
Lack of help for this condition can lead to extremely serious consequences. Since hypoglycemic coma develops rapidly, the assistance provided must be prompt. Ordinary people can diagnose a diabetic coma by a sharp decrease in the patient's blood pressure, weakening of the pulse, and softness of the eyeballs. Only a qualified doctor can bring a person to his senses in this state, so an ambulance should be called as soon as possible.
Signs in women over 40
After 40 years of age, there is a danger of developing both type 1 and type 2 disorders. The main reasons for developing this pathology are a sedentary lifestyle and overeating. The autoimmune system begins to attack the pancreas, where insulin is produced. It's not known why, but thin women have a higher risk of developing diabetes without actively developing symptoms.
Insulin injections are rarely required. The main focus of treatment is on a low carbohydrate diet. A healthy lifestyle will help support the body in the fight against the problem. The main thing is not to get caught up in unhealthy sweets and other temptations. Otherwise, all previous treatment will go to waste.
Impaired glucose metabolism
To understand why sugar levels rise, it is necessary to determine the specific disorder in the process of carbohydrate metabolism. Glucose is a monosaccharide that actively nourishes the brain and provides energy to the entire body. It is formed from amino acids from eaten proteins and polysaccharides obtained from carbohydrate foods.
In a healthy body, after resorption (absorption) of a monosaccharide into the systemic circulation, its main part interacts with insulin. The pancreatic hormone moves glucose molecules into the cells and tissues of the body. To cover physical and mental energy costs, timely delivery of the monosaccharide, its adequate perception by cells and rational consumption are necessary.
A failure of a well-functioning mechanism causes:
- temporary inhibition or complete stop of insulin synthesis by pancreatic cells;
- decreased cellular sensitivity (sensitivity) to the hormone, otherwise insulin resistance.
In both cases, excess glucose accumulates in the blood, which is fraught with the development of diabetes mellitus.
Signs in women over 50
Typically, menopause begins at age 50 or older. It disrupts the metabolism in the body, provokes obesity and problems with the cardiovascular system. Also, changes in hormones lead to irritability and stress, which negatively affects the immune system.
This period of life is characterized by the development of type 2. It can be hidden, and you will not understand what signs may indicate the development of the disease. It is important to undergo timely examinations and tests to identify possible problems. This especially applies to those whose parents and other relatives suffered from this disease.
Sugar analysis: how to prepare
In order to obtain an objective result from the analysis, you cannot ignore several simple but mandatory rules.
- two days before the day of blood donation, you should give up even small doses of alcohol;
- Twelve hours must pass after eating food;
- It is not recommended to brush your teeth on the appointed day.
You can conduct a blood test either in the laboratory or at home yourself. To do this, you will need a glucometer - a device designed specifically for this purpose. The accuracy of its indicators is comparable to laboratory ones.
There is also another type of analysis called “2hGP”. What makes it different is that it is done exactly two hours after you have eaten.
How to protect yourself from diabetes
Prevention of the development of increased glucose production is quite simple. You need to follow a few tips:
- Lead an active lifestyle. If you have a sedentary job, take long walks in the evenings. Give up weekends spent on the couch watching TV. This is especially true for overweight people.
- Proper nutrition. Skip sweet baked goods in favor of whole grain ones. Add light protein foods to your diet, try not to eat foods with complex carbohydrates. Convenience foods and fatty foods are your main enemies.
- Avoid stress. Learn to protect yourself from factors leading to grief and worry. Learn to avoid negative emotions and don't allow yourself to get angry too often.
- Monitor your blood pressure closely. Frequent pressure changes lead to weakening of blood vessels and the entire body.
Consequences of diabetes in women
Without timely treatment, you risk getting serious complications, getting rid of which will be extremely difficult. The main dangers plaguing diabetics who do not adhere to doctor’s recommendations are:
- Constant swelling. Persistent swelling throughout the body is a consequence of excessive fluid retention in the body.
- Trophic ulcers. They are characteristic of a long course of the disease, which did not respond to appropriate treatment.
- Gangrene. Damage to the blood vessels of the extremities results in amputation. This outcome is typical for an advanced form that has been going on for many years.
- Coma. An extremely rare consequence of a severe form of the disease. This state is preceded by clouding of consciousness and loss of a sense of reality.
Diagnosis of diabetes in the clinic
Today, diabetes can be diagnosed in any clinic. The doctor will prescribe a series of tests to help determine your glucose level, the possible stage of the disease and the characteristics of your body.
- Blood and urine analysis. Shows your glucose level and helps guide you on the right diet to prevent disease.
- Analysis for glycosylated hemoglobin. Helps recognize fluctuations in blood sugar levels.
- Glucose tolerance. Determines the presence of disease and the level of insulin sensitivity.
What to do, how to treat
The main treatment is a low-carbohydrate diet. It is supplemented by taking medications, physical activity and insulin injections. Pills and insulin will be of little use without limiting carbohydrates in your diet. Study the article “Diagnostics of diabetes mellitus”, get examined and make an accurate diagnosis. Then read and follow the step-by-step type 2 diabetes treatment plan or type 1 diabetes management program. Try to drink at least 30 ml of fluid per 1 kg of body weight per day to prevent dehydration. Read about folk remedies for high sugar below.
What to do if your sugar and cholesterol are high
Watch Dr. Bernstein's video about the relationship between impaired glucose metabolism, high cholesterol, and a lack of thyroid hormones. Understand how to calculate the risk of a heart attack based on the levels of “bad” and “good” cholesterol in the blood.
Find out what cardiovascular risk factors to watch for besides cholesterol. A low-carbohydrate diet simultaneously improves blood sugar and atherogenicity. It does not matter whether total cholesterol decreases because it is not an important risk factor. Too low cholesterol is harmful to the brain. It increases the risk of death from traffic accidents, suicide and other causes. The video talks about this in detail.
After watching it, you will find out:
- what is the difference between high and low density lipoproteins;
- what role do triglycerides play?
- what is fibrinogen, homocysteine, serum ferritin and other cardiovascular risk factors.
Worry less about cholesterol. Remember, your ultimate goal is to avoid heart attacks and strokes, not just to lower your cholesterol so the doctor will praise you the next time you see him. High blood sugar is definitely harmful. But with high cholesterol, everything is not so clear.
What pills should you take for high blood sugar?
For slender and thin people who have developed autoimmune diabetes, no pills will help. They need to start taking insulin right away. If the patient is overweight, you need to take the medicine metformin.
Read more:
- Why is metformin prescribed - indications for use
- How to take: optimal doses and schedule for diabetes and weight loss
- Metformin: reviews from diabetics, losing weight and doctors
- Contraindications - problems with the liver and heart, and especially with the kidneys
- How to replace metformin - stronger tablets and insulin
Modern medications for type 2 diabetes are useful in some cases, in addition to metformin. However, none of them is a panacea for high blood sugar. They are expensive, and their use is not always justified. You need to understand them carefully before you buy and start taking them.
Read more about the newest medications for type 2 diabetes of the latest generation. The material will be useful for those who are already taking or are going to be treated with Forxiga, Jardins, Invokana, Suglat, Bayeta, Victoza, Lyxumia, Trulicity, Ozempic, Galvus, Januvia, Ongliza, Tragenta, Vipidia, Galvus Met, Janumet, Comboglise Prolong, Vipdomet.
If your blood sugar is 9.0 mmol/l or higher, you should immediately start injecting insulin, and then think about taking pills. A low-carbohydrate diet comes first in treatment, regardless of your pill regimen, insulin injections and physical activity. Without switching to a healthy diet, all other activities will be of little use.
Is it possible to take pills for high sugar without a doctor's prescription?
Fatty liver is a disease called fatty liver disease. In its complex treatment, metformin tablets are often used, which are also prescribed to patients with type 2 diabetes. It is usually possible to take metformin on your own initiative, without a doctor’s prescription. And it brings benefits. Provided that you have no contraindications.
Before you start taking metformin, carefully read the instructions for use. Figure out what the dosage regimen should be to minimize side effects. Also get blood and urine tests that check your kidney function. The original metformin tablets are the imported drug Glucophage. It is more effective than analogues, and at the same time has an affordable price.
The best treatment for fatty liver is a low-carb diet. Metformin and any other pills will give you no more than 10-15% of the effect compared to a healthy diet. After switching to a low-carbohydrate diet, fatty hepatosis goes away quickly and, without exaggeration, miraculously. Other complications of impaired metabolism recede later.
Do statin cholesterol medications increase sugar levels?
Cholesterol statins increase blood sugar by about 0.5-1.0 mmol/L. Diabetics may need to slightly increase their insulin or pill doses to compensate for this effect. Whether you should take statins is a controversial issue. To avoid a second heart attack - most likely, yes. For the prevention of the first heart attack - unlikely. There are rumors that statin manufacturers are downplaying the side effects of their pills. Read here a detailed and objective article about these medications.
Again, a low-carb diet improves blood cholesterol levels along with glucose levels. Get blood tests for cholesterol and other cardiovascular risk factors. Then switch to a low-carb diet. After 6-8 weeks, get tested again. Most likely, you will be so pleased with the results that you can do without statins. For triglycerides, you don't have to wait 6-8 weeks. They return to normal within 3-4 days.