The cecum is the initial section of the large intestine. Malignant tumors are quite common in it: they make up about 20% of all cases of colorectal (colon and rectal) cancer. If the disease is diagnosed early, the tumor can usually be removed surgically and put into remission. In advanced stages, when a cure is not possible, doctors may prescribe therapy to control symptoms and prolong the patient's life.
Our expert in this field:
Ryabov Konstantin Yurievich
Chief surgeon, oncologist, endoscopist
Call the doctor
The Medicine 24/7 clinic uses the most modern techniques to treat cecal cancer. We use the latest generation of drugs; our surgeons perform interventions in an operating room equipped with the latest equipment. We know how to most effectively combat this disease and accept patients with any stage of colorectal cancer.
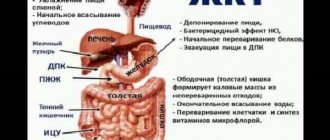
A little anatomy The cecum is a dome. The final section of the small intestine, the ileum, flows into it, and then the cecum passes into the colon. The appendix, a vermiform appendix, also extends from it.
The cecum is located in the lower right side of the abdomen. Water and nutrients are absorbed in it, and feces begin to form.
Caecum and appendix: structure and role in the body
The cecum and appendix are different concepts. The appendix is a process closed on one side that extends from the dome of the cecum. Separated from the cecum by a sphincter. Its length ranges from 2 to 13 centimeters (see photo below).
Previously, scientists considered this organ to be vestigial, that is, inherited from our ancestors and not performing any role in the body. It has now been proven that it plays an important role in the body, namely, it participates in the formation of the immune system. People with a removed appendix are less likely to tolerate inflammation in the intestines, they are more likely to experience dysbiosis and are more prone to infectious diseases.
The cecum is located in the region of the right iliac fossa. Plays an important role in processing the liquid component of the intestinal contents and absorption of liquid. It performs these functions due to its special structure, the presence of suction cells and liberkühn glands.
Anatomical features
The normal cecum is without a mesentery.
Normally, the cecum does not have a mesentery. Thanks to this, the organ, which is not fixed to the posterior wall of the abdominal cavity, always remains very mobile.
Read: The length of the human rectum, its age characteristics
However, in some anomalous cases, the cecum and ileum share a common mesentery. Doctors consider this situation to be a pathology. The presence of the mesentery can play a critical role if surgery on the cecum is necessary.
An organ firmly fixed in the abdominal cavity is very difficult to remove. A similar situation arises with another anomaly: the absence of peritoneum on the posterior wall of the cecum with the replacement of this membrane with postcolic fascia.
Symptoms of problems in the cecum
Despite its small size, this organ is susceptible to many diseases. It is most often affected by typhlitis (inflammation of the cecum), appendicitis, and cancer.
During inflammatory processes, pain usually occurs on the right side of the iliac region. However, pain may radiate to the groin area. The pain can be either sharp or dull depending on the form of inflammation.
Appendicitis
Inflammation of the appendix can only be eliminated surgically.
Inflammation of the appendix can only be eliminated surgically. Usually this disease is diagnosed quite successfully and quickly due to the following characteristic signs:
- nausea and vomiting syndrome;
- tension and soreness of the abdominal muscles;
- bowel problems (usually diarrhea);
- temperature increase;
- general weakness;
- specific pain in the right iliac region.
Read along with this article:
- What is the length of the adult intestine, its features and functions
- Anatomy of the colon and its main functions
- Anatomy of the human intestine: what's what
- Large intestine: anatomy, features of the children's large intestine
- Chronic appendicitis: symptoms, diagnosis and treatment methods
- Digestive processes that occur in the small intestine
- Human intestine: intestinal length, general information, features...
- What are the differences between the parts of the small intestine?
- In which side does appendicitis hurt? Symptoms of appendicitis:...
Causes of pathologies of the cecum
The most common causes of inflammatory processes in the organ are:
- unbalanced diet (abundance of flour, fatty foods, lack of fiber in the diet);
- chronic constipation;
- infectious processes, namely bacterial infections of the gastrointestinal tract;
- dysbacteriosis;
- food allergies.
Typhlitis can often be caused by inflammatory processes in the appendix.
The causes of small intestinal cancer, as well as oncologies of other organs, have not yet been precisely established. According to some data, oncology of this organ can be provoked by:
- unhealthy diet rich in flour and fatty foods;
- hereditary predisposition;
- work in hazardous conditions;
- stress;
- constipation;
- polyps of the cecum;
- elderly age.
Life of a patient with an ostomy
Pain
It is already clear that after surgery to remove a malignant tumor, a person will have to live with a colostomy bag. In other operations, it is removed after the surgical site has healed. For a person, living with a stoma is a big psychological blow. Therefore, a large number of patients simply refuse to wear such a device, even realizing that it will alleviate the condition.
However, there is nothing to be ashamed of - the toma is not noticeable under clothes, it is made of a material that does not allow odors to pass through. This is a necessary measure; it helps a person to move on with his life. Yes, you won’t be able to go to the beach or go to the sauna with friends. But you will be able to live!
How to live after surgery
After surgery, the patient is prescribed a strict diet. Food must be pureed and products that cause fermentation should not be used. A detailed diet is usually prescribed by your doctor.
There will be a special tube in the rectum through which the intestines will need to be washed. This is done in a clinical setting.
Cecum
The main thing for the patient is to follow the doctor’s recommendations. Some traditional medicine will help alleviate the condition. They will not be able to cope with the disease on their own, but in the postoperative period they will significantly alleviate the condition. Usually these are hemostatic, sedative, analgesic, wound-healing herbs and herbal mixtures.
But some of them have a laxative effect and can provoke increased gas separation and fermentation. This is a contraindication for this disease. Which herbs to take should only be decided with a doctor. May this disease never affect you. Be healthy!
Diseases of the cecum and appendix
Typhlitis
Typhlitis is an inflammation of the mucous layer of the cecum. The pathology is usually infectious in nature. Sometimes inflammation can spread from neighboring organs. The most dangerous complications of the disease are paratyphlitis and tissue necrosis. The disease is determined at an appointment with a gastroenterologist, where the final diagnosis is made.
The doctor palpates the abdomen, paying attention to the presence of lumps and splashing sounds. X-ray and scatological examinations are carried out.
Tiphlit happens:
- spicy;
- chronic.
Treatment of the disease is usually conservative. In case of acute typhlitis, hospitalization in a hospital is indicated. The gastroenterologist prescribes a strict diet, antibiotics, enzyme and anti-inflammatory drugs.
If chronic typhlitis regularly recurs after conservative therapy, surgical intervention is indicated. If the pathology is fungal in nature, antifungal drugs are prescribed:
- fluconazole;
- pimafucin and others.
Diagnostic methods
The main method for diagnosing cecal cancer is colonoscopy. During this procedure, the doctor examines the intestinal mucosa and finds pathological changes on it. You can perform a biopsy: obtain a fragment of suspicious tissue and send it to the laboratory for examination under a microscope.
At the Medicine 24/7 clinic, colonoscopy is performed by experienced endoscopists. We perform the procedure under light anesthesia using safe drugs, so patients tolerate it comfortably and painlessly.
Take care of yourself, book a consultation now
In 10% of cases, the endoscope fails to reach the cecum due to adhesions and other pathological changes. In such patients, a “virtual colonoscopy” can be performed: they are given a solution of a radiocontrast substance to drink at night, and the next day a computed tomography is performed. This is not as accurate a diagnostic method as endoscopic examination, but it helps to detect malignant tumors with a diameter of more than 6 mm.
In order to assess whether the cancer has spread to neighboring structures, to regional lymph nodes, and whether there are distant metastases, additional tests may be prescribed: computed tomography, MRI, chest x-ray, bone x-ray, angiography (contrast x-ray of blood vessels), ultrasound of organs abdominal cavity, PET scan.
Prevention of diseases of the cecum
Proper, balanced, regular nutrition with quality foods is the best prevention of gastrointestinal diseases, including pathologies of the cecum. A healthy lifestyle, regular exercise, fresh air, stress prevention are the key to a healthy intestine.
Prevention of constipation and timely treatment of other pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract, adequate sleep, a rational work and rest schedule also reduce the risk of diseases of the small intestine.
Despite its small size, the cecum, like any other human organ, is susceptible to the development of some serious diseases.
The most common of them are inflammation, appendicitis, and neoplasms. In order not to start the disease, when the first alarming symptoms appear, you should seek medical help as soon as possible.
Adenocarcinoma
Weakness and fatigue can be a symptom of some kind of disorder.
This oncological tumor disease is considered quite common among other similar pathologies. The main symptoms of this disorder are:
- anemia;
- weakness and fatigue;
- blood in stool;
- weight loss;
- flatulence;
- stool disorders;
- characteristic abdominal pain.
In the early stages, adenocarcinoma can be quite successfully treated with chemotherapy and radiation therapy. Thus, in 70% of patients who underwent these procedures, the disease did not recur for 5 or even more years.
Unfortunately, the later adenocarcinoma is diagnosed, the less chance the patient has for a successful and final recovery.
Topographic location
Part of the cecum is projected to the right side of the groin.
As for the specific location in the abdominal cavity, in the vast majority of people the cecum is located just below the upper edge of the ileum.
That is, the organ is located closer to the front wall of the abdomen. Part of the cecum is projected onto the right side of the groin.
So, its dome is directed towards the small pelvis and is located only 5 cm above the inguinal ligament.
At the junction of the cecum with the ileum there is a special organ - the intestinal papilla. In conjunction with muscles, it is capable of acting as an anti-reflux mechanism. This device, operating on the valve principle, is called the Bauhinium valve.
Thus, from above the cecum borders on the ileum. In front - with the thin and ureter. On the right - almost in close contact with the abdominal wall. And behind and below - with sheets of peritoneum.
Functions
The main function of the cecum is its direct participation in the digestive process. It is this organ that is responsible for the normal absorption of chyme (or rather, its liquid part). However, the work of the cecum cannot be called “irreplaceable”. If its function is disrupted, the rest of the intestine will cope with the digestive process quite calmly.
A separate line should describe the functions of the appendix of the cecum. This organ does not take part in the digestive process. However, it plays a very important role in the formation of human immunity. This is where most of the lymphoid follicles are located. And the cells they produce, in turn, are responsible for protecting the body from any foreign agents.
Ileocecal angle
The place where the ileum ends and the cecum begins is called the ileocecal angle, i.e. it includes the terminal part of the ileum, the cecum with the appendix and the ileocecal junction.
More often, the ileum “merges” into the cecum in its medial wall, forming a different angle: obtuse, acute, straight.
The ileocecal angle has a specific function - it works like a valve, which allows you to isolate the large and small intestines from each other and avoid backflow (reflux) of the contents of the large intestine into the small intestine. The cecum is well fixed to the posterior abdominal wall, which helps the doctor to easily find it and the appendix during surgery.