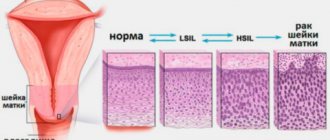
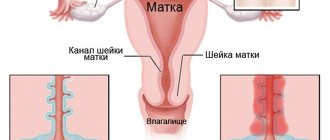
The main reason for performing cytology of a smear from the cervix is to establish the presence of a pathological process, which is accompanied by the appearance of modified cells.
Such processes include precancerous conditions, the appearance of benign or malignant neoplasms. This procedure is characterized by complete painlessness and speed.
Indications for cytological examination
The indication may be:
- conception planning;
- diagnosing viral infections;
- several births in a row;
- the need to determine the cause of problems with conception;
- metabolic disorder;
- genetic predisposition to cancer;
- obesity;
- the need to introduce a spiral;
- cervicitis;
- diabetes;
- hormone therapy;
- endometritis;
- violation of cycle periodicity;
- preparation for surgery.
Streptococcus smear
Normally, women contain a small number of opportunistic organisms - cocci. If there are few leukocytes and there are no signs of inflammation, do not pay attention to this indicator. An increase in leukocytes to 50 in the field of view of the microscope means that vaginal dysbiosis has begun. It develops due to poor nutrition, hypothermia, physical exertion, and taking antibiotics.
The presence of a large number of leukocytes in a smear - more than 50 - means the presence of a sexually transmitted infection. In this case, a more detailed examination with tank culture is prescribed. Treatment is prescribed after identifying the type of infection and selecting drugs to which this type is most unstable.
Performing scraping
Preparation for the biomaterial collection procedure
All you need to do is follow simple recommendations:
- 1-2 days before the examination, do not douche;
- abstain from intimate life for 2-3 days;
- stop using sanitary tampons and vaginal products;
- 2 hours before the examination do not urinate.
The most optimal period for collecting material from the cervix is 5-6 days after the end of menstruation.
Material collection technique
The patient should be on the gynecological chair:
- Mirrors are used to improve visualization.
- A brush is inserted into the cervical canal.
- The material is applied to a labeled glass slide.
- The strokes are recorded.
Labeling of cytology results
Marking options:
- 1 - normal variant;
- 2 — atypical transformations;
- 3 - dysplastic changes;
- 4 - precancer;
- 5 - cancer.
What does cytology show?
The result of cervical cytology can be divided into positive and negative:
- A positive analysis indicates that atypically altered cellular inclusions were found in the cervical tissue. They have a changed morphological structure, shape, and can be observed in different quantities.
- If the result is negative , no cellular changes are detected; this is a normal indicator.
Changes in cell structure are divided into 5 stages:
- Stage 1 . The study picture is not alarming and is within normal limits.
- Stage 2 . The inflammatory process is within relative normal limits. The number of modified cells is relatively small. This serves as a reason for prescribing additional diagnostic measures.
- Stage 3 . The study may reveal cells with changes in the nucleus or cytoplasm. This result is not a deviation from the norm. Most often, it is a risk factor that a woman may develop cancer. In this case, a histological examination is mandatory.
- Stage 4 . Indicates the initial degeneration into an atypical form of a small number of cells. There is a pronounced change in the nucleus, chromosome, and cellular contents. Re-appointment of cytological and histological analysis is required.
- Stage 5 . It is characterized by a high level of modified cells, this is the reason for conducting a comprehensive examination and prescribing appropriate therapy.
Material for cervical cytology
Oncological diseases of the cervix (90% of all cases) affect the stratified epithelium; much less often, the glandular layer is involved in the pathological process.
In this regard, the following material is collected:
- Columnar epithelial cells in the area of the cervical canal (endocervical cells) are taken.
- Flat epithelial cells are collected from the vaginal side of the cervix (ectocervical cells).
- Cells that are formed at the junction of columnar and squamous epithelium will be taken and subjected to cytological examination.
Interpretation of a cytological examination of a cervical smear
Pap test interpretation
| Class | Meaning |
| 1 | norm |
| 2 | there is a decrease in the level of cellular elements |
| 3 | cell hyperpelasia |
| 4 | atypical cells are visualized |
| 5 | cancer cells are detected |
Deciphering a smear for cytology using the Betsed method
The following results may be observed:
- the norm is characterized by the absence of designations;
- violation of vaginal microflora - HPV;
- dysplasia - CIN I-III;
- cancer - Carcinoma.
Cervical smear for tuberculosis
Gynecological examination for genital tuberculosis is not informative. Tests for the presence of Koch's bacillus must be taken directly from tissues; uterine scrapings and vaginal washings are placed in a nutrient medium for reproduction. Analyzes show the presence of Langhans giant cells characteristic of tuberculosis. Additional methods are x-ray of the pelvic organs, ultrasound, which reveals:
- displacement of the uterus due to adhesions;
- the presence of tuberculous tubercles;
- uneven inner surface of the pipes.
All these signs indicate a possible tuberculosis process in the tissues, which requires consultation with a phthisiatrician.
Atypical cells have been identified - what does this mean for the patient?
In such a situation, it is considered justified:
- repeated scraping from the cervix;
- colposcopy;
- UAC;
- biochemistry;
- HPV test.
It is important to strictly follow the doctor’s instructions, this will allow you to get the right result.
To summarize, I would like to focus on the fact that women need to carefully monitor their health and regularly undergo cytological examination of the cervix, because they are entrusted with the responsible function of procreation.
Making a diagnosis after the study
The transcript of the study results contains information for a specialist and is not a final diagnosis. It is difficult for a patient without special education to understand highly specialized terms. This information cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-medication, therefore, with any test results, you should consult a gynecologist.
If the test results are positive, the patient may be prescribed a repeat test and additional diagnostic methods:
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs;
- extended colposcopy;
- cervical biopsy.
- bacterial sowing;
- PCR diagnostics.
Types of oncocytology
Oncocytology is performed by three diagnostic measures:
- Cytology with Leishman staining is a widely used method. It is used in most cases in antenatal clinics.
- Pap test (Papanicolaou smear) - the technique has gained popularity in private laboratory institutions and abroad. The degree of reliability of this diagnostic method is significantly ahead of the first type. The analysis shows a complex level of staining of the smear.
- Liquid cytology is a modern diagnostic method. Equipment for diagnostics is available in rare laboratories. The technique guarantees increased information content and reliability. Biotissues are collected into a special microflora (liquid) for further examination. The cells are then purified and concentrated to a fine, smooth surface. This way, the mucous epithelial tissues do not dry out when transported to a medical facility for microscopy. Thanks to this property, the accuracy of the resulting information increases.
The first two points are actively used by gynecologists and oncologists during examinations of patients. For the procedure you will need two glasses. One is designed for the analysis of the exocervix, and the other is for the analysis of the endocervix. To prescribe a referral for diagnostics, the doctor indicates the data of adults:
- FULL NAME;
- age;
- address;
- established diagnosis;
- period of the last menstrual cycle;
- chosen treatment technique;
- biopsy site.
The biomaterial is collected using a cytobrush. The prepared products are placed in personal packaging and sent to the laboratory within two days.
What changes are possible?
Benign changes may include:
- Detection of trichomonas, candida fungi, coccal infections, anomalies caused by infection with the herpes virus.
- Cellular atypia provoked by inflammatory reactions: metaplasia, parakeratosis, keratosis.
- Atrophic changes in epithelial cells in combination with inflammation: hyperkeratosis, colpitis, metaplasia.
Dysplastic changes and atypia suggest the following conditions:
- Atypia of unknown origin (ASC-US).
- High risk of presence of cancer cells in the material (HSIL).
- Precancerous atypia: varying degrees of dysplasia.
If cancer cells are detected, it is necessary to prescribe additional examination methods and a subsequent course of therapeutic correction (conservative or surgical treatment) with constant cytological monitoring.
What is coccobacillary flora in a smear?
How often should you get a smear test?
A healthy woman undergoes an annual gynecological examination, taking a smear for oncocytology from the vagina and cervix as a preventative measure. Patients over 55 years of age are required to undergo a cytological test every six months. In some situations, the frequency of examination is determined by the attending physician. Many patients neglect the importance of medical examinations.
Doctors recommend spending more time on your own health. In particular, people who are at risk due to an increased likelihood of developing cancer are required to undergo examinations and examinations. Risk factors include:
- Age over 35 years.
- Long-term use of hormonal medications.
- Developing endometriosis and cervical erosion.
- Chronic inflammatory focus in the pelvis.
- Complicated hereditary cancer history.
- Development of tumor growths in other organs.
- Immunodeficiency pathology, as well as HIV diseases.
- Regular and noticeable disruptions in the menstrual cycle.
- HPV, herpes, cytomegalovirus infection and STDs.
- Having sex at an early age.
- Regular change of sexual partners.
- Consumption of drugs and alcohol-containing liquids in significant quantities.
- Long-term smoking and use of tobacco products.
- Long-term use of contraceptives.
- Mothers of many children or women who have given birth multiple times.
It is important to take into account the false positive and false negative results of examinations. Reduced reliability of the results is observed in the following cases:
- injury or contamination of the prepared preparation;
- incorrect collection, preparation or transportation of biomaterial;
- insufficient preparation for analysis;
- taking a smear on the day of your cycle;
- the presence of talc that got from the doctor’s gloves onto the epithelial tissue;
- examination of girls under 20 years of age. In young women, under the influence of active hormonal levels, degenerative or reactive changes in the epithelium are observed.
If a woman has the indicated symptoms, a negative or positive result, and the patient is at risk according to the listed parametric factors, but the smear does not reflect the altered state of the body, the examination is duplicated.
Contraindications
It is contraindicated to collect biological material for cytological studies in the following cases:
- during pregnancy, especially after the 20th week, a cytological smear is not performed, since intervention in the cervix can negatively affect the condition of the fetus;
- with menstrual bleeding;
- with cervicitis;
- in the presence of colpitis (vaginitis) – inflammation of the vaginal mucosa.
The results of a cytological analysis done during inflammatory processes of the genital organs may show a false-positive or false-negative oncocytology result.
Material collection technique
Schematic representation of the collection of biomaterial for a smear
To obtain material that will be subjected to cytological examination, the doctor makes a scraping from the exocervix - the outer part of the cervix - and from the mucous lining of the vagina using an Eyre spatula. To obtain a scraping and subsequent examination of a smear from the cervical canal, a special probe is used - endobrush. Its use makes it possible to obtain biomaterial in quantities sufficient for analysis.
A gynecologist’s set of tools for obtaining material may include:
- Air spatula;
- spirette - an instrument for aspiration of material from the endocervix;
- endobrush;
- tweezers;
- gynecological speculum;
- Volkmann spoon.
The sequence of actions during the procedure includes:
- Gynecological examination of the cervix in the speculum. At the same time, the vaginal walls are expanded and scraping is performed, which can cause a feeling of slight discomfort.
- At the same time, material is collected for microflora analysis.
- The resulting samples of biomaterial are applied to glass and fixed, then labeled and sent for analysis to the laboratory.
Ultrasound of the cervix: methods and procedures during pregnancy
The procedure for obtaining biomaterial takes no more than 15 minutes.
Labeling of cytology results
Changes in the results of cytological analysis of the designation presented in the table below.
| Designation (class) | Decoding |
| Poor quality biomaterial, unsuitable for analysis. | |
| 1 | The results are normal. |
| 2 | Atypical changes are present. |
| 3 | Confirmation of dysplastic changes. |
| 4 | Precancerous condition. |
| 5 | Invasive cancer. |
Any degree of dysplastic changes is a signal confirming the need for further research and the appointment of adequate therapy.