Treatment of dry and wet gangrene in the 21st century does not require amputation, and the experience of our center shows this. In most surgical departments of the country, gangrene still remains a disease with a high rate of amputation and death. The use in medicine of modern methods of restoring blood circulation in the limb and reconstructive plastic surgery technologies makes it possible to save the leg and the ability to walk for the vast majority of patients. Such technologies are concentrated in specialized limb salvage centers, such as the Innovative Vascular Center.
Gangrene can be cured and it is actually very simple. After all, it is enough to restore blood flow to the leg, remove dead tissue and heal the remaining wounds. However, these simple principles are still practically not followed anywhere, because some doctors and departments restore blood flow, while others deal with the wound process and removal of dead tissue.
For the treatment of dry gangrene of the lower extremities, they offer a variety of droppers, blood thinners, vasaprostan and other miracle remedies. And when it really becomes clear that such treatment for gangrene of the legs does not eliminate the symptoms, then in a regular surgical department one remedy is used - high amputation.
This outcome encourages patients and their relatives to seek methods of treating gangrene without surgery. Various “folk” remedies are used, from which the infection only flourishes. This includes chewed bread crumbs, salt and urine, and many other “remedies for gangrene” applied to the affected areas. From them, the inflammatory process develops and spreads faster, inevitably leading to amputation for health reasons.
In such a development of events, in most cases, doctors are indirectly to blame, who perceive any tissue necrosis as the need to “save the patient” with the most radical method of treatment. They either do not know information about modern technologies, or they do not believe in it and do not convey it to patients.
Classification
There are several types of diabetic foot, depending on the disorders that occur in the patient’s body.
- Ischemic diabetic foot. In ischemic diabetic foot, the blood supply to the patient is disrupted. Blood circulates poorly through the vessels of the legs, as a result of which the foot becomes swollen. The color of the skin on the legs changes, and the patient experiences severe pain while walking. The ulcers in such a patient have uneven edges. Usually the ulcers are located on the toes, they react painfully to the touch, but there is no pulsation. Due to poor circulation, the skin on the feet of patients is pale and cold to the touch. Ulcers are not accompanied by the development of calluses.
- Neuropathic diabetic foot. This type of foot is characterized by a violation of the nerve endings of the patient’s legs. Tactile sensitivity worsens, the skin begins to crack and dry out. It is possible to develop flat feet and concomitant orthopedic diseases. The ulcers in such a patient have smooth edges. There is no pain, and the pulsation is normal. Most often, such ulcers are located on the soles of the feet. Patients experience decreased sensitivity and increased blood flow. The color changes towards red, the foot is hot to the touch.
- Mixed form. It is characterized by a combination of signs of neuropathic and ischemic forms and is manifested by damage to both nerves and blood vessels. The leading symptoms depend on which part of the pathogenesis is more pronounced. This form of the disease is especially dangerous, since the pain syndrome in this case is weakly expressed or absent altogether - patients are not always in a hurry to seek help (“after all, it doesn’t hurt”) and come to the doctor only when the ulcer has reached a large size and has developed in the tissues irreversible changes that cannot be treated with medication.
Onset of the disease
Having discovered the primary symptoms of gangrene on the leg, you must immediately see a doctor. The sooner adequate therapy begins, the more favorable the treatment prognosis will be. If the disease is detected at this stage, treatment will be justified, otherwise, without amputation of a finger, foot or leg, the person will not survive completely. How does gangrene begin?
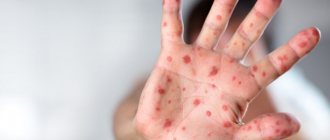
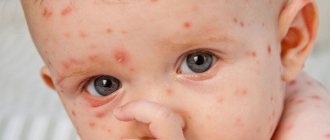
Photos of gangrenous phenomena of the foot in diabetes
The initial stage of foot problems such as gangrene in diabetes is the development of diabetic foot in the patient. The disease often develops in older people, who are likely to have malnutrition of tissue structures due to microangiopathy and neuropathy.
The initial stage of gangrene of the leg in diabetes mellitus is shown in the photo:
Moreover, even a minor injury, scratch, callous formation, in combination with impaired blood circulation, thrombosis, congestion in the leg area and infection, entail incipient necrosis and gangrenous phenomena.
There are dry and wet varieties of gangrene. The dry type of gangrene in diabetics develops at a rather slow pace.
Dry gangrene of the lower extremities at the initial stage is shown in the photo:
This gangrene of the foot begins with itching, a feeling of coldness in the legs, and the feet feel a burning sensation. Then there is a loss of sensitivity, periodic convulsive attacks occur. The skin becomes overdried, peels, and turns black. The leg takes on a mummified appearance. Skin death in the affected areas increases. No foul odor is observed, and the state of health is not disturbed.
Wet gangrene in diabetes develops immediately. A photo of the initial stage of wet gangrene of the leg can be seen below:
At the same time, the leg begins to increase in size and becomes green or purple. A sharp, fetid aroma of rot begins to be felt. The disease quickly spreads to healthy areas of the skin, fiber, muscle and bone tissue. The beginning of the process of necrosis provokes the covering of skin areas with small bubbles. Pressing on the damaged areas provokes crunching sounds.
The diabetic’s health begins to deteriorate, blood test results become worse, symptoms of leukocytosis appear, and an increase in ESR is observed.
To save the patient's life, immediate amputation of the affected limb is necessary.
Gangrene in the toes
Gangrene of the toes in diabetes occurs due to a lack of sensitivity in this area and impaired blood supply to the extremities. Due to the fact that a diabetic ceases to feel pain in the legs, there is a high probability of injury to the fingers, since any blow to them can go unnoticed. Damage to the skin in the area of the finger begins to fester and quickly leads to skin necrosis, destruction of tissue structures, and suppuration.
In order to stop infection of healthy tissues, the finger is amputated. Another point in the development of gangrene of the fingers is the loss of patency by the vascular system of the fingers. Often such gangrene develops over a long period of time. As a result of such violations, the tissue structures of the fingers begin to dry out, leaving no wounds, so infection does not form. A mummification effect occurs. In this form, the toes can be preserved through surgical treatment of the vascular system.
The development of gangrene in the elderly
Often, in older people, whose body is subject to dehydration due to age-related changes, under the influence of diabetes and other diseases, dry gangrene is observed, but there is also wet gangrene. Dry is characterized by very strong and sometimes unbearable pain and swelling of the limbs. Next comes loss of sensitivity. After which there are two options for the development of circumstances: injury to the legs with the addition of a purulent infection, or drying out of the legs and acquiring a coal-black color. Treatment of gangrene in older people is complicated by slow regeneration processes of the body.
Gangrene can be treated without amputation at the Innovative Vascular Center
Treatment of gangrene without amputation in Moscow is carried out in a specialized hospital of the Innovative Vascular Center - the Clinic of Innovative Surgery (CIS). In 2011, according to the ROASH report, our clinic took a leading position in performing vascular reconstructions on the arteries of the leg and foot.
The Innovative Vascular Center is a clinic in Russia where modern high-tech methods of restoring blood flow in the legs, advanced technologies of X-ray endovascular surgery, vascular and reconstructive plastic microsurgery are put into use.
Every year we successfully operate on more than 650 patients with critical ischemia and gangrene of the legs. Modern treatment of gangrene can be carried out by a team of experienced vascular and endovascular surgeons, as well as doctors skilled in the management and closure of necrotic wounds. Such a team can achieve impressive results in the treatment of gangrene. This team must include specialists who not only know how to restore blood flow, but who also know how to treat a patient with multiple vascular lesions, severe comorbidities and serious wound complications.
Wet gangrene, necrosis, long-term non-healing wounds, and black color of the finger are not a reason for amputation for our team, but should be the reason for active surgical tactics to save the limb. We manage to save the leg in most patients with threatening limb ischemia. We are fighting to save our leg until the last possible moment.
In many other “limb salvage centers” there is a separation of vascular, endovascular and reconstructive plastic surgery, so there is no possibility of a holistic approach to the treatment of critical limb ischemia.
Symptoms of gangrene of the leg
In most cases, the symptoms of the disease are the same in its different forms. Only a few distinctive features make it possible to accurately determine the type of violation. The first manifestation will be coldness of the extremities, pale skin in the area of the future location of gangrene. Itching and peeling of the skin may occur.
As the disease progresses, the skin swells (in the case of a wet, gasy, bedsore form) or dries out greatly and becomes dense (in the case of a dry form). The source of inflammation spreads over large areas, unless the patient has dry gangrene. Next, the process of decay begins, the skin becomes bluish, purple or even black.
In the dry form, it is completely dried out, there is no purulent or serous discharge.
Dry gangrene of the leg. Photo
With wet and gas gangrene, foul-smelling, cloudy liquid and pus are constantly released from the affected area. The surface shines, swells, the limb increases in volume. It is worth noting that with any form of the disease, an unpleasant putrid odor emanates from the leg. With the dry variety it is weakly expressed, but with the wet variety it quickly fills the room in which the patient is located.
As the disease progresses, dry gangrene dries out the limb, while wet gangrene affects the deeper layers. After some time, you can see exposed muscles in the wound that look like boiled meat. A characteristic sign of the gas form of the pathology will be crepitation or a kind of crunching sound that can be heard when palpating the affected limb.
Common symptoms of the disease include weakness, nausea, headache, weight loss, increased local and general temperature, lameness or complete loss of mobility, constant pain in the limb, especially in advanced stages. As the disease progresses, other symptoms appear, including a decrease in blood pressure, increased breathing, and fever.
How does gangrene manifest?
Signs of gangrene vary depending on what type of pathology develops.
Dry
In this case, the “culprit” of the disease is impaired venous or arterial circulation or its complete stop. This explains the fact that the first manifestations at the onset of gangrene development are associated with insufficient blood flow. Symptoms include:
- "Crawling" sensation.
- Tingling in the legs.
- Pain syndrome. Sometimes it is acute, disturbing during physical activity, but subsiding when at rest.
- Weakness in the limbs that occurs during exercise.
- Paleness of the outer integument.
- Feeling cold.
- Lameness.
If blood circulation in the extremities is completely stopped, then the symptoms of gangrene of the leg will be as follows:
- Presence of black skin tone. This color is characteristic of the dry type of necrosis.
- Reducing the parameters of the injured leg. To determine, it is enough to measure the length of these parts of the body.
- Excessive dryness in the problem area, cessation of activity of the sweat glands.
- Increased tissue density due to moisture deficiency.
- Stopping hair and nail growth on the affected leg.
Patients also show signs of general intoxication. But they are weakly expressed, because the body manages to fight toxins released into the circulatory system.
Wet
The clinical picture for this type of pathology is more extensive. Local and general symptoms are observed, since the infectious process affects not only the leg itself, but also the internal systems of the body. Among the local signs the following are distinguished:
- Blueness of the skin or its acquisition of a dark purple color.
- Painful sensations in the affected area.
- An increase in local temperature in the area where pathogenic microflora is actively multiplying, and its decrease in areas that have already died.
- Swelling of the injured leg.
- The appearance of a putrid odor.
Wet gangrene is also accompanied by general signs of intoxication of the body, since the immune system cannot cope with the elimination of harmful substances released into the blood. Patients complain of the following symptoms:
- High body temperature.
- General weakness.
- Decreased appetite.
- Nausea that occurs regularly.
- Attacks of dizziness.
- Excessive sweating.
In childhood, seizures often occur. This is due to the fact that the body is not yet able to fight such a dangerous disease. In older people, the body does not respond adequately to pathology, so the manifestations may be mild.
Anaerobic necrosis
With this type of gangrene, symptoms are also divided into local and general. Pathogenic microorganisms spread through the legs at high speed, releasing many waste products into the circulatory system, which poisons the internal systems.
The area affected by the gas type of necrosis has the following features:
- Pale skin.
- Low local temperature.
- The appearance of blue or red spots.
- Tissue swelling that is constantly increasing.
- Putrid odor from the affected area of the body.
- Discharge from wounds of a cloudy liquid that smells unpleasant and has a greenish or brown tint.
- The appearance of a crunch when palpating the sore limb.
When the muscles in the wound area are exposed, the tissues resemble cooked meat, having a white tint and separation into individual fibers.
Symptoms of general intoxication with gas gangrene appear quite pronounced. Most often they cause the death of the patient. These signs include the following:
- Weakness throughout the body. It can be so severe that it becomes difficult for a person to move.
- High body temperature.
- Sleep disorders.
- Impaired consciousness. Sometimes a delusional state is observed.
- Regular vomiting that does not bring relief.
- Reduced blood pressure.
- Cardiopalmus.
Pathogenic microorganisms can infect internal organs, which will disrupt their functioning and cause the death of the patient in a short time. Therefore, it is important to promptly identify anaerobic necrosis during gangrene and eliminate it.
Bedsores
This type of disease occurs when pressure is placed on tissue for a long time. The necrotic process develops gradually. If blood flow is impaired, the outer skin becomes pale, then the local temperature decreases, and numbness appears.
Next, swelling of the skin forms. In later stages, the compressed areas of the legs turn black. If treatment is not timely, an infectious process develops, aggravating the course of the disease and causing symptoms of general intoxication.
Diagnostics
Timely completion of diagnostic procedures and a comprehensive examination of the body plays an important role in the formation of a further course of therapy on the path to full restoration of the functionality of the sore leg. To do this, the patient is prescribed the following types of tests:
blood from a vein for biochemical research to determine changes in its qualitative composition, which is quite possible against the background of an acute inflammatory process occurring inside the foot; blood from a finger to determine and further control blood sugar levels (especially important in those clinical cases when the patient has been unable to reduce the concentration of glucose in the body with the help of medications for a long period of time); a smear from the wound surface, if gangrene has already reached the stage where ulcers have formed on the skin or diabetic foot syndrome has developed (sampling of biological material on a sterile cotton swab is necessary so that doctors have the opportunity in laboratory conditions to establish the strain of bacteria that provokes purulent inflammation in the tissues of the lower limb); donating urine allows you to determine the condition of the kidneys of a sick person, since they also suffer from excess sugar levels, and their tissues are damaged in the process of purifying viscous blood saturated with sugar crystals.
If the damage to the skin is critical and the attending surgeon suspects that the disease has already reached the bone tissue, then the patient is additionally prescribed an x-ray. This diagnostic method will allow you to find out whether the leg bone is involved in the inflammatory process.
Drug therapy
Treatment methods for pathology are determined on an individual basis. It is usually not possible to restore the affected area. The doctor’s priority task is to determine the causes of the development of pathology and preserve all healthy tissue. If disorders arise as a result of changes in general health indicators, medical measures are usually complex.
If gangrene of the leg is detected in the initial stages of development, the lesion is not huge in scale, you can save the limb and manage with conservative treatment methods. Such therapy usually includes:
- Taking medications to reduce inflammation and block infection in healthy areas. These can be antibacterial agents, complex ointments (Iruksol) and other medications.
- Changing your diet, taking multivitamin complexes and medications to stimulate the immune system. The method of strengthening the body’s protective functions is selected simultaneously by several specialists.
- Physiotherapy. It is considered advisable to use a number of hardware (for example, infrared) to remove dead cells, stimulate the regenerative functions of tissues and prevent the further spread of necrosis.
- Exercise therapy course. Gymnastics is usually prescribed during the rehabilitation period, when drug therapy produces positive results.
If suppuration is present, gangrene of the leg spreads over large areas, it is not possible to do without surgical intervention. In this case, it is important to eliminate all dead tissue and restore the blood supply necessary for proper nutrition of the cells.
Treatment of gangrene in diabetes mellitus
Various techniques can be used to treat gangrene. Therapy without amputation is practiced; specialists resort to surgical intervention. In rare cases, we can talk about folk recipes.
Treatment without amputation
Therapy without amputation is a drug-assisted approach. Intravenous administration of a glucose solution of physiological composition is acceptable; plasma or even blood substitutes can be used. For restorative purposes, antibiotic injections may be prescribed. Gangrene can be treated through the use of various heart medications.
The use of novocaine blockades deserves special attention, which eliminates vascular spasm
Speaking about treatment without surgery, pay attention to:
- use of vitamins, anticoagulants and diuretics;
- use of drugs that have thrombolytic effects;
- carrying out a procedure such as blood transfusion according to indications.
Considering that gangrenous lesions are associated with very severe pain, painkillers are prescribed along with detoxification therapy.
A sterile bandage is applied locally to the damaged areas of the external tissue.
It is important that it is soaked in antiseptic compounds, such as ointments. They are necessary because they help stop the further spread of the infection.
However, ointments made on the basis of antibiotics will not have a general healing effect in the presented situation. In case of diabetes, corrective insulin treatment should be considered an obligatory part of the restorative tactics of non-surgical intervention.
Surgical methods
Surgical treatment methods can be used, namely surgical sanitation of the pathology focus. In this case, the problem area is cleansed, which eliminates subsequent infection and tissue damage. Surgical techniques include balloon angioplasty, as well as stenting of the arteries of the lower extremities.
In addition, in some cases, experts insist on endarterectomy (resection of atherosclerotic plaques from the lumen of the vessel), and bypass surgery. In the most severe situations, when any other treatment methods are impossible, amputation of the problematic part of the leg is used.
ethnoscience
As noted earlier, treatment of gangrene with folk remedies can also be provided. A multicomponent ointment can be used. To prepare it, combine 50 grams. rosin, unsalted lard, honey, as well as laundry soap and refined sunflower oil. Next, the mass is boiled, and after cooling, finely chopped garlic, aloe and onion are added (also 50 g each)
Please note that:
- the composition will need to be mixed thoroughly;
- Before use, it is recommended to heat it in a water bath;
- It is recommended to apply to problem areas only when warm.
Rye bread deserves special attention. It is necessary to use fresh rye bread, which is carefully chewed. A compress is formed from the resulting mass and applied to sore spots.
It is important to consider that when grinding components in another way, there will be no restorative effect. This is partly due to the fact that bread reacts with saliva, due to which the damage heals much faster
A special pine tincture demonstrates excellent results. To prepare it, you will need to chop the young needles of any coniferous plant (they should not be more than one cm in length). You can dry them and keep them in a paper bag, or you can use them fresh.
Speaking about the preparation algorithm, pay attention to:
- about five tbsp. l. pine needles are soaked in a liter of water;
- additionally use onion peels and rose hips (one tablespoon each);
- the product is brought to a boil and kept on fire for six minutes;
- it is necessary for the composition to infuse for eight hours.
It is recommended to filter it and use it instead of water within 24 hours. It is permissible to use no more than 600 ml in one day. Preventive measures deserve special attention.
When is surgery indicated?
Some patients often experience rapid development of necrosis. Sometimes tissue death leads to the “drying out” of the limbs and subsequent infection of the affected area. In such situations, doctors decide to amputate in order to save the patient’s life.
Currently, the following surgical options are used in medical practice:
- Prosthetics. Restoring blood flow through the introduction of a prosthesis is a fairly popular technique. The surgeon installs it in an artery or vessel, due to which blood subsequently flows to all tissues and cells. This option allows you to prevent relapses of pathologies such as gangrene of the leg.
- Treatment with bypass surgery. This is a fairly serious operation. Its main purpose is to allow blood to flow to the tissues through a special shunt - a vessel formed artificially.
- Endovascular surgery. This is a modern technique for restoring vascular patency. The surgeon inserts a catheter with a built-in balloon. The device then moves down the artery to the affected area and dilates it. To avoid re-narrowing, doctors usually install a special stent.
If gangrene of the toe develops due to the presence of plaques that interfere with the normal supply of nutrients, thromboendarterectomy is performed.
Treatment of gangrene is a rather complex process that does not always allow saving a limb. If there are factors predisposing to the development of pathology (diabetes mellitus, blood disorders, mechanical injuries and damage), additional consultation with specialized specialists is required. A special category includes bedridden patients and elderly patients in whom gangrene of the legs is highly likely to develop. Such people require special care and periodic examination to assess vascular patency.
Symptoms of a finger or toe injury
The skin initially becomes pale and cold to the touch. Then their color changes to marbled, bluish and dark brown. When the tissues are completely destroyed, the fingers turn black. Sensitivity to touch and temperature changes is reduced. Patients may experience tingling, itching, burning or unbearable pain. The pulse in the arteries of the feet is not detected.
In dry gangrene, destruction is limited to the zone of lack of blood flow. The tissues dry out, the volume of the limb decreases. With the wet type, the skin is swollen and rotting occurs. Disintegrated tissues have a characteristic fetid odor; toxins from them penetrate into the blood, causing a general reaction in the body.
Symptoms of gas gangrene
Gangrene is a serious consequence of diabetes mellitus
With diabetes mellitus, a sharp restriction of oxygen supply to the lower extremities progresses, which leads to necrosis of parts of the body, that is, to gangrene.
It is a serious complication in the later stages of diabetes mellitus. If the disease lasts for twenty years, then diabetic foot develops in 80% of those suffering from this disease, resulting from damage to blood vessels and nerve endings.
With chronic elevated glucose levels, changes occur in the walls of blood vessels, as well as in nerve fibers
It is important to note that vascular damage occurs at all levels (large, small, capillaries)
Consequently, all this impairs the supply of blood and oxygen to the tissues of the lower extremities; the reason for this is also their greater distance from the heart. Diabetic polyneuropathy, which also develops in the patient, reduces skin sensitivity, and therefore he feels the deterioration of the tissues of the legs at a later stage. The sufferer also does not notice the appearance of minor injuries on the feet that do not heal for a long time. Here it would be appropriate to recall the low resistance to various pathological infections, the development of which causes trophic ulcers, often being the main cause of gangrene.
In diabetes mellitus, dry gangrene most often develops, the cause of which is progressive blockage of the circulatory system. This type of pathology does not worsen the general health of the patient for a long time; severe intoxication does not manifest itself. But if an infection gets into already changed tissues, the disease can move from a dry state to a wet one (see photo). And this is fraught with general intoxication of the body and, as a consequence, death. Therefore, with such a developing picture, urgent amputation of the lower extremities is required.
Preventive actions
Many people are interested in what gangrene of the leg looks like (photo). The initial stage of this pathology usually develops slowly, which makes it possible to consult a doctor and undergo a course of treatment. Can this disease be prevented?
First of all, doctors advise observing basic hygiene rules, because gangrene often occurs after infection and dirt penetrate into an open wound. In addition, if alarming symptoms appear, you should immediately seek help from a doctor. Only a qualified specialist after a diagnostic examination will be able to confirm the diagnosis and recommend adequate therapy.
It is important to carefully and promptly treat wound surfaces. If you are at risk of developing gangrene, you must periodically undergo health assessment examinations and promptly treat concomitant pathologies (diabetes mellitus, pancreatitis).
Diagnostics
Signs of diabetic gangrene include:
- decreased sensitivity or its complete loss;
- deformation of the ankle, feet, limited mobility;
- swelling or reduction in the volume of the limb, depending on the type of gangrene;
- in the presence of an ulcer - signs of infection, discharge of pus;
- weakening of tendon reflexes;
- increased blood glucose (from 7.5 mmol/l before meals), glycated hemoglobin (from 6.5%), low-density lipoproteins, cholesterol and triglycerides;
- glucose and ketone bodies are determined in the urine;
- sowing of ulcer discharge - detect bacterial flora, determine sensitivity to medications;
- Ultrasound with Dopplerography - decreased blood flow, obstruction, cholesterol plaques, dense arterial walls with low mobility, calcium deposits, thrombosis;
- angiography – extensive damage to the bloodstream;
- X-ray of the foot - destruction of articular surfaces, bone tissue, decreased mineral density, osteomyelitis (inflammation of the bone, bone marrow).
Watch the video about ultrasound of the veins of the lower extremities:
https://youtube.com/watch?v=qVlKHniwrk8
What symptoms indicate illness?
The first sign of pathology is severe pain. The discomfort is so strong and painful that the patient tries to alleviate his condition by any means. Over time, the intensity of the pain only increases and persists until the final death of the nerve fibers.
Another symptom is a change in skin tone. The color of the affected area may vary from bluish to greenish. Patients also complain of numbness of the limbs, loss of sensitivity, and severe cramps. My feet get cold all the time, even in warm weather. Small ulcers gradually develop on the skin, which heal very slowly.
Signs of gangrene of the leg may vary depending on the form of the pathology. Currently, doctors distinguish three types of the disease: wet gangrene, dry and gas. Next, we will consider each option in more detail.
Recommendations for patients
Basic recommendations for patients contain answers to the following questions:
What not to do?
- do not walk barefoot, especially on the street, in public places;
- do not steam your feet, do not wash them with hot water;
- do not use heating pads;
- do not do salt baths;
- do not use ointment dressings without a doctor’s prescription;
- do not use products to soften calluses;
- do not use other people’s socks, shoes, or visit a public bathhouse;
- do not come close to open fire and heating devices;
- do not treat your feet or cut your nails yourself if your eyesight is poor;
- do not self-medicate. Do not treat calluses, abrasions, corns, hyperkeratoses, or cracks on your own.
When to contact a specialist?
- with the development of an ingrown nail;
- for bruises, abrasions, burns;
- with darkening of the fingers, pain in the calves when walking and at rest;
- loss of sensation in the feet;
- for wounds of any size and any reason;
- for ulcers and suppurations;
- when the deadline prescribed by the diabetic foot department doctor has come, or any questions regarding the feet have arisen.
What should you always do?
- strictly monitor blood glucose levels, consult your endocrinologist in time;
- stop smoking;
- wear cotton or wool socks (not synthetic), loose leather shoes;
- do foot exercises every day, walk for at least 2 hours;
- Treat fungal nail infections (darkening, splitting of the nail) with a dermatologist;
- be examined at least once a year (and if there are changes - once a month) in the diabetic foot department.
What to do every evening?
- carefully examine your feet, using a mirror to examine hard-to-reach areas (if your eyesight is poor, you should use the help of your family);
- wash your feet with warm (never hot) water with baby soap or a slightly pink solution of potassium permanganate;
- thoroughly dry the skin with a personal towel, especially the spaces between the fingers (blot, do not rub);
- lubricate the skin with a thin layer of softening (vitaminized, bactericidal) cream;
- treat the interdigital spaces with vodka;
- if necessary, cut your nails very carefully, leaving them not very short, cutting the nail straight (if you have poor eyesight, cutting your nails yourself is prohibited).
Folk remedies
Treating diabetic foot at home can also be done. But for this, certain conditions must be met: constant monitoring by a specialist is required, the stage of development of the syndrome should in no case be associated with complications. It is in this case that it will be truly acceptable to be treated with folk remedies.
The following products and compositions can be used:
- Burdock or burdock leaves will also help cope with diabetic foot. They are equally effective both fresh and dried. The active components in the leaves allow you to obtain a powerful tonic and wound-healing effect. It is best to make lotions or compresses from them - apply a leaf to the wound several times a day. You can also make a decoction of 1 teaspoon of dry mixture per 250 grams of water. The resulting decoction will help normalize lymph flow and remove excess fluid from the body.
- Blueberries are a unique berry that can quickly bring blood sugar levels back to normal. The antioxidants it contains help improve blood flow and restore metabolism. Try to eat a glass of this berry every day during each meal. In winter, you can use frozen berries or brew dried leaves.
- You can also cure diabetic foot with regular kefir. This dairy product contains unique bacteria that penetrate the skin, soften it and accelerate the healing process. To achieve a better effect, it is recommended to sprinkle the surface treated with kefir with dried pine needles. This will help protect your skin from fungal infections.
- Clove oil is a unique remedy that is a storehouse of useful substances. It helps to quickly heal wounds, kill all pathogenic microorganisms, and also restore natural blood circulation. If you regularly treat your ulcers with it, they will heal quickly and stop causing you any discomfort.
- A decoction of chamomile, nettle, oak bark and burdock will help restore trophism in the limbs. To prepare it, take all these components in equal proportions and mix thoroughly. After this, take 3 tablespoons of the herb per 1 liter of boiling water and leave to steep for about 2-3 hours. Make lotions from the resulting decoction; you can use it to treat your feet.
Diagnosis of gangrene of the leg
The disease is quite easily diagnosed without the use of additional equipment. Several methods are used.
| Method | Description | Venue, price |
| General survey | During the interview, the specialist strives to identify the probable cause of gangrene, so the patient must talk about chronic diseases and other conditions that he has suffered throughout his life. | In any private and public clinic, free of charge |
| Examination of the patient and the affected area | The first stage will be a general examination, measuring body temperature and blood pressure. After this, the doctor examines the skin and mucous membranes. Next, the directly affected limb is examined and the degree of neglect of the condition is determined. | It is also carried out in every medical institution free of charge. You may need to pay 200-500 rubles in a private clinic. per appointment |
| Clinical and biochemical blood test | Helps assess the patient’s general condition and the functioning of internal organs. Presence of signs of inflammation. Blood is drawn from a vein and then sent to the laboratory. | Standard methods that are carried out in any clinic. In private the price ranges from 400-600 rubles. |
| Bacteriological analysis of secreted pus | The sample is taken when the disease enters the necrotic stage. For dry gangrene, this method is not used, since the wound does not secrete pus. | It is carried out everywhere, the price is approximately 500 rubles. |
| Bethe test | The test helps to quickly distinguish gas gangrene from wet gangrene. It is carried out at the necrotic stage, when the specialist is able to separate a small sample of dead tissue. After this, the sample is placed in saline solution. If it floats up, then it is gas gangrene; if not, it is wet. | Available for use in any institution, usually does not require payment |
The most effective diagnostic method is visual examination and palpation of the affected area. An experienced doctor will be able to immediately determine the degree and form of the disease. If in doubt, a Bethe test is performed. Additional hardware techniques are not used.
When to see a doctor
Gangrene of the leg is treated by a surgeon in a hospital. The patient can always study photos of the affected limbs to independently detect signs of the disease. When the first symptoms appear, you should immediately visit a surgeon. You should not expect the condition to progress.
Typically, accurate diagnosis of the disease is possible only at an advanced stage, when the patient requires immediate treatment, often surgical. Therefore, you should not rely on the examination result. The first signs should be a cause for concern.
Diagnostics
In principle, to make this diagnosis, it may be sufficient to examine the foot of a patient with diabetes and detect the characteristic changes described above. However, to clarify the diagnosis, the patient is usually prescribed additional examination methods and consultations with specialists.
When making a diagnosis, as well as at each subsequent examination, the patient is prescribed:
- determination of glycemic profile and glycosylated hemoglobin;
- determination of blood lipid levels (LDL, HDL, cholesterol, triglycerides);
- ankle-brachial index measurement;
- consultation with an endocrinologist;
- consultation with a surgeon (with assessment of neurological deficit and measurement of vibration sensitivity threshold);
- consultation with a neurologist;
- consultation with an ophthalmologist (with a mandatory examination of the fundus to identify vascular pathology).
Patients with severe foot deformities are prescribed x-rays of the feet followed by consultation with an orthopedist.
Patients with absence of pulses in the peripheral arteries of the feet or clinical signs of intermittent claudication undergo Doppler ultrasound and color duplex mapping of the arteries of the lower extremities, followed by consultation with a vascular surgeon.
Patients with existing ulcers in the foot area undergo a culture of wound discharge, followed by determination of the sensitivity of the culture to antibiotics; in the case of deep ulcers, radiography of the feet.
Causes
Contrary to popular belief, gangrene can occur not only after gunshot wounds or other injuries to the extremities. It can also be observed during obstruction (“blockage”) of various vessels by blood clots or plaques, damage to the nerves of the extremities, as a result of certain infections, etc. Having determined the cause in a timely manner, it is possible to assume the form of the disease and choose the optimal treatment.
| View | Most common reasons | Which organs are most often affected? |
| Dry |
|
|
| Wet |
| Internal organs:
Limbs (most often feet). |
| Gas (synonyms - anaerobic, airless or gas infection) | There is only one reason - the presence of a sufficiently deep wound that was infected with clostridia (bacteria living in airless space). However, for the development of gas gangrene, a number of conditions are necessary:
| Muscles, subcutaneous tissue and skin in any part of the body. As a rule, the disease begins to spread from the arms or legs. |
| Bedsore | For the development of a full-fledged bedsore, 60-70 hours of pressure on the tissue is enough. Patients with the following pathologies are at greater risk of its formation:
| Soft tissues in the area of the sacrum, spine, hip joints, shoulder blades. |
| Noma | This form of gangrene develops mainly in children weakened by infection. As a rule, these are measles, meningitis or rubella. | Tissues of the cheeks, lips, gums and deep cellular spaces of the face. |
When making a diagnosis, one should also take into account the symptoms of gangrene that the patient complains of. They are determined by the form of the disease and help guide the initial diagnosis.
Surgery
Unfortunately, conservative therapy cannot always help with this disease, and this is often due to the patient seeking medical help late or a condition complicated by other pathologies.
It is recommended to treat SDS with surgical methods in the following cases:
- if there is a need to remove necrotic areas occupying a small area;
- when vascular plastic surgery is required, restoring their walls and improving their patency;
- damaged vessels need to be replaced - this intervention is called autovenous shunting;
- when installation of supporting meshes on vessels is required - stenting;
- if necrotic processes have spread so much that amputation of the affected fragment is required - one or more toes;
- in severe cases, gangrenous lesions lead to the need to remove the foot, part of it, or part of the leg, but the doctor makes such a decision when risks to the patient’s life arise.
As can be seen from the above, in most cases, diabetic foot is still treated, but this is a long process that includes various measures.
Symptoms of neuropathy in diabetes
Patients' complaints that their feet are cold all the time, that I cannot warm my feet even in warm socks, that my feet turn blue, are typical for patients with polyneuropathy. At the same time, pain and numbness, a crawling sensation, are added. First, the toes are bothered, and then the process spreads to the foot and lower leg.
Dry gangrene is considered the easiest and most favorable form. The second type of diabetic gangrene is wet gangrene.
Diabetic wounds on the fingers, hands and feet are accompanied by the following symptoms:
- increased body temperature;
- swelling of the limbs;
- loss of sensation in the limbs, especially in the morning;
- decreased skin elasticity;
- redness of the skin;
- formation of foci of rotting.
Complications
Dry and wet gangrene, if untimely or improperly treated, can cause serious consequences. One of the dangerous complications is sepsis. It is formed in the wet form of the pathology, which spreads over large areas and provokes the penetration of toxins into the blood.
If pathogenic microorganisms penetrate the internal organs, the functioning of the latter will be disrupted, which will significantly worsen the patient’s condition. Lung gangrene is especially dangerous. It often causes death.
How long do you live with the disease?
How long do diabetics who suffer from gangrene live? The dry type of gangrenous phenomenon is not able to have any effect on the patient’s life expectancy and in very rare cases becomes the root cause of death of a diabetic. The patient can die only from the disease, which was the main cause of the development of gangrene. But with the wet type of gangrene, a patient without the necessary therapy can last only three days, sometimes even less. Therefore, at the beginning of treatment, every minute is important.
The implementation of preventive measures and timely adequate therapy is the key to maintaining health and, as far as possible, long life for a diabetic.
Prevention of gangrene in private nursing homes “Longevity”
In the Longevity boarding houses, elderly guests are provided with comprehensive services, including regular examinations by doctors, as well as a set of preventive measures to prevent the development of this serious illness. At the initial stage, the disease can be prevented or the process of necrosis can be stopped in time. Experienced boarding house specialists know how gangrene begins in the elderly, what it looks like, so they can easily detect not only the beginning of gangrene, but also its precursors by the symptoms.
In addition, our guests are provided with:
- full care and supervision for the elderly and sick 24 hours/7 days a week (for bedridden patients - special medical beds with anti-decubitus mattresses);
- 5-6 balanced meals a day (dietary meals are prescribed if necessary);
- comfort in the rooms, choice of accommodation (1, 2, 3-bed rooms);
- individual psychological assistance, organized leisure, walks, interest groups.
The boarding houses are located in quiet and cozy places in Moscow and the Moscow region (in Ramenskoye, Vidnoye, Zelenograd, Belozerki). All houses have their own fenced area with picturesque nature.
Our guests, no matter how severe their illnesses, do not feel lonely and abandoned. Here they always feel support, help and confidence in the future.
How many people live with gangrene without lower limb amputation?
Life expectancy with gangrene of the leg largely depends on the type of necrosis. If this is a dry type of gangrenous tissue destruction, then the patient can live from 10 to 20 days, and patients with a strong heart, immune system and well-functioning kidneys demonstrated longer life spans. The whole point is that the quality of such life is critical and a sick person, if he does not receive painkillers from the narcotic category, simply suffers from severe pain, which can often cause shock and cardiac arrest.
The wet type of gangrene develops even more rapidly and without intensive drug therapy does not leave the patient a single chance of recovery. In this case, a person can live without amputation for no longer than 10 days. During this period, the pathogenic microflora in the soft tissues of the limb will reach its peak population increase, cadaveric decomposition of the flesh will become so dynamic that the patient’s body simply will not be able to cope with such a volume of toxins, the kidneys will no longer cope with the function of purifying the blood and death will occur. The only difference is that if with dry gangrene the pain syndrome is present, but it is not so acute, then the wet type of gangrene is even more painful.
Life with necrosis of the lower extremities is possible only if a person takes responsibility for his health, or is a physician and is well versed in the symptoms of this disease. At the first signs of illness, he did not hesitate and immediately sought medical help from a surgeon, and the doctor, in turn, began treatment for the area of potential necrosis - immediately. Only in such a situation is it really possible to live with gangrene, to treat it effectively and to curb the progression of the disease, preventing the pathogenic infection from affecting larger areas of the leg and completing the process of tissue decay by surgically amputating the limb. Despite all the efforts of medical personnel, even in this case, an individual selection of potent medications and a long course of therapy will be required.
Prevention of pathology
Prevention of gangrene is as follows:
- Careful care of the wound to avoid the penetration of pathogenic microflora into it.
- Treatment of diabetes mellitus.
- Prevent skin exposure to high or low temperatures.
- Timely treatment of diseases of the body that can cause necrosis of the limbs.
- Strengthening the immune system.
- Maintaining a healthy lifestyle.
Gangrene is a disease that can be very life-threatening if you do not get rid of it in time. Therefore, you should immediately contact a medical facility if the slightest signs of pathology occur, and not try to cure the disease on your own.
Why do leg problems develop?
“Sweet disease” of any type is considered a threat to the patient’s lower extremities. Against the background of prolonged hyperglycemia, vascular damage occurs. The peculiarity of the condition is that the inner layer of the arteries in a healthy person must produce special substances that allow the vessel to expand. In diabetics, this substance is synthesized in small quantities. The permeability of the vascular walls increases, and a significant amount of monosaccharides enters the endothelium.
Glucose provokes the synthesis of a large number of glycosaminoglycans, lipids and proteins. As a result, the lumen of the arteries narrows and blood supply is disrupted. In large vessels, lipids are massively deposited on the inner wall, turning into atherosclerotic plaques, which also interfere with normal blood flow.
Tissues stop receiving the required amount of blood, oxygen, and other nutrients and begin to die. The result is areas of necrosis.