Lymph nodes are an important part of the human immune system; they are among the first to protect the body from various infections, and also indicate the presence of a pathological process in the body. In a healthy person, the lymph nodes do not manifest themselves in any way. If they increase, pain, swelling and other manifestations, it is necessary to consult a doctor as soon as possible for diagnosis and treatment, since these symptoms indicate not only local infections, but also serious systemic pathologies.
Kinds
Inflammation of the lymph nodes (lymphadenitis) can be serous or purulent. The second option occurs in a more aggravated form, with violent clinical manifestations. Depending on the statute of limitations, the pathology can be acute or chronic. If the underlying disease that caused the damage to the lymph nodes is not eliminated, it takes on a chronic form. This makes you feel worse and delays the onset of recovery. The type of disorder of the lymph nodes is determined only with the help of ultrasound. Inflammation can also be primary or secondary. In the first case, it occurs separately, independently, in the second - against the background of the underlying disease.
Symptoms
The following symptoms indicate damage to the inguinal lymph nodes:
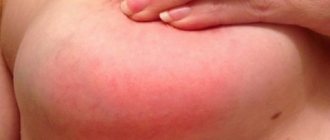
- Their visual increase due to swelling of the structure
- Increased body temperature
- Sealing of lymph nodes
- Feeling of weakness, loss of appetite, insomnia, which together indicates intoxication of the body
- Increased pain in the lymph nodes when palpated
- Impaired mobility in the hip joint
- Desire to frequently change body position to make you feel better
If the lymph nodes are suppurated, the predominant symptoms are severe hyperthermia, decreased blood pressure, dizziness and inability to stand for a long time. The stage of the inflammatory process is determined in a laboratory manner and taking into account the answers of other types of diagnostics. If there is a malignant process in the patient’s body, in 90% of cases lymphadenitis occurs only when the cancer progresses and forms metastases. Distant foci of malignant tumors affect the lymph nodes along with the pelvic bones, lungs and brain.
Choose a specialist, read reviews and make an appointment with a gynecologist online
Establishing diagnosis
Not a single doctor can immediately tell you what can cause an enlarged lymph node. In order to correctly determine the cause, a number of examinations should be carried out:
- Visual inspection. Assess the size of the compaction, determine the presence of purulent contents and find out. What is the condition of the nearby lymphatic structures?
- UAC. Laboratory diagnostics allows you to determine the level of leukocytes in the blood, ESR and C-reactive protein.
- Hardware diagnostics. To visualize the internal structures of the node, ultrasound or MRI is performed.
- Biopsy. A pinch from the affected area (internal) is taken if lymphoma is suspected.
- Flora smear. Taken by a gynecologist to identify sexually transmitted diseases or STIs. Oncocytology is mandatory.
Causes
Common causes of inguinal lymphadenitis in women are the presence of a pathological process in the body, trauma to anatomical structures located near the pelvis and perineum. The development of pathology is preceded by the progression of infection or inflammation in parts of the genitourinary system, a malignant process, and damage to muscle fibers. Somewhat less often - individual intolerance to substances, drugs, food. Also, damage to the lymph nodes manifests itself in purulent processes in the gluteal region, sacral or coccygeal region, and genitals. These include abscess, furunculosis, paraproctitis, aggravated by hemorrhoids.
Oncological neoplasms
Lymphadenitis occurs when a malignant tumor process develops in the body. In this case, the anatomical structures become dense, large, and painful.
Enlarged lymph nodes are accompanied by symptoms such as:
- Weakness, dizziness, lack of appetite, decreased blood pressure
- Severe pain syndrome
- Increased body temperature (rare)
- Pallor, blood discharge during urination, defecation
- Difficulty in adopting a comfortable and pain-free body position
Inflammation of the lymph nodes occurs only with a malignant neoplasm - a benign tumor process rarely contributes to such aggravation. A common cause of inguinal lymphadenitis is cancer of the uterus, ovaries, bladder, rectum or colon. To determine the location of the malignant process and confirm the nature of the tumor, the patient visits an oncologist, undergoes a CT scan, MRI, biopsy, and donates blood to determine tumor markers.
Viral infections
Microorganisms such as the herpes virus, as they spread in the blood, contribute to the development of numerous symptoms, including lymphadenitis. Additional symptoms are increased body temperature, weakness, headache and dizziness, hypotension, refusal to eat, nausea. If a woman's inguinal lymph nodes become inflamed, she may potentially have genital herpes. Characteristic rashes in the form of blisters appear on the mucous membrane of the genital organs. They cause pain and make it difficult to sit. Treatment is predominantly antiviral.
ARVI, colds and hypothermia
Infection with viral microflora occurs under conditions of reduced immunity. The body's protective properties are weakened after blood loss, regular hypothermia, and insufficient intake of vitamins and minerals from food.
Circulation of a pathogenic pathogen in the blood is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- increased body temperature
- chills
- headache
- weakness
- nasal congestion
- lack of appetite
- sore throat
- dizzy
Additionally, there is a significant decrease in blood pressure levels. Lymph nodes do not become inflamed immediately after the virus enters the blood. The symptom occurs simultaneously with other clinical manifestations of ARVI. After eliminating the cold infection, the lymph nodes independently return to their physiological state. Treatment of ARVI is carried out exclusively with antiviral drugs. The use of drugs from the antibiotic group for colds is contraindicated and is permissible only in the presence of a secondary bacterial infection.
Vaginal candidiasis
Thrush, or vaginal candidiasis, is a consequence of the progression of fungal microflora inside the vagina. A favorable environment for the proliferation of microorganisms of the genus Candida is moist and warm. Causes of the disease:
- poor intimate hygiene (especially during menstruation, after sexual intercourse and after visiting the toilet)
- presence of diabetes mellitus
- intestinal dysbiosis
- unprotected intimacy with a partner who does not perform hygiene procedures
- long-term or uncontrolled use of antibiotics
Reduced immunity contributes to the entry of fungal microflora into the vagina. Weakening of the body's protective properties is caused by a condition after a recent operation, fasting or following a strict diet; early postpartum period. Symptoms of vaginal candidiasis are itching inside the vagina, discharge of cheesy secretion, pain during intimacy.
Inflammation of the lymph nodes occurs with aggravated forms of vaginal candidiasis. Basically, if the disease takes a chronic course, or when a woman is treated incorrectly for this pathology. The inflammatory process in the lymph nodes is eliminated on its own immediately after the elimination of the fungal infection of the vagina.
Mechanical injuries
Injuries to soft tissues (including mucous membranes) that occur inside the urogenital tract or gluteal region are accompanied by lymphadenitis in 90% of cases. Inflammation of the lymph nodes occurs mainly due to suppuration of the injured epithelium, if the wounds were not promptly treated with an antiseptic. Associated signs in this case are redness of damaged tissues, swelling, and increased pain. Immediately after the bacterial wound infection is stopped, the lymph nodes return to normal.
Fungal microorganisms
Mycoses and candidiasis (depending on the type of fungal microflora) contribute to inflammation of the lymph nodes. This is how the body’s immune response to the penetration of a pathogen into the blood is manifested. The woman is treated with antifungal drugs, taking into account the characteristics of the identified microorganism.
Sexually transmitted diseases
Urogenital infections - chlamydia, gonorrhea, syphilis, trichomoniasis, manifest themselves with numerous symptoms. Among them:
- Purulent, curdled or foamy vaginal discharge
- Pain during intimacy
- Increased urination
- Infertility
- Itching in the genitals
- Menstrual irregularities
Inflammation of the lymph nodes occurs both in the acute form of sexually transmitted diseases and in their chronic course. Anatomical structures assume a healthy state on their own, immediately after eliminating a sexually transmitted infection.
Reproductive system problems
Inflammatory diseases of the reproductive system are manifested by the development of numerous symptoms, including damage to the lymph nodes. A similar thing happens with adnexitis and endometritis. This is an inflammation of the appendages and uterus, which can occur in acute or chronic form. Main symptoms of pathologies:
- Pain in the lower abdomen and lumbosacral back
- Menstrual irregularities
- Discomfort during intimacy
- Discharge of pathological secretion from the vagina - purulent, mucous, with a strong unpleasant odor
- Infertility or frequent miscarriages
- General weakness, irritability
- Increased body temperature
Protracted lymphadenitis indicates the progression of pathogenic microflora in a woman’s body. Examination of a smear of vaginal secretion allows us to determine the type of microflora and prescribe therapy in accordance with the detected pathogen. Treatment of infectious and inflammatory pathologies consists of antibiotic therapy, the use of non-steroidal drugs, sexual rest, and enhanced hygiene.
Allergic reactions
Intolerance to certain substances (food, wool, hair, dust, cosmetics or perfumes) manifests itself in a wide range of symptoms. In women, inflammation of the inguinal lymph nodes can be caused by an allergic reaction to factors such as:
- latex from which condoms are made
- pads, vaginal tampons
- underwear fabric
- products intended for intimate hygiene
Allergy symptoms include severe itching and swelling of the vaginal tissue, redness of the vulva, discharge of cheesy secretion, plaque on the mucous membrane of the labia. Additionally, pain occurs when urinating. If an allergy develops, a woman needs to take an antihistamine (Suprastin, Diazolin). Medicines in this group stop the activity of irritants, eliminate itching, help eliminate swelling of the mucous membranes, and reduce redness and irritation of the skin.
Lymph nodes in women return to normal on their own 1-2 days after the allergic reaction is suppressed. It is equally important to exclude repeated exposure to the irritant: you should choose a different type of contraception and use other personal hygiene products.
Muscle strains during sports
Unregulated physical activity leads to damage to muscle fibers. Symptoms of the condition are pain, swelling in the area of injury, redness of tissue, increased general temperature. There is also limited mobility in the torso and difficulty in adopting a body position. In women, inflammation of the lymph nodes occurs with increased tension in the oblique and rectus abdominal muscles (after excessively intense abdominal pumping in the gym).
What happens in the lymph nodes
Inflammation, regardless of the cause, always follows the same pattern. Any of the above factors (viruses, bacteria, tumor cells) damage the structures of the lymph node, as a result of which biologically active substances are released from the damaged cells. The latter trigger a cascade of responses designed to stop the further spread of the pathogen. These include:
- vasodilation, leading to stagnation of blood in the lymph node area;
- increased vascular permeability to blood plasma and immune cells;
- release of the liquid part of the blood into the lymph node tissue with the formation of edema;
- migration of leukocytes from the bloodstream into the cavity of the lymph node.
It would seem that the lymph nodes are filled with immune cells, why are they not able to cope with the pathogen themselves? The fact is that T-lymphocytes work in close cooperation with other immune cells and without their help they “do not see” the enemy. In addition, their main function is the destruction of the body’s own cells in which any changes have occurred. Neutrophils and monocytes in the blood are responsible for antimicrobial protection; they are the ones who rush in large numbers to the site of inflammation in response to a distress signal.
The further development of events depends on at what stage it is possible to destroy the enemy:
- serous inflammation ends at the stage of edema formation and immune activation;
- purulent – with the death of a large number of neutrophils, lymph node cells and bacteria;
- phlegmon - with purulent melting of the lymph node capsule and the spread of the process to the adjacent subcutaneous fat.
Possible complications
Purulent lymphadenitis is dangerous for the development of an abscess and sepsis. In the first case, we are talking about extensive tissue inflammation, in the second – about blood poisoning. Both pathologies are dangerous due to the development of death. The main manifestations of these violations:
- increase in body temperature to high numbers
- swelling and redness of the tissue surrounding the inflamed lymph node
- headache, weakness, dizziness
- decrease in blood pressure readings
Also possible complications of lymphadenitis in the groin in women are osteomyelitis, thrombophlebitis. Inflammatory damage to the bone marrow and veins is indicated. If the problem lymph node lies close to a blood vessel, it is potentially susceptible to damage in the absence of proper treatment.
Swelling of nodes
In women, the inguinal lymph nodes, which are located in the pelvic area, may become swollen.
This disease is called lymphadenitis and refers to secondary infections that appear after untreated primary diseases:
- influenza and ARVI;
- measles;
- rubella;
- genital herpes;
- chlamydia;
- ureaplasmosis;
- thrush;
- gonorrhea;
- syphilis.
Organ diseases also affect the swelling of lymph nodes:
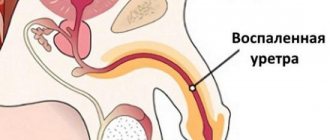
- bladder – urethritis;
- oncology of the pelvic organs;
- intestinal problems;
- disorders in reproductive function of an inflammatory nature (colpitis, balanoposthitis).
The nodes also swell with severe, prolonged allergic reactions.
In addition to swelling, the following symptoms may appear:
- fever or chills;
If the inguinal lymph nodes are enlarged in women, this can cause chills and fever. - discomfort when walking or other movements;
- changes in skin color in the area of inflammation;
- pain on the inner thigh, which can radiate to the stomach;
- lethargy;
- migraine;
- deterioration in general health.
Which doctor should I contact?
A lymphologist is involved in identifying and eliminating diseases associated with the lymphatic system. But since not every hospital has a doctor of this profile on staff, visiting a therapist is acceptable. This specialist will conduct an examination, interview, and, based on a preliminary diagnosis, prescribe diagnostic methods.
If the presence of infectious and inflammatory processes in the organs of the urogenital tract is established, the woman is treated by a gynecologist or urologist. When damage to the lymph nodes is a consequence of a sexually transmitted disease, therapy is prescribed and monitored by a venereologist. If lymphadenitis develops due to intolerance to drugs, food or other substances, you will need to consult an allergist.
Choose a specialist, read reviews and make an appointment with a gynecologist online
Inspection
When visually examining a patient, the doctor must carefully examine the size of the lymph node and its mobility. The following signs may indicate acute inflammation:
- pain in the lymph node upon palpation;
- swelling of the tissues that are located next to the inflamed lymph node;
- the lymph node is motionless due to the fact that it has fused with neighboring tissues;
- dense consistency of the lymph node;
- bright red color of the skin over the lymph node.
If the doctor discovers that there is softening of the tissue in the center of the lymph node, then this is a sign of the formation of purulent masses inside the node. When a purulent abscess is independently opened in the groin area, phlegmon is formed - a compacted zone without clear boundaries. Pus may be released through the fistula tracts.
When a tumor forms, inflammation in the lymph node is mild:
- the skin over the lymph node does not differ in color from the rest of the skin;
- the lymph node is not connected to adjacent healthy tissues;
- there is no pain;
- On palpation the lymph node is hard.
Diagnostics
To establish a diagnosis and identify the root cause of inflammation of the lymph nodes in the groin area, a woman needs to undergo:
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs
- Laboratory testing of blood, urine (biochemical, clinical, bacteriological, to determine RW, blood group and Rh factor, tumor markers)
- Smear to establish vaginal microflora
- Allergen test (if lymph node damage is associated with intolerance to certain substances)
- Computed or magnetic resonance imaging
- Examination on a gynecological chair
If a woman’s condition is caused by a malignant tumor process, a biopsy of the lymph node or organ in which the tumor occurred is performed. After taking a tissue sample, it is sent for histological examination. Additional tests and diagnostic procedures are prescribed depending on the individual characteristics of the clinical case.
Lymph node: functions and features
Lymph nodes are small extensions of the lymphatic system that play the role of a natural filter . The lymph passing through it is cleansed of harmful substances and pathogenic microorganisms.
That is why this system reacts faster than others to the appearance of an infection in the body.
The lymph nodes of the groin area are responsible for cleansing the fluid of the pelvis and lower extremities . When microbes appear in this area, such a node is one of the first to respond to infection.
Read more about the functions and movement of lymph here.
Treatment
Serous lymphadenitis is eliminated with the help of antibiotics and physiotherapeutic procedures. Antibacterial therapy involves the use of broad-spectrum antibiotics. Stopping the activity of the pathogen helps eliminate the underlying pathology and inflammation of the lymph nodes themselves. Of the physiotherapeutic procedures, the most effective is electrophoresis.
The method promotes:
- eliminating swelling of the lymph nodes
- suppression of the activity of pathogens
- normalization of blood circulation and lymph flow in the affected area
- reducing pain
Purulent lymphadenitis with abundant accumulation of pathological contents is an indication for drainage of the inflamed node. Simultaneously with drug treatment, the patient is prescribed nutritional correction. During therapy, food should be especially fortified. You should also increase your water balance. The recommended volume of fluid consumed is up to 1.5 liters per day, which allows you to flush pathogenic microflora from the body. To increase immune abilities, the patient is prescribed the use of vitamins. Use Neurobex, Neurorubin, Milgama or ascorbic acid and B vitamins separately.
In case of aggravated forms of lymphadenitis, surgical intervention is performed - puncture of the anatomical structure with subsequent evacuation of purulent contents. An ointment with antibacterial properties is applied to the wound - streptocidal, ichthyol or Levomekol. Then the medicine is secured with a bandage, which must be replaced once every 12 hours until the signs of the inflammatory process are completely eliminated.
If lymphadenitis is caused by urogenital infections, her sexual partner is treated at the same time as the woman. Vaginal candidiasis is eliminated not with antibiotics, but with antifungal drugs - Clotrimazole or its analogues. The use of antibacterial agents only aggravates the course of fungal infection of the vagina.
Undergoing physiotherapeutic procedures
Very often, doctors recommend physiotherapy to sick women diagnosed with inguinal lymphadenitis. They are aimed at eliminating inflammation in the affected area, reducing pain, and destroying harmful microorganisms.
Effective hardware treatment methods still remain:
- UHF can eliminate inflammation in a short time.
- Ultrasound treatment – promotes resorption of the inflammatory infiltrate.
- Irradiation with ultraviolet rays eliminates inflammation.
You might be interested to know about: Quick-acting laxative in tablets
All procedures in the physiotherapy room should be carried out regularly, exactly as prescribed by the doctor. If the amount that was prescribed is not enough, the doctor will increase the treatment process.
Prevention
To avoid the development of inflammation of the lymph nodes in the groin, a woman should:
- Refuse excessive physical activity, approach the issue of sports training competently, and do not perform sudden loads.
- Avoid casual sex.
- Dress according to weather conditions, do not get too cold.
- Avoid suppuration of wounds, promptly treat damage to the epithelium with an antiseptic.
- If you are at high risk of developing diabetes, check your blood glucose levels regularly.
- Reduce inflammation in a timely manner - treat teeth when caries appears, eliminate tonsillitis.
- If there are indications for the use of antibiotics, drugs that normalize the intestinal microflora should definitely be used at the same time. This will avoid the development of vaginal candidiasis, which is accompanied by inflammation of the lymph nodes.
- To refuse from bad habits.
- During menstruation, use not only pads, but also tampons.
- Regularly strengthen the body's immune properties.
Additional preventive measures include selecting the optimal method of contraception, avoiding excesses in sexual activity, and taking hygiene measures. Inflammation of the inguinal lymph nodes in women in 90% of cases is associated with the presence of a pathological process in the urogenital tract. Regardless of the type and stage of development of the disease, restoring health requires an integrated approach. This includes the use of medications, diet, maintaining sexual rest until complete recovery, and taking hygiene measures. The type of underlying disease against which the lymph nodes become inflamed is of decisive importance. Aggravated forms of the lesion are eliminated surgically.
Stages of lymphadenopathy
Inguinal lymphadenitis in women with infections goes through several stages of development:
- Catarrhal;
- Hyperplastic;
- Purulent-necrotic.
Catarrhal stage
After the penetration of various pathogens, blood vessels dilate and local blood flow increases. The size has not yet increased, but palpation is likely to cause pain.
Hyperplastic stage
The multiplication of the pathogen activates the immune response, the permeability of the vascular wall increases and exudate collects between the cells. The size of the node increases, it can be easily felt under the skin. When surrounding tissues are involved in the process, an area of redness appears on the skin.
Purulent-necrotic stage
If treatment is not started in a timely manner, toxins released by dead microorganisms destroy cells, forming a cavity with purulent contents inside. Multiple lesions of the lymph nodes lead to severe intoxication. If the capsule ruptures and pus escapes into the abdominal cavity, life-threatening complications may develop - peritonitis and sepsis.