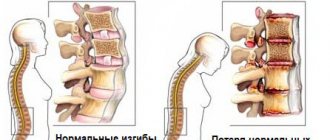
Each of us has faced a situation where medical attention is urgently required. For such emergencies, a home first aid kit is needed. It should not consist of medicines purchased in reserve: it should contain only the most necessary means.
The list of medications depends on whether there is a person with chronic diseases in the family. Also, your home first aid kit should contain first aid supplies. What should be in an ideal home medicine cabinet, and what should not be? Let's sort it out in order.
Long-lasting and new generation
In the treatment of hypertension, which is a chronic disease, medications that act for a long time are still preferable, that is, they have a prolonged effect.
The advantage of tablets that lower blood pressure over a long period of time is that they do not cause withdrawal symptoms if a dose is accidentally missed, and also do not require repeated use throughout the day, which is inconvenient for many patients.
New generation long-acting medications for high blood pressure include:
- Lercanidipine, Amlodipine - calcium channel blockers;
- Nebivolol (selective beta-blocker), Carvedilol - (non-selective alpha and beta blocker);
- Fosinopril (ACE inhibitor);
- Cardosal (olmesartan) is an AT receptor blocker;
- Rasilez (aliskiren) – selective renin inhibitors, the newest pharmacological group.
Despite the obvious advantages of drugs invented relatively recently, you should not strive to immediately switch to these blood pressure pills. This is usually expensive and not always justified, because old proven drugs have not lost their effectiveness with the advent of new ones and continue to be the medications of choice for many patients.
Medication Information
Roza Ismailovna Yagudina , Doctor of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Professor, Head. Department of Organization of Drug Supply and Pharmacoeconomics, Head. laboratory of pharmacoeconomic research of the First Moscow State Medical University named after. THEM. Sechenova (Moscow), editor-in-chief of the journal “Pharmacoeconomics. Modern pharmacoeconomics and pharmacoepidemiology.”
Information about medications: facets of one phenomenon
Medicines are a whole world, and each medicine has several information fields associated with it. First of all, this is information about the pharmacological properties of the drug. This is what is most interesting to consumers. This information includes data on pharmacological properties, pharmacodynamics, pharmacokinetics.
In addition, each drug is associated with information about its storage conditions, its physicochemical properties, and stability. Another aspect is the vacation policy. Drugs may belong to controlled groups that are available only by prescription. There is also information related to the legislative regulation of the circulation of medicines. In addition, there is information related to economic aspects, the price of the drug, and the pharmacoeconomic characteristics of the drug. There is information related to the history of the development and use of drugs.
Of course, for pharmacy workers involved in the dispensing of drugs to the population, the pharmacological properties of the drug are of utmost importance - the mechanism of action, contraindications, drug safety, interaction with drugs, with food, dosage regimen, chronopharmacology, and so on.
Secrets of the name
The life of a drug begins with its name. Medicines, like humans, have several names.
Chemical name
This name is assigned in accordance with the requirements of the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC). It is important for chemists, for example, for those who control the quality of drugs. This information is also needed by drug developers; it allows them to reproduce the structure of the active substance.
International Nonproprietary Name (INN)
This is one of the most important titles for specialists in the field of medicine and pharmacy. It is assigned to the active substance in a medicinal product, has worldwide recognition and is public property. The INN reflects the essence of the drug’s action and is assigned by a special commission of the World Health Organization in accordance with a special procedure. In 1953, the first list of INNs for pharmaceutical products was published. Now WHO regularly publishes the journal “WHO Drug Information” and the reference book “International Nonproprietary Names for Pharmaceutical Substance. Cumulative List" with a list of INNs.
A number of countries also have national generic names, for example, in countries with innovative pharmaceutical industries - Japan, the USA, and the UK. Russia does not have a system of national names.
The INN is necessary so that we can unambiguously understand which drug we are dealing with in all the variety of drugs that appear after the expiration of the patent for the original drug. The fact is that, in addition to the international nonproprietary name, many drugs also have trade names. For example, there are 52 trade names for the INN diclofenac, 38 trade names for the INN ciprofloxacin, 33 trade names for the INN paracetamol, and so on. In addition, different medicinal products (MDs) are created based on the same pharmaceutical substances. For example:
nitroglycerin - 25 LP;
penicillin - 55 LP;
paracetamol - 125 LP;
diclofenac - 205 LP.
Total: 410 drugs were created based on four pharmaceutical substances.
Currently, the total number of INNs reaches approximately 8,000 and continues to increase annually by 100–120 new names.
INNs belonging to substances of the same pharmacological group must have “common stems”, based on which doctors and pharmacists can determine their belonging to a specific group of drugs that have similar pharmacological properties. Most often, ancient Greek and Latin roots are used in the names of medicines, but recently there has been a tendency to also use roots from European languages.
Tradename
This is the name under which the drug is registered and sold on the pharmaceutical market. Trade names can be brand names (proprietary names, trademarks), or they can simply be a generic name - in this case, the drug is called by its INN. Brand names are registered as trademarks and are protected by legislation in the field of intellectual property protection.
Sometimes a brand, due to its wide popularity, can cost even more than the drug itself. For example, everyone knows the drug “No-shpa”, but not everyone knows drotaverine. Brand promotion is the main goal of a company's advertising activity. However, now the situation will change, since from July 1, 2013, an order of the Russian Ministry of Health will come into force, which establishes the need to issue prescriptions using international nonproprietary names (Order of the Russian Ministry of Health dated December 20, 2012 No. 1175n “On approval of the procedure for prescribing and prescribing medications, as well as prescription forms for medications, the procedure for completing these forms, their recording and storage”).
Example
| Chemical name | 5-methoxy-2-[[(4-methoxy-3,5-dimethyl-2-pyridinyl)methyl]sulfinyl]-1H-benzimidazole |
| International nonproprietary name | omeprazole |
| Tradename | Pleom 20; Omipix; Losek; Losek-MAPS; Gastrozol; Zerocide; Romesek; Promez, Omitox; Ulkozol; Omitox; Ocid; Ultop; Chelicid; Omeprus; Cisagast; Ocid; Omecaps; Omez; Omeprazole-Acri; Omeprazole-NS; Omeprazole-Richter; Omeprazole Sandoz; Omeprazole |
Deadly mistake in title
The name of the drug can be considered an element that ensures the safety of its use. In the United States, a study was conducted on the causes of errors in the use of medications that led to the death of a patient. In 10% of cases, the cause of the error was a confusion of drug names! (Source: Analysis of 469 reports of fatal errors in the United States over 6 years. Phillips J. et all. JAMA, 1998, 279, 1200-5.) If another drug with a similar name is used instead of one drug, it can be fatal. That is why special attention is paid to the choice of drug names.
In Russia, the examination is carried out in accordance with the requirements of the Federal Law “On the Circulation of Medicines”. It is impossible to come up with any name for a drug that you want and release it on the market. There are special rules for compiling names that promote the safety of their use.
There is another problem that is often not taken seriously, but it can lead to serious errors - the illegibility of the doctor's handwriting on the prescription. During the Soviet Union, they even specifically fought this problem: they collected illegible prescriptions in pharmacies, and then held meetings in clinics about this. Now, of course, such methods are no longer relevant. This problem will probably be solved by issuing a prescription using a computer.
What will the issuing of prescriptions using INN change?
From July 1, 2013, only INN will be indicated in all recipes. What does this mean for pharmacy professionals? Of course, there will be even greater responsibility than before, since mass issuance of prescriptions using INN will begin and patients will have to be consulted much more often when choosing drugs within the framework of one INN. But you should not be afraid of this responsibility, since even today, in accordance with current legislation, a pharmacy worker can carry out synonymous substitutions within the framework of one INN. Computer databases and reference books help him navigate the large assortment. However, the pharmacy employee must also keep in mind information about the peculiarities of dosing, drug interactions, and the characteristics of different dosage forms.
A list of interchangeable drugs will soon be developed at the legislative level, which should make the work of a pharmacy specialist easier. The need for this list is due to the fact that not all drugs released under the same INN can be considered completely interchangeable. For example, biosimilars are not always interchangeable (more information about these drugs can be read in KS No. 3, 2013 “Biosimilars: a new group of drugs and the problem of identity,” editor’s note). The pharmacy specialist must be very careful during the consultation. He must examine the prescription, clarify whether there is an allergy to the drug, what concomitant diseases there are, and so on - there are entire consultation algorithms for this. Also, the pharmacy specialist must carefully consider the choice of dosage form, since not all dosage forms are interchangeable. In the absence of a drug with the required dose of the active substance, it is not always possible to replace it with a synonym, since, for example, film-coated tablets often cannot be divided into parts, otherwise the active substance will be inactivated or its prolonged action will not be ensured. The tasks facing a pharmacy specialist are very complex, so the requirements for the pharmacological training of pharmacy workers will constantly increase.
Instructions for use
An important issue with drug information is how it is distributed and where it can be found. The most widespread source of information about medicines is the instructions for medical use, which is an integral part of the drug dossier.
It is very important that the instructions contain the most complete information about the drug. For example, in the 90s, instructions for the use of medicinal products released within the framework of one INN could differ so greatly in the amount of information they provided about contraindications and side effects that an uninitiated consumer might think that a synonym with fewer side effects more secure. In fact, it's the other way around. The more detailed the manufacturer's instructions for use are, the higher the degree of evidence of the effectiveness and safety of this drug. Why else do serious reputable companies pay so much attention to information about the drug? Because if the company does not indicate any side effect or contraindication in the instructions for use and this becomes apparent during use, the patient may sue. There are examples of similar claims against companies abroad. For example, in 2010, one of the largest multinational pharmaceutical companies paid 400 thousand US dollars to the family of a person who died from the use of one of the drugs. As it turned out, the drug was not fully tested.
Until 2000 in Russia, very different information could be found in the instructions for use of drugs within the same INN. That is why in 2001, the requirement was legislated that, with regard to contraindications and side effects, instructions for the use of drugs within the framework of one INN should be comparable with a standard clinical and pharmacological article (OST “State Information Standard for Medicines. Basic Provisions”, OST 91500.05.0002-2001). This is an official document containing information about the basic properties of the drug that determine its effectiveness and safety.
Today in practice one can find examples of differences in the instructions for use of drugs released under the same INN. For example, the instructions for use of “Analgin” (INN metamizole sodium) indicate “aspirin asthma”, blood diseases, and diseases accompanied by bronchospasm as contraindications. But the instructions for use of the drug with the trade name “Metamizole sodium” do not indicate these contraindications. The lists of side effects also differ slightly. The instructions for use of Analgin indicate side effects not described for Metamizole sodium: decreased blood pressure, impaired renal function and other side effects. And the instructions for Metamizole sodium describe side effects not mentioned for Analgin - granulocytopenia, hemorrhages.
What should the instructions for use contain?
The draft instructions for use of the medicinal product must contain the information provided for in paragraph 16, paragraph 3, article 18 of the Federal Law “On the Circulation of Medicines” No. 61 of 04/12/2010:
a) name of the medicinal product (international nonproprietary or chemical and trade names);
b) dosage form indicating the names and quantitative content (activity) of pharmaceutical substances and excipients;
c) pharmacotherapeutic group of the drug;
d) indications for use;
e) contraindications for use;
f) dosage regimen, route of administration, if necessary, time of taking the drug, duration of treatment (including in children before and after one year);
g) precautions for use;
h) symptoms of overdose, measures to provide assistance in case of overdose;
i) an indication, if necessary, of the characteristics of the action of the drug upon first administration or upon its withdrawal;
j) a description, if necessary, of the actions of the doctor (paramedic) or patient when one or more doses of the drug are missed;
k) possible side effects when using the drug;
l) interaction with other drugs and (or) food products;
m) indication of the possibility and features of medical use of the drug by pregnant women, women during breastfeeding, children, adults with chronic diseases;
o) information about the possible effect of a medicinal product for medical use on the ability to drive vehicles and machinery;
o) expiration date and an indication of the prohibition of using the medicinal product after the expiration date;
p) storage conditions;
c) an indication of the need to store the medicinal product in places inaccessible to children;
r) indication, if necessary, of special precautions when destroying unused medicinal products;
<�…>
t) name, address of the manufacturer of the medicinal product and address of the place of production of the medicinal product;
x) vacation conditions.
Other sources of information
There are a huge number of sources of information about medicines, for example, reference books, some of which are official and unofficial. The latter have primarily advertising purposes. Which sources of information are primarily important for a pharmacy specialist?
The State Register of Medicines is the main official document that contains information about medicines and is published in Russia annually. This register determines the range of drugs, which is the most important characteristic of the national pharmaceutical market and healthcare of any country.
Unofficial reference books . For example, VIDAL, RLS, “Great Russian Encyclopedia of Medicines”, “Synonyms of Medicines”, “Pharmacological Directory”, “Directory of Medicines” and others. It is important to pay attention to the fact that the quality of information placed in drug reference books is not regulated in any way by law. In this regard, information about the same drugs in different reference books may be presented differently. And you cannot rely only on unofficial reference books. They may be of high quality, but they have their own specific task - to provide basic, rather than exhaustive, information. When comparing articles in different reference books about drugs released within the same INN under different trade names, it turns out that the list of contraindications, indications, and side effects may differ.
Remembering everything is the task of a pharmacy specialist
Sometimes both specialists and people far from medicine and pharmacy underestimate the danger of drugs and pay much more attention to their safety in other areas of life. Meanwhile, according to statistics, the probability of an accident due to a plane crash is only 1 in 3 million. But the risk of an accident as a result of treatment is 1 in 300. In the United States, more than 100 thousand people die per year from adverse reactions to medications, which is twice as many as from transport injuries (46 thousand people per year). The doctor is primarily responsible for the correctness of drug therapy, but the pharmacy specialist who dispenses the drugs also bears no less responsibility.
What information should a pharmacy specialist first pay attention to when dispensing a drug? There is a whole list of information - this includes pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, dosage regimen, and drug interactions. The pharmacist must not only dispense the drug, he must carry out a whole range of procedures related to the examination of the prescription and informing the patient. This is the essence of our profession. The patient is often unable to correctly understand the contents of the instructions for use. And if the pharmacy specialist does not explain all the important points to him, then the patient may end up using or storing the medicine incorrectly.
In order to constantly develop as a professional, a pharmacy employee must constantly study - read instructions, study the drug database. You cannot take advanced training courses every five years. You need to develop constantly. That is why the practice of a credit system is being introduced all over the world, when a person gains “credits” over the course of five years by participating in conferences and various events. These credits count in lieu of a portion of the time he would otherwise have to spend in formal courses every five years. Of course, the manager plays a big role in organizing the training of pharmacy staff. He must understand that qualified personnel are the most important competitive advantage of a pharmacy!
Alphabetically
Both doctors and pharmacists recommend that patients memorize the names of their medications or always carry a prescription for them with them. To facilitate this task, we post a list of the most common active ingredients in alphabetical order, indicating pharmacotherapeutic groups:
- aliskiren – renin inhibitors;
- amyl nitrite – nitrates and nitrate-like agents;
- amiloride + hydrochlorothiazide – diuretics;
- amlodipine – calcium channel blockers (hereinafter referred to as CCBs);
- atenolol, acebutolol – beta-blockers;
- acetazolamide – diuretics;
- bendazole – antispasmodics, vasodilators;
- betaxolol, bisoprolol – beta-blockers;
- bosentan – other antihypertensive drugs, vasodilators;
- valsartan – angiotensin II receptor blockers (hereinafter referred to as ARBs);
- verapamil - CCB;
- gallopamil - CCB;
- hydrochlorothiazide – diuretics;
- zofenopril – an angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor (hereinafter referred to as ACEI);
- isosorbide dinitrate and mononitrate – nitrates and nitrate-like agents;
- irbesartan, candesartan - ARB;
- captopril – ACEI;
- carvedilol - alpha and beta blockers;
- clonidine – centrally acting vasodilators;
- lercanidipine – 3rd generation CCB;
- lisinopril – ACEI;
- losartan - ARB;
- metoprolol – beta-blockers;
- Moxonidine is a centrally acting agent;
- monopril - ACEI;
- nebivolol – beta-blockers;
- nitroglycerin – nitrates and nitrate-like;
- nimodipine, Nifedipine - BCC;
- olmesartan medoxomil - ARB;
- perindopril – ACEI;
- pindolol, propranolol - beta-blockers;
- ramipril – ACEI;
- rilmenidine – I1-imidazoline receptor agonists;
- sotalol – beta-blockers;
- spirapril – ACEI;
- spironolactone – diuretics;
- talinolol, Timolol – beta-blockers;
- telmisartan - ARB;
- torasemide – diuretics;
- trandolapril - ACEI;
- felodipine, phendiline - BCC;
- fosinopril – ACEI;
- furosemide – diuretics;
- cilazapril – ACEI;
- cinnarizine – CCB;
- enalapril – ACEI;
- enalaprilat – ACEI;
- eprosartan - ARB;
- esatenolol, esmolol – beta-blocker.
Most of the medications listed are available with a prescription.
A cardiologist will help you choose the right drug
Cephalosporins
The wide spectrum of influence includes representatives of the 3rd and 5th generations of cephalosporins. A destructive bactericidal effect was observed against gram-negative (enterobacteriaceae, hemophilus influenzae, gono- and meningococcus, Klebsiella, moraxella, protea), anaerobic (peptococci, peptostreptococci, bacteroides, clostridia) and gram-positive microbes.
3rd generation:
Parenteral:
| Representatives | Tradename | Method of application, price (rub.) |
| Cefotaxime | Claforan | Powder for injection solution: 0.5-2.0 g. x 1 time per day intramuscularly or intravenously slowly. 120-150 |
| Cephosin | Powder for injection solution: 1.0 g each. every 8-12 hours intramuscularly, intravenously slowly/drip. 50-75 | |
| Ceftazidime | Fortum | Powder for injection solution: 1.0-6.0 g. x 1 time per day for 2-3 intravenous/intramuscular infusions. 450-530 |
| Ceftidine | Powder for injection solution: 1.0-6.0 g. x 1 time per day intravenously/intramuscularly. 155-200 | |
| Ceftriaxone | Ceftriaxone | Powder for injection solution: 1.0-2.0 g. x 1 time per day intramuscularly/intravenously. 30-900 |
| Azaran | Powder for injection solution: 1.0 g. dissolve in 3.5 ml of 1% solution of lidocaine hydrochloride, intramuscular injections 1 time per day. 2350-2600 | |
| Cefoperazone | Cephobid | Powder for injection solution: 2.0-4.0 g. per day for 2 intramuscular injections. 250-300 |
| Tsefpar | Powder for injection solution: 2.0-4.0 g. every 12 hours intravenously/intramuscularly. 35-105 |
Oral:
| Representatives | Tradename | Method of application, price (rub.) |
| Cefixime | Suprax | Capsules: 0.4 g each. x 1 time per day. 700-780 |
| Suprax Solutab | Effervescent tablets: 0.4 g each. x 1 time per day or 0.2 g. x 2 times a day, dissolve in advance in a glass of water. 800-1000 | |
| Pantsef | Tablets: 0.4 g each. once a day or 0.2 g. twice a day. 380-590 | |
| Ceftibuten | Tsedex | Capsules: 0.4 g each. once a day. 800-1000 |
| Cefditoren | Spectraceph | Tablets: 0.2-0.4 g. x 2 times a day. 1350-1440 |
5th generation (parenteral):
| Representatives | Tradename | Method of application, price (rub.) |
| Ceftobiprole | Zeftera | Lyophilisate for injection solution: not used in the Russian Federation. |
| Ceftaroline | Zinforo | Powder for injection solution: 0.6 g. every 12 hours intravenously for an hour. 25000-27000 |
The most effective and safe
The most difficult question patients ask is which medications are the most effective and safe. You need to understand that selecting a medicine, and especially blood pressure pills, is a long process that requires taking into account the individual characteristics of the body, concomitant diseases, and tolerance to the components of the medicine. Without careful selection, which can take more than one week, even the most “branded” medications may turn out to be completely unsuitable in a certain situation.
Today, the latest developments of antihypertensive drugs are becoming popular, which are actively used in European countries - renin inhibitors, 3rd generation calcium antagonists, centrally acting medications described above.
Medicines from the ACEI group with perindopril as an active ingredient have not lost their relevance. For liver diseases, lisinopril-based blood pressure tablets are preferable.
Medicines of the sartan group based on valsartan and losartan are also considered one of the most effective.
For patients with atrial fibrillation, tachycardia, or coronary artery disease, beta-blockers with nebivolol are appropriate.
For hypertensive patients suffering from angina pectoris, it is better to choose a combination drug, for example, ACEI + CCB.
The most effective and safest medication will be the one that is selected taking into account all the individual characteristics of a particular patient.
Common diseases and cures for them
To replenish your first aid kit with medications, you need to assess the habits and needs of each family member, make a list, and then purchase the necessary medications.
Cold
Increased temperature is observed during inflammation and colds, when the body fights viruses and infectious diseases. Temperatures exceeding 39 degrees are harmful to both children and adults. At the first symptoms, you need to have an antipyretic drug on hand:
- ibuprofen;
- panadol;
- Nurofen;
- efferalgan;
- acetylsalicylic acid.
Antigrippin, Grippostad, Theraflu, Coldrex effectively help with flu and colds.
Pinosol contains menthol and essential oils, which are not harmful and do not cause side effects when you need to eliminate a runny nose. For nasal congestion, Galazolin, Naphthyzin, and Sanorin are also taken.
For gargling and inhalation, you can use eucalyptus leaves or calendula plants. Linden tincture will help reduce fever.
For angina, lozenges or spray are used - Ingalipt, Hexoral, Strepsils, Faringosept.
Allergy
It is one of the new diseases that is caused by hypersensitive immunity caused by poor diet, polluted environment, and household chemicals. An allergic reaction develops quickly and causes a lot of inconvenience.
Tavegil, Suprastin, Diphenhydramine have a high impact, are quickly eliminated from the body, but cause drowsiness. Long-term use may lead to addiction, resulting in reduced effectiveness.
The absence of sedation is inherent in Fenistil, Zyrtec, Claritin. You need to take one capsule per day.
If medications do not have a positive result, you should not risk your health; it is better to consult a specialist.
Preparations for the treatment of burns and wounds
Every first aid kit should contain iodine, brilliant green, hydrogen peroxide, used as a disinfectant for treating wounds and bleeding.
Wundehil, Healer, Rescuer will help in the rapid healing of wounds and burns.
Gastrointestinal problems
Heartburn and stomach cramps can be relieved with antacid medications: Gastal, Phosphalugel, Maalox. They will help reduce pain and neutralize the effects of increased hydrochloric acid.
To improve digestion after a heavy meal, you can drink Mezim, Festal, Pancreatin, Enzistal.
Infusions of chamomile or St. John's wort will help relieve heaviness in the stomach.
Eliminate diarrhea, gas in the abdomen, diarrhea and rumbling Enteros-gel, Smecta, activated carbon, which is taken at the rate of one tablet per 10 kg of body, Phthalazol, Loperamide.
You can cope with vomiting with the help of Motilium, available in suspension or tablets.
For pain in the heart
It is best to use tincture in drops or valerian extract in tablets. Corvalol, volidol drops or capsules, and motherwort tincture are suitable for calming the nervous system.
Painkillers
Science is one of the most difficult. The effectiveness of pain medications and the feeling of pain is an individual thing.
For headaches they take Citropak, Spazmalgon, Citramon. Baralgin and Tempalgin help with dental problems. Movalis, Noshpa, Ketanov will relieve menstrual pain.
Ointments
Anti-inflammatory and wound-healing ointments are effective for cosmetic and medical purposes.
Zinc ointment is used for inflammatory processes on the body and face, dries the skin, and has an antiseptic effect.
Tetracycline ointment contains an antibiotic and helps eliminate the infectious and inflammatory process on the skin caused by animal bites.
Salicylic ointment effectively fights the appearance of blackheads, rashes, and pimples.
Hydrocartisone 1% ointment relieves inflammation on the skin due to insect bites or contact with plants that cause irritation.
Dressing
A sterile bandage is needed for dressings.
An elastic bandage is used to fix fractures and apply compresses for bruises.
The tourniquet will stop the bleeding.
Plaster strips with an antiseptic effect and plates of different sizes.
Review Reviews
The same theory - about the absence of a universal antihypertensive drug suitable for everyone - is confirmed by reviews of blood pressure pills. Forums where the topic of which antihypertensive drugs are the most effective and safe are discussed are replete with reviews of a wide variety of medications from various pharmacological groups.
A new drug from the group of I1-imidazoline receptor agonists, Moxonidine, is gaining more and more positive reviews. Patients call it effective and at the same time inexpensive.
Among reviews of blood pressure pills, there is often an opinion that medicine is not able to explain the causes of arterial hypertension, so medications are selected “blindly.” But this is not entirely true. Even if the causes of hypertension cannot be established, antihypertensive therapy can still significantly reduce the risks of developing cardiac or cerebral accidents, and this should not be neglected. Moreover, the choice of blood pressure pills is huge.
Preventive agents
The assessment of care for cardiovascular diseases is measured by the risk of death, so complex therapy is aimed at preventing acute conditions: myocardial infarction, pulmonary embolism, stroke.
Groups of drugs that prevent cardiovascular accidents:
- statins;
- fibrates;
- antianginal agents;
- antihypertensive drugs.
Herbal medicines and metabolic agents are used as auxiliary therapy, which has a mild restorative effect with a minimum number of adverse reactions.
Regular use of medications reduces the risk of mortality from cardiovascular “events.” Histology determines the stabilization of pathological processes, the limitation of foci of fatty infiltration and necrosis.
Fast acting
In a critical situation, when high blood pressure manifests itself as the worst symptoms of hypertension, there is a need to quickly lower blood pressure. In such cases, blood pressure tablets with quick but short-term action are usually used:
- Furosemide - this diuretic can simply cause a collapse in blood pressure, so its use should be previously agreed with a doctor;
- Moxonidine is one of the newest drugs of the I1-imidazoline receptor pharmaceutical group; it acts centrally;
- Nitroglycerin - this nitrate is recommended for hypertension complicated by angina pectoris;
- Capoten (captopril) - an ACE inhibitor can quickly reduce blood pressure for 6-8 hours;
- Nifedipine, a calcium antagonist, is an essential medicine in the medicine cabinet of many hypertensive patients;
- Clonidine is a centrally acting blood pressure tablet that, even in small doses, quickly and effectively reduces blood pressure;
- Propranolol - let us remind you that the use of drugs from the group of beta-blockers is justified only for coronary artery disease or AF.
As you can see, there is also no shortage of tablets to quickly reduce blood pressure. But it is advisable to select them for emergency situations under the guidance of a doctor.
Bandages and cotton wool in the first aid kit
Your home first aid kit must include bandages, adhesive plasters, and cotton wool. You need to have both narrow and wide bandages. Bandages are needed to bandage wounds and to secure splints that are applied for fractures.
A bactericidal adhesive plaster is needed to close the wound. The adhesive plaster can be used only for small wounds, because, sticking to large areas of skin, it is difficult to remove later. The adhesive side of the patch may cause mild irritation.
Even if the wound is small, it must be closed: it is better to wrap it in a bandage and tie it loosely.
A patch with an adhesive inside without a bactericidal layer can be used for compresses on wounds. For example, having covered a wound or inflamed surface with streptocide, syntomycin emulsion or Vishnevsky ointment, you need to put a small cotton swab on top and only then attach a patch.
The cotton wool should be in a sterile bag, the same one in which it is usually purchased at the pharmacy. Cotton wool is applied to wounds for disinfecting and healing compresses. You probably have to use cotton wool more often than any other item in your home medicine cabinet. Cotton wool is especially needed if there is a newborn in the house. Use sterile cotton wool to wash the eyes and clean the baby’s nose. Cotton wool will be needed to wash and disinfect wounds and abrasions that appear in large quantities in small tomboys.
A hemostatic tourniquet is required. Of course, when purchasing it, you don’t need to prepare yourself for the worst that can happen in life. Just don’t forget that you need to get out of many unpleasant situations with the least losses - for this you should always have everything you need at hand.
A hemostatic tourniquet is a rubber tube. With its help you can stop bleeding and save a person.
Using a hemostatic sponge, you can stop the bleeding and close the wound surface.
Inexpensive
If we rank the most inexpensive but effective medications for high blood pressure, the first place will most likely be taken by medications of the enalapril group (ACEI class).
Diuretics are also cheap medications for high blood pressure.
Inexpensive ones can also include:
- nitrates and nitrate-like agents;
- calcium antagonists of the 1st and 2nd generation;
- beta blockers;
- centrally acting vasodilators.
Many patients call Moxonidine SZ, produced by the Russian production company Severnaya Zvezda, an inexpensive but extremely effective (at a minimum dose) medicine.
List of what should be in a home medicine cabinet
Let us open the list of what should be in a home medicine cabinet with a thermometer.
A thermometer is perhaps one of the most necessary and necessary things in a home first aid kit. This is what we use as soon as we feel mild signs of illness. The mercury scale of a thermometer shows how the body reacts to a possible disease. As a rule, an increase in temperature, that is, a thermometer reading above 37 °C, indicates the body’s struggle with the onset of the disease. The thermometer should be stored in a special case and should be handled with care.
It's nice to have an electronic thermometer. It measures the temperature within 2 minutes. The numbers are displayed on a special board. There is no need to worry about the device breaking and spilling mercury.
Each first aid kit should have a syringe (syringe bulb), a heating pad complete with a tube and tips for enemas.
The next thing that should be in your home medicine cabinet is a device for monitoring blood pressure - a tonometer, especially if there is an elderly person in the house.
Be sure to purchase several pipettes for your home medicine cabinet, with blunt tips, so as not to accidentally damage the mucous membrane when instilling them. Mustard plasters and jars are needed. It is better to purchase mustard plasters in small quantities, as they can become damp. Mustard plasters are stored wrapped in thick paper, but not in cellophane. It is better to put the jars in a separate box. Jars and mustard plasters are used for persistent colds that do not go away for a long time.
Taken “under the tongue”
To speed up the effect, some blood pressure pills are recommended to be taken sublingually - that is, do not swallow them with water, but slowly dissolve them in the mouth. Under the tongue there is a dense network of blood vessels that are capable of absorbing liquids in the mouth.
Thus, the medicine, under the influence of the salivary glands located there, enters directly into the blood, bypassing the digestive tract. Typically, fast-acting high blood pressure tablets are taken under the tongue:
It must be remembered that a rapid drop in pressure is no less dangerous than its increase, therefore, to relieve a crisis, it is necessary to dissolve no more than 1 tablet under the tongue.
Required Items
Dressing
What you need to have:
- cotton wool, sterile bandage, gauze pads, which may be needed to apply a bandage for wounds, cuts and bruises;
- plasters – medical for fixing the bandage and bactericidal for applying to abrasions and cuts;
- elastic bandage – for fixing a limb during sprains and dislocations.
Before treating the wound and applying a bandage, be sure to disinfect your hands with an antiseptic solution (such as chlorhexedine).
Medical devices
Increases in temperature and jumps in A/D also occur in healthy people. Therefore, a thermometer and tonometer should be included in the list of necessary items for the first aid kit.
What are the best for lowering blood pressure?
A doctor will never immediately offer his patient the “best medicine,” even if he has treated thousands of patients with it. The best can only be the medication that is determined for treatment through careful and lengthy selection for you personally. Therefore, all questions regarding choosing the best blood pressure pills should be discussed with your doctor. We will once again remind you about the most effective and safe medications available in pharmacies. These are blood pressure tablets based on:
- lisinopril, perindopril and their combinations with other antihypertensive groups;
- amlodipine, lercanidipine;
- Alisicrene;
- nebivolol;
- moxonidine;
- valsarana, olmesaratana;
- indapamide, hydrochlorothiazide and others.
Although drug reviews and testimonials are interesting, they should not be used as a guide for self-medication.
Today, there is a new fashion trend among hypertensive patients - attempts to give up blood pressure pills and counter hypertension with a healthy lifestyle. This is, of course, a commendable trend, but it should still be monitored by a doctor, since during an exacerbation of the disease it may not be enough. Patients also respond differently to non-drug methods of lowering high blood pressure.
- Some people find it helpful to go out into the fresh air and take a leisurely walk.
- Others resort to hot or alternating foot baths.
- Still others massage the neck area, shoulder girdle and shoulder blades.
- Still others drink decoctions of chokeberry and viburnum or eat handfuls of these berries.
- Many people find it helpful to hold their breath for 2-3 seconds while taking a deep breath (repeated 3-4 times).
- Rubbing your temples with grapefruit or other citrus peel also helps relieve the symptoms of hypertension.
All these methods do not have a hypotensive effect for long - for a maximum of 4 hours, so it is unlikely that it will be possible to manage only with them in case of severe hypertension.
List of disinfecting medications: what should be in your home medicine cabinet
Disinfectants are the first thing that should be in a home medicine cabinet, and a detailed list of medications can be seen later in this article.
So, let's start assembling a home first aid kit. The first thing you should put there are antiseptic (disinfectants), that is, a 3% solution of hydrogen peroxide, iodine, potassium permanganate, boric acid, brilliant green solution, chloramine B.
A solution of potassium permanganate, or potassium permanganate, is used as a disinfectant. It is sold in pharmacies in the form of a powder with red-violet crystals. Dissolve this powder in water. You need to use potassium permanganate wisely, otherwise you can dry out the skin very much. The solution, ready for use, should be light pink in color.
Since potassium permanganate is used quite often, you can make a solution of a rich dark purple color and add a small amount of this solution to the water for rinsing and washing.
A solution of potassium permanganate must be in the house where there is a newborn child. Potassium permanganate is also used in gynecology for washing and douching. You can gargle with a 0.1% solution for reddened tonsils or small wounds in the mouth. This remedy is well suited for children. External wounds can be washed with a 0.5% solution. If the wounds, for example, fester, then you can use a stronger solution - 2-5%. A solution of the same concentration can be used for large festering wounds and for treating burn surfaces.
Very weak solutions of potassium permanganate are suitable for internal use. A 0.02-0.1% solution can be used for various poisonings, for example, poisons, for gastric lavage.
Potassium permanganate perfectly destroys various unpleasant odors. Brilliant green, or brilliant green, as this drug is more often called popularly, can be used to lubricate pustular formations on the skin, to disinfect wounds, abrasions and cuts. Zelenka is used to lubricate skin rashes caused by chickenpox. Zelenka also helps with childhood stomatitis. In this case, brilliant green is used to treat the inflamed areas of the oral mucosa. Zelenka disinfects well, but does not dry out the skin.
Iodine tincture, like brilliant green, is used to disinfect wounds. Iodine is an excellent remedy for cauterizing inflamed areas of the skin. Iodine is also used as a resolving agent.
A 3% solution of hydrogen peroxide is used both as an external disinfectant and as an internal one. They can be used to gargle with sore throat and stomatitis, and to wash festering or poorly healing wounds. Hydrogen peroxide is also used for gynecological diseases.
Perhydrol is a stronger solution of hydrogen peroxide. It can be used for large festering wounds. Such a solution may be too strong for children’s skin, so it is better to treat the wound directly with a cotton swab soaked in the solution.
Hydrogen peroxide perfectly destroys unpleasant odor, so a 3% solution can be used to rinse the mouth for diseases of the nasopharynx.
conclusions
- Anti-pressure pills should be selected taking into account the characteristics of each patient’s body, hereditary predispositions, chronic diseases and susceptibility to the active substances of drugs.
- The choice of antihypertensive drugs today is huge, and medicine continues to improve existing ones and create new ones.
- Only a doctor can navigate the sea of antihypertensive drugs and choose the best, most effective and safe medication.
Active substance
Each medicine has several names:
- trade
- international nonproprietary (INN) or grouping, or chemical
Trade name
unique for each manufacturer. It is necessary to distinguish drugs from different manufacturers.
Example of trade names of drugs containing the active substance ibuprofen:
- Dolgit
- Nurofen
- Ibuprofen-Akrikhin
- Faspik
- Mig and others
INN
is the name of the active substance.
An example of an active substance and a preparation containing it:
- ibuprofen (Nurofen, Mig)
- doxycycline (Unidox Solutab, Doxylan)
- acetylsalicylic acid (Aspirin, Upsarin UPSA)
Group name
assigned to a medicinal product if it does not have an INN or several of them.
Examples of group names:
- chondroitin sulfate
- tolperisone + lidocaine
- cod liver oil
Chemical name
- the name of the active substance, reflecting its composition and chemical structure.
The doctor must write a prescription in Latin using the INN. If there is no INN, the prescription is written by generic or chemical name. The drug is prescribed by its trade name if it does not have an INN, generic or chemical name.
The pharmacy employee offers you medications with the active ingredient that the doctor indicated in the prescription. Drugs with the same active ingredient can be produced by different factories. In this case, they will have different trade names.
Analogs must have equivalent active ingredients. To find a drug, use the service for selecting analogues by INN.