Endogenous bronchial asthma is a special form of the disease not associated with allergic reactions of the body. As a rule, this course of the disease occurs due to complications of bacterial, viral or respiratory infections affecting the respiratory system. The endogenous form of asthma is more often observed in children. This diagnosis is characterized by a prolonged inflammatory process in the respiratory organs, as well as excessive sputum production, which provokes severe bronchospasm and suffocation.
Exogenous bronchial asthma is a special form of a disease of allergic origin. The disease develops as a result of the body's immune response to certain irritants. Chemical elements affecting the mucous membrane of the bronchioles provoke attacks of suffocation, which, as a rule, stop after the allergen is eliminated. Repeated exposure to irritants causes complications, so the patient is recommended to completely avoid contact with hazardous substances that cause an allergic reaction.
Forms of bronchial asthma
Bronchial asthma of exogenous and endogenous forms differ in origin, but have similar symptoms, therefore, before starting treatment of the disease, it is important to accurately determine the provocateur of this pathology.
General information on the disease
Endogenous bronchial asthma belongs to the category of rarer pathologies of all that have been identified so far. Pathology is recorded in approximately 3-5% of people who have reached 40 years of age. Quite often representatives of the weaker half of humanity encounter this pathology. This is based on the fact that one of the main causes of this pathology is a tendency to diseases of the general respiratory system.
A pathology of this kind is in no way associated with genetic predispositions, that is, the process begins to take shape completely independently of the patient. The development process is carried out strictly according to a predetermined scenario. It all starts from subtle signs and ends with more obvious symptoms. The symptoms greatly complicate the most basic processes of human life. If this pathology is not addressed and treated, after some time asthma will become a more serious syndrome.
Important: If you take into account the development factors of this disease, you can quite effectively stop this pathology, and at the very initial stage of development.
High-quality treatment can only be carried out under the close supervision of a professional pulmonologist and other experienced doctors. This is the only way to achieve a positive result during the treatment process, as well as gain the opportunity to live a more fulfilling life.
Factors influencing the development of endogenous bronchial asthma
The development and course of the disease is influenced by 5 main factors:
For exogenous and endogenous bronchial asthma, the season plays a special role, because patients react sharply to significant temperature changes, as well as changes in atmospheric pressure.
If an infection of various origins enters the bronchi, the body launches an immune mechanism to fight it. The body’s counter-reaction is the release of a specific biologically active substance, which leads to activation of the cells of the bronchial mucosa. At the same time, both structural and functional transformations occur in the bronchi themselves: the mucous membrane can be characterized as edematous, and the smooth muscles of the bronchi as close to a constant spasmodic state.
The infection-dependent form of the disease is more common in children who are prone to persistent infectious diseases of the upper respiratory tract. In this case, endogenous asthmatic bronchitis should be considered as chronic bronchitis with an asthmatic component.
A provoking factor for infection-dependent endogenous bronchial asthma can be tobacco smoke, which is especially dangerous for internal causes of the disease, both with reversible and irreversible obstruction of the respiratory tract.
There are many classifications of bronchial asthma. Because of this, making the correct diagnosis and prescribing the correct treatment for an individual patient is not an easy task. Especially when it comes to the endogenous origin of the disease. However, timely contact with a qualified specialist will not only alleviate the patient’s condition in a short time, but also improve the overall prognosis of the disease.
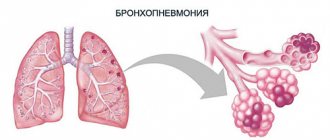
The essence of bronchial asthma. Photo: pulmohealth.com
Forecast
Asthma is a chronic disease, and the prognosis in adults usually depends on the severity of the disease. In some cases, the disease may go into longer periods of remission. Typically, in moderate cases of asthma, clinical manifestations may improve over time.
Only about 10% of cases have a very severe and permanent condition that does not respond to therapy. In such patients, there is an irreversible decrease in lung function, as well as changes in the walls of the airways.
Death from asthma attacks is relatively rare and can be prevented by taking medications.
In general, the prognosis for bronchial asthma is very good . More than half of children with asthma have no symptoms as adults if the disease is caught and treated early, but in some cases asthma can recur even after a decade of absence. In any case, the airways remain vulnerable for life.
Main causes of the disease
The main factor in the development of such a problem as exogenous bronchial asthma are various past and incompletely treated diseases of the respiratory system. For the most part, this includes various problems with the oro- and nasopharynx. Also, the cause may be a fixed high susceptibility to the influence of various irritants and allergens. It is worth paying attention to such common causes of the disease as:
- Problems in the functioning of the endocrine system;
- The form of the disease cannot develop if the body’s defenses are sufficiently stable, as well as with a normal level of metabolism;
- The formation of this pathology is often influenced by problems such as polyps, infections and other factors that aggravate breathing.
As noted above, the disease most often occurs in women; they are most susceptible to various allergens. Women have a fairly sensitive endocrine system; it often malfunctions. This situation often develops against the background of long-term use of hormonal drugs, from incorrect surgical intervention, or against the background of the use of various components that often provoke allergies. Another fairly common cause is deformation of the chest, as well as the general pulmonary bronchial sphere. In such a situation, the disease can develop according to a rather complex algorithm; accordingly, treatment will be associated with a serious number of complications.
The appearance and development of the disease is influenced by various diseases and breathing problems that were suffered in childhood. The main cause is tuberculosis, which, in addition to converting asthma into an endogenous form, can cause more serious health problems. It is for this reason that it is so important to treat all stages of tuberculosis in the most timely manner.
Despite the fact that the pathology due to allergenicity is more common in women, men can also suffer from it. As a rule, these are people who face the problem of oxygen starvation. These are pilots, firefighters, rescuers. In these cases we are talking about a form such as acquired bronchial asthma.
If one of these factors is noted in a person after 30 years of age, it is necessary to undergo competent medical diagnostics to establish the pathology itself, to determine the form of bronchial asthma. To carry out an accurate diagnosis, fluorography analysis is performed, blood and sputum are donated. In this case, the picture associated with the main causes of the pathology will be complete, and accordingly, full effective treatment will be prescribed.
Asthma in young mothers
Asthma in pregnant and lactating women cannot affect the female body, but no one can say in advance how hormonal changes will affect asthma itself. The course of the disease can either improve or worsen. Although inhaled hormonal drugs have virtually no side effects and do not fundamentally affect the development of the fetus, treatment of a pregnant woman should only be carried out under medical supervision. During childbirth, despite severe stress, asthma attacks are very rare, however, during surgical delivery and simply pain relief during labor, they try to avoid anesthesia, giving preference to any option of local anesthesia. Breastfeeding is not prohibited for asthmatics.
The material was prepared by Ekaterina Anatolyevna Tafintseva, a general practitioner and head of the hospital at the Medicine 24/7 clinic.
Features of endogenous asthma
Endogenous asthma is the rarest form of bronchial disease. It is not transmitted hereditarily, so it can arise completely unexpectedly, due to a certain factor contributing to the development of this form. As a rule, the cause of endogenous asthma is untreated diseases of the respiratory tract, as well as the oropharynx and nasopharynx.
According to statistics, women are more often susceptible to the endogenous type of bronchial asthma, which is due to a greater tendency to respiratory diseases and hormonal instability of the weaker sex.
The disease has a progressive formation. Initially, the patient is bothered by minor symptoms, but soon these signs intensify noticeably and take on a pronounced form. With this course, important vital processes in the human body are complicated, so it is very important to identify the endogenous type of asthma at the initial stage of development in order to begin a timely fight against this dangerous disease.
Probable causes contributing to the formation of endogenous asthma:
- disturbances in the functioning of the endocrine system;
- weak immunity;
- improper metabolism in the body;
- infections in the respiratory organs that make breathing difficult.
The most dangerous development of the endogenous form is observed when detecting deformation of the chest or lungs, as well as in the bronchial region. With this course of the disease, a serious pathology is determined, accompanied by multiple complications.
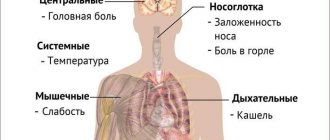
Symptoms
The first sign of endogenous bronchial asthma is discomfort when inhaling air. Some symptoms resemble the development of a cold: sneezing, nasal congestion, runny nose, etc. At night, the patient may experience characteristic suffocation. Pain in the thoracic region often occurs. Gradually, the symptoms take on a more pronounced form, which does not allow the person to lead normal life activities.
To additional signs
Endogenous asthma also includes severe wheezing, shortness of breath, and in some cases redness or rash appears on the skin. A sick person may complain of frequent, long-lasting headaches. At night, people with this diagnosis often suffer from insomnia.
Women who have certain hormonal problems often experience a deterioration in their overall health. Naturally, all these signs cannot be eliminated without treatment, so a visit to a pulmonologist should be immediate!
The progressive development of endogenous asthma is observed in people of mature age. In patients 50 and older, symptoms develop very quickly, intensifying every day. In order to prevent a life-threatening complication, it is recommended that when the first signs of bronchial asthma are detected, you seek help from a medical institution at your place of residence.
Complications of an asthma attack in the early stages
The first signs of bronchial asthma are not always limited to a prolonged cough and short-term blockage of breathing. If changes accumulate in the body over a long period of time, even the initial phase of the disease can be dangerous for the patient. Additional stress is added by the inability to use an inhaler, since the medicine has not yet been selected. But if you know in advance a possible scenario for the development of events, then you can maintain composure and immediately call an ambulance, or ask others about it. So, special measures need to be taken if the first signs of asthma are complicated by the following manifestations:
- It is not possible to restore deep breathing, so it is replaced by frequent and superficial breathing. With this type of breathing, the chest does not move along its normal amplitude, its fluctuations are reduced to a minimum. The amount of air taken in and exhaled rapidly decreases, while the inhalation phase increases, which is why the chest gradually increases in volume.
- As you exhale, you can hear a dry, whistling wheeze. The wheezing characteristic of asthma occurs due to a blocked lumen in the bronchi. To hear it, you do not need special medical equipment - the vulture is clearly audible even at a distance of one and a half to two meters.
- The patient takes a forced position. A unique manifestation of bronchial asthma, manifested in the desire to take a body position that maximally facilitates air circulation through the respiratory system. The person sits down, lowers his arms and legs, and slightly tilts his body forward. For convenience, the patient can grab any vertical support with his hands - for example, the headboard of the bed. You should not try to “unbend” the patient in a forced position - it really helps him maintain relatively stable breathing. Make sure the person is able to remain in this position before calling emergency medical attention.
As a rule, these symptoms of bronchial asthma occur only if mild asthmatic attacks have not been stopped for a long time. But in some patients, asthma develops rapidly, which makes it almost impossible to distinguish a clear line between the first and second phases of the chronic disease. Instead, there are different degrees of asthma attack, most likely in the first months of asthma - mild and moderate. Signs of asthma in adults and elderly patients can be complemented by developing heart failure, which often shifts attention to itself. Try to balance the treatment, paying enough attention to both the heart and the respiratory system. If you suspect that you or your loved ones have asthma, try to see a doctor after the first attack. If this is not possible, pay special attention to the development of the disease at night. It is during the night period that prolonged asthmatic attacks occur, accompanied by complications. It often occurs in the first months due to the fact that suffocation occurs only at night, and during the day the patient suffers only from a dry cough. Stay vigilant and take nighttime asthma symptoms as seriously as daytime symptoms.
Symptoms of pathology
Manifestations of this form of the disease begin with relatively minor discomfort, with unpleasant sensations during basic breathing. Along with this, the patient begins to develop a fairly high susceptibility to certain allergens. At the initial stage, a person experiences problems such as redness of the nose, slight coughing, and sneezing. All this is aggravated by the flowering of various spring and summer plants, as well as by contact with wool. The main difficulty of this disease is that all the symptoms are very similar to the common cold. If such symptoms do not go away within one or two months, we can judge that asthma is developing. As the pathology develops, signs and symptoms such as:
- Problems begin with worsening respiratory problems - it is simply impossible to inhale and exhale normally;
- Increased degree of susceptibility to various allergens;
- Short and rare attacks of suffocation, which most often occur at night;
- Feeling pain in the chest;
- As the disease progresses, the chest may become constricted, especially if it has been injured or infected.
Based on everything said above, it can be noted that over time the symptoms become more and more dangerous and threatening, the person can no longer carry on in his usual way. If the disease is not treated or treated incorrectly, bronchial asthma in its exogenous form develops quite quickly.
Important: When the very first symptoms that were presented above develop, you should immediately contact a pulmonologist, who will prescribe the correct recovery cycle and help you achieve stable remission.
What does exogenous bronchial asthma mean?
Exogenous (atopic, allergic) bronchial asthma is a specific inflammation of the bronchi, in which the trigger is an external allergen. The most common factors that provoke attacks are:
- plant fingers;
- mites living in house dust;
- mold spores;
- animal hair;
- medications, especially aspirin (aspirin-induced asthma);
- chemical substances.
The genetically determined overproduction of immunoglobulin E plays a role in the formation of exogenous asthma, which contributes to the development of inadequate respiratory reactions to substances that do not cause pathological reactions in a healthy person. The symptoms and classification of allergic asthma do not differ from those of the endogenous type of the disease.
Preventive measures
The following recommendations are given as measures to prevent asthma:
Hardening
- maintaining a healthy lifestyle;
- elimination of bad habits, especially smoking;
- hardening;
- Regular exercise or sports.
It is also necessary to maintain room hygiene and prevent it from becoming dusty. It is better not to place a lot of flowering plants in the bedroom, as their pollen can provoke an attack of suffocation.
Proper nutrition plays a big role in regulating internal processes, so you should not abuse fatty, overly salty or spicy foods, alcohol and sweet carbonated drinks. It is recommended to eat more vegetables and fruits, drink enough water, and take additional vitamin complexes in winter and spring.
Additional manifestations
When describing certain additional symptoms of endogenous asthma, professionals note the presence and development of allergic reactions, which may take the form of a rash or slight redness. The pathology also manifests itself in soft wheezing, which a person makes when he wants to perform a respiratory cycle. At the initial stage, the patient may be plagued by unpleasant phenomena such as headaches. It can be quite strong, but short-lived. There is also a general deterioration in well-being, which is especially pronounced in women who have hormonal problems.
There are many people whose endogenous form of asthma is accompanied by a bad mood and psychological state. They often face problems such as mood swings and frequent panic attacks.
Regardless of gender, age and characteristics of manifestation, the disease must be diagnosed and treated immediately after the first signs of pathology appear. In the process of treating endogenous bronchial asthma, it is advisable to use several methods simultaneously - drug therapy, traditional methods of treatment, physiotherapy and preventive measures.
The rate of formation of symptoms, as well as the weakening of the body in bronchial asthma, in the absence of treatment is very high and gives a rather unfavorable prognosis. There is a risk that the disease will take a serious form, various complications will appear, and in a more advanced form, you may encounter the development of a life-threatening condition. The patient does not develop a specific form of asthma, but a more serious pathology. If in this case the medical history is studied, bronchial asthma and its mixed form will be listed on the first pages, and professionals know how difficult it is to treat, especially in pediatrics.
Important: At the first signs, the patient needs to undergo proper diagnosis and treatment of the pathology in order to maintain the opportunity to lead a full healthy lifestyle, so as not to encounter such unpleasant symptoms as suffocation during an asthmatic attack, chronic bronchitis, and so on.
Prevention
In order to prevent the occurrence and development of bronchial asthma, the following measures can be taken:
- Minimizing possible allergenic factors;
- Compliance with sanitary and preventive requirements (wet cleaning, ventilation, air humidification);
- Timely treatment of acute respiratory viral infections and acute respiratory infections;
- Constant care about the level of immunity.
Pneumonia: symptoms and treatment in adults
Is it possible to cure pneumonia at home - this article will answer.
Which inhaler is better, compressor or ultrasonic //drlor.online/preparaty/ot-kashlya/kompressornyj-ili-ultrazvukovoj-ingalyator-kak-sdelat-pravilnyj-vybor.html
Classification of asthma
In order to most accurately classify the disease, let us pay attention to it in two directions. First, we will give the distribution of the disease by form, depending on the severity of its course. From these positions, the disease can be classified as follows:
- Intermittent form - has the mildest course. Attacks are usually short-lived and infrequent (usually less than once a week). Attacks at night practically do not occur at all (less than 3 times a month). In addition, the indicators of the respiratory function of the lungs are at least 80% of the values required for a given patient (a person of the same gender, age, weight, height and race).
- Mild persistent form - characterized by exacerbations that occur more than once a week, but do not exceed the number of exacerbations once a day. The patient's sleep can often be disturbed, and attacks at night occur 2 or more times per month. Respiratory function indicators are the same as in the intermittent form of the disease.
- Persistent form of moderate severity - characterized by the fact that attacks of suffocation occur no less than once a day. There is a decrease in the patient's physical activity, as well as sleep disturbances. Once a week or more often, an asthmatic person notices the onset of asthma symptoms at night. Respiratory function indicators are about 60% of the required values.
- Persistent severe form - characterized by the fact that the patient experiences asthma attacks every day. Night attacks are also common. Physical activity is limited very significantly, and functional respiratory parameters are less than 60% of the required values.
From the standpoint of the origin of bronchial asthma, it can be divided as follows:
- The exogenous form of asthma is caused by the fact that any allergen that the patient inhales from the environment enters the respiratory tract. After this allergen enters the bronchial mucosa, symptoms of the disease arise or intensify.
The circles conventionally depict substances inhaled by the patient that irritate the bronchial mucosa.
- The endogenous form of asthma is usually caused by pathogens of respiratory (breathing) infections (respiratory viruses, for example), as well as excessive emotional or physical stress.
Respiratory viruses, which are one of the causes of endogenous asthma, are conventionally depicted. - Asthma of mixed origin is a combination of endogenous and exogenous forms of the disease.
If the exogenous component is set A, and the endogenous component is set B, then the mixed form of the disease is the intersection of these sets (area A∩B – asthma of mixed origin)
Asthma of mixed origin deserves special attention, since there are more reasons for the development of an attack in a patient with this form of the disease than in a patient whose form of asthma is isolated.
Use of drugs in practice
Instructions for use for Budesonide for inhalation, Salbutamol, Salmeterol and other similar drugs are very similar, so some general recommendations can be made.
So, to stop the oncoming attack of suffocation, one or two doses of the aerosol are inhaled. To do this, you need to turn the balloon over with the valve down and, clasping the mouthpiece with your lips, take one or two deep breaths. If there is no improvement within five minutes, the procedure is repeated. Combinations of several drugs and daily preventive dosage are selected by the doctor individually, based on the patient’s age and the severity of the disease.
If the instructions for use for Budesonide for inhalation or any other drug have been lost, it can be restored using the appropriate search query.
Attention! Under no circumstances should you self-medicate or take medications not according to instructions. This can lead to side effects (if the dosage is exceeded) and complications (if the dosage is too low).
Diagnostic methods
Before prescribing the most competent treatment, the doctor must examine the patient and provide a competent substantiation of the diagnosis. Contacting a professional will guarantee that the examination will be carried out as thoroughly as possible, and that all data will be correctly deciphered. The examination process is divided into such important procedures and activities as:
- Studying the medical history.
- Visual and physiological examination.
- Listening to the lungs.
- Submission of laboratory urine, blood and sputum for laboratory testing.
- Fluorography, radiography and ultrasound.
Of all the procedures, sputum culture is very important, with the help of which you can effectively identify the general level of damage to the entire organism as a whole. An examination using special equipment will allow you to see darkening in the bronchi, which may indicate their damage. In the blood, the doctor will see the ratio of red blood cells and white blood cells; their number in asthma can be significantly increased. Protein is found in the urine of a person with asthma.
Important: For patients with endogenous asthma, such examinations are prescribed every six months. In this way, it will be possible to keep the general condition under control, thereby avoiding the rapid development of complications.
Based on the findings, this specialist prescribes competent treatment, which will quickly improve the patient’s condition and eliminate all unpleasant symptoms. The peculiarity of this pathology is that from time to time it is necessary to adjust the therapy, since each stage of the disease requires its own special means of treatment.
Complications
Often bronchial asthma is complicated by the appearance of pulmonary emphysema and secondary pulmonary heart failure.
In the absence of timely treatment, the so-called status asthmaticus. This complication has three stages:
- Stage 1. Referred to as the initial compensation stage. It is, in fact, an attack of suffocation prolonged for a long time (more than 12 hours). At this stage, patients stop producing sputum and develop resistance to bronchodilator (antispasm) drugs.
- Stage 2: Also known as the decompensation stage. At this stage, the drainage function of the bronchi is disrupted. Because of this, a disorder occurs - a lack of oxygen in the blood and an excess of carbon dioxide.
- Stage 3. Stage of hypercapnic coma. Characterized by a further decrease in oxygen content in the blood and an increase in carbon dioxide content. Because of this, severe neuralgic disorders, hemodynamic disturbances can occur, and in some cases, the death of the patient is possible.
Diagnosis and treatment
Standard diagnostics for suspected asthma include:
- visual examination of the patient, listening to the pulmonary parenchyma and studying the medical history;
- laboratory tests (blood, urine, sputum);
- sputum culture, which allows a specialist to identify the degree of damage to the body;
- fluorography;
- spirometry;
- radiography;
- skin tests (for allergic development);
- Ultrasound diagnostics.
If an endogenous form of asthma is detected, the patient is advised to undergo regular diagnostics, every 6-7 months. Preventive examination allows you to maintain control over the patient’s condition, avoiding possible risks of complications.
Drug therapy in the treatment of bronchial asthma of endogenous, mixed and exogenous forms involves the use of combination drugs that stop attacks of the disease and prevent the risks of complications during relapses.
Particular attention should be paid to the treatment of bronchial asthma with mixed genesis. In addition to symptomatic therapy, the patient is prescribed a basic course, including anti-inflammatory drugs, corticosteroids, beta-2 agonists and other medications.
When treating bronchial asthma, a course of acupressure, exercise therapy, breathing exercises under the guidance of an experienced specialist, aeroionotherapy or acupuncture may be prescribed. These procedures effectively promote recovery and significantly reduce the risks of attacks and complications.
If drug treatment does not bring the expected results, the patient may be indicated for surgical intervention, which involves the total elimination of accumulated secretions in the respiratory organs and correction of the deformity, if such a pathology was identified during the examination. After the operation, the patient’s condition noticeably improves, and all aggressive symptoms disappear.
Some people suffering from this disease use traditional medicine methods for treatment. A variety of decoctions, tinctures of medicinal herbs, compresses and inhalation procedures can give a positive effect, but before starting treatment in this way, you must consult with your pulmonologist!
Please follow and like us:
Effective treatments
This form of pathology of a special endogenous type in approximately 90% of situations cannot be treated with standard beta-2 drugs. This is what significantly complicates general therapy, but involves the use of more serious hormonal agents, mucolytics, bronchodilators, and corticosteroids. To obtain the most positive result, and quite quickly, professionals use two treatments at the same time, and in some cases more. The prescription of each drug is carried out strictly on an individual basis. The doctor relies on the characteristics of the course of the disease, the degree of its development, in addition, the attending physician constantly monitors the treatment process.
Along with medications, patients who suffer from asthma are prescribed special inhalers. If a patient has been diagnosed with endogenous asthma, these therapeutic devices cannot be avoided. Only with their help can you quickly and fairly painlessly stop an asthmatic attack, since the medicinal components are inhaled into the oral cavity, immediately penetrating the affected respiratory organs. During periods of exacerbation, but only in the absence of fever, the doctor may prescribe the use of mustard plasters, cups and special medicinal compresses.
Taking rehabilitation courses in specialized sanatoriums and resorts helps very well. The effectiveness of such treatment is based on the fact that during the treatment process, patients are given daily medications and preventive medications, as well as a wide range of physiotherapeutic procedures.
If the patient consults a doctor late enough, drug treatment may not be enough. For more serious forms and stages of development of endogenous asthma, patients are often prescribed surgery.
Operations for asthma
If standard drug therapy does not give a positive result, that is, there is no improvement within 2-3 months, if the phlegm that constantly collects in the bronchi does not come out, surgical intervention is mandatory.
During the standard operation, the accumulated secretion is removed, as well as the total cleansing of sputum from the area that was severely deformed during the development of the pathology. The patient who has undergone the operation feels the following benefits:
- Carrying out more gentle drug therapy;
- Complete refusal of hormonal drugs or a significant reduction in their dosage;
- Sustained improvement in overall well-being;
- Elimination of psychological stress and anxiety.
Operations are carried out as quickly as possible, modern equipment is used, anesthesia is selected individually, which will be safer in a given situation.
A noticeable and significant improvement in well-being usually occurs after about 1-2 weeks. If the disease has been seriously advanced, the period may be a little longer. As a restorative therapy, as well as at the initial stage of the disease, the doctor can prescribe a treatment regimen using traditional methods.
Treatment with folk remedies
Endogenous bronchial asthma can be cured with folk remedies. It is worth knowing that therapy of this type mostly refers to complementary or restorative therapy. The use of folk recipes as an independent treatment is very rarely used.
Important: Folk remedies, like medications, can only be used after prior consultation with a specialist. The reason is that asthma in most cases is allergenic, and traditional methods can provoke a similar reaction.
Very often, asthmatics are prescribed the following types of therapy. Each of them is aimed at achieving the most positive result and eliminating asthma. Among the most basic methods of therapy are:
- Drinking herbal drinks and decoctions, as well as beneficial plants - horseradish and turnips.
- The use of mustard plasters, various compresses and cups is very effective.
- Using folk remedies, you can independently prepare medicinal nasal drops, special means for gargling and inhalation.
As part of the general recovery course, a special hypoallergenic product can be used. This can be honey and products based on it, but you can take it only if you are not allergic.
A decoction made from the following components, taken in equal volumes, helps very well with endogenous asthma:
- Melissa;
- Coltsfoot;
- Strawberry leaves.
A small amount of propolis is added to these components and the entire composition is poured with boiling water. The amount of water is calculated based on the volume of raw materials, it can be 200 or 400 ml. The resulting composition must infuse for at least 40 minutes before use. After this, the mixture is filtered, cooled and can be taken. The decoction must be drunk only fresh; in extreme cases, 48 hours after preparation are allowed. It is advisable to drink the product before each meal.
To consolidate the result, you should use home inhalations using potatoes. Its vapors make breathing much easier. This recipe effectively cleanses the ducts, thins the mucus, due to which it is removed from the lungs much faster.
Summing up
A competent approach to the treatment of endogenous asthma, its correct diagnosis and prevention will help the patient quickly restore his health. To avoid any pathology after treatment, you should completely avoid contact with allergens and lead a healthy lifestyle. Daily physical activity is important - walking, swimming, and exercise. This will increase metabolism and accordingly strengthen the body’s immune forces, which in turn will effectively resist asthma.
Tags: Bronchial asthma, Endogenous bronchial asthma