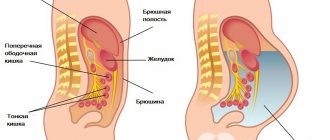
Lymph nodes are filters that cleanse lymph from bacteria, viruses, toxins and cellular breakdown products. All of these agents enter the lymph from peripheral tissues and are neutralized by immune cells in the lymph nodes. In addition, the maturation of the T-cell component of immunity occurs in them: T-helper and T-killer cells, which are responsible for the antitumor and antiviral defense of the body.
Lymph nodes that collect lymph from a specific part of the body are called regional. From the lower extremities, perineum and genitals, lymph flows through the inguinal lymph nodes. They lie to the right and left of the perineum in the area of the inguinal ligament and large vessels of the lower limb, covered on top with subcutaneous fat and skin. Inflammation of the groin lymph nodes is called groin lymphadenitis. The disease occurs in people of both sexes and develops more often in children, young and mature people.
It should be understood that not any enlargement of the lymph nodes in the groin is called lymphadenitis. A similar reaction occurs when exposed to viral infections, excessive sun exposure, autoimmune processes, overheating and indicates activation of the T-cell component of immunity. Immune cells in the nodes actively multiply and develop, which leads to functional hyperplasia (increase in number) of lymphoid tissue. In healthy people, up to 5 groups of lymph nodes can be enlarged, which is not considered a pathology. The ending -itis in the word lymphadenitis means inflammatory changes in the tissue of the lymph node, which will be discussed below.
What is lymphadenitis
This diagnosis is made when the lymph nodes are inflamed. The disease is the body's response to infection and develops when microbes and their toxins enter the blood or lymph. Inflammation in the groin area is often associated with diseases of the pelvic organs and has 3 stages:
- Serous lymphadenitis - local swelling occurs, the temperature rises to 37 degrees.
- Purulent - the inguinal lymph nodes become fused with neighboring tissues, pathological exudate (liquid) begins to accumulate, and an abscess occurs.
- Complicated - lymphadenitis affects fatty tissue, phlegmon develops, and urgent medical intervention is required.
Why is swollen lymph nodes in the groin dangerous?
If the disease is not treated, the inflamed node begins to collapse, and the pus spreads to neighboring tissues. This leads to sepsis - blood poisoning, which develops rapidly and is dangerously fatal. Other complications of lymphadenitis:
- Fistulas are channels through which exudate flows out from the purulent cavity.
- Cellulitis is suppuration of tissue with tissue melting; in the photo it looks like extensive swelling.
Diagnostic measures
It is not difficult to reach a verdict of “inguinal lymphadenitis.” As a rule, this is possible already during the first examination by a doctor in this area. First, the doctor carries out measures to identify the cause of the increase in the volume of lymph nodes, based on which they determine how to treat the disease.
This issue is dealt with by a therapist, surgeon, and urologist. Laboratory tests are ordered:
- general - blood, based on the results of which one can detect a pathological process of an inflammatory nature occurring in humans: a high leukocyte sedimentation rate, increased neutrophils during an infectious lesion, eoinophils during an allergic reaction and parasitic infestation, monocytosis indicates a venereal disease;
- general - urine: protein and leukocyte cells are changed in quantitative terms.
To confirm the diagnosis, instrumental diagnostic measures are prescribed:
- ultrasound examination of the lymph node: determine the degree of pathological changes, the nature of the process;
- X-ray examination: also helps to determine the condition of the lymph structures;
- biopsy: prescribed if there is a suspicion of a pathological process of an oncological nature.
Based on the results of the measures taken, the most effective treatment is prescribed.
Types of inguinal lymphadenitis
The disease is divided into types according to the reasons for its development and the form of its course. If 1-2 lymph nodes are inflamed, this is a local disease, and if a whole group in the groin area is affected, it is a generalized or general disease. According to the affected area, unilateral and bilateral lymphadenitis is distinguished. Other types of disease:
- Acute – characterized by severe pain in the groin area, a rise in temperature and a general deterioration of the condition. Severe symptoms persist for up to a week.
- Chronic - the lymph nodes are constantly dense and enlarged, gradually harden, the general condition of the patient is satisfactory.
- Primary - such lymphadenitis occurs rarely and is associated with the entry of pathogenic microorganisms through damage to the skin or mucous membranes.
- Secondary – occurs due to infections in other parts of the body, sexually transmitted diseases caused by chlamydia, ureaplasma.
- Specific – develops in severe systemic diseases: typhus, syphilis, metastatic cancer, tuberculosis.
- Nonspecific - lymphadenitis occurred against the background of an infection caused by cocci, viruses, fungi.
- Infiltrative - the skin is not changed, the inflamed lymph node is enlarged, compacted, but the neighboring tissues are healthy.
- Indurative - the development of lymphadenitis is slow, the symptoms are erased, the nodes atrophy.
- Caseous - lymph nodes in the groin area are fused with neighboring tissues, inflammation occurs with necrosis and suppuration. During recovery, scars form.
How does the disease manifest itself?
The clinical picture depends on the causes and form of the disease. First, lymphadenopathy develops: round lumps measuring 1.5-2 cm appear in the groin area on the right or left. They create discomfort, but do not hurt. Children 1-6 years old experience lymphadenitis more severely: with high fever, nausea, and weakness. Inflammation of the lymph nodes in the groin in women and men has the same symptoms:
- hyperemia (redness of the skin) of the groin area;
- pain on palpation, walking;
- temperature increase;
- increase in leukocytes and ESR in blood tests;
- chills, weakness, headache, loss of appetite - with purulent lymphadenitis;
- swelling in the area of the affected lymph nodes;
- the appearance of fistulas through which cheesy masses or liquid are released;
- sharp pain in the lower abdomen, vaginal discharge in women - with lymphadenitis due to sexually transmitted infections.
Clinical manifestations
General symptoms of inguinal lymphadenitis:
- discomfort in the perineum, increasing when walking;
- increase in nodes;
- mild or severe pain on palpation;
- feeling of tension and burning in the perineum;
- formation of a fistula, discharge of pus or colorless fluid;
- severe tissue swelling;
- change in skin color over the affected node;
- immobility during fusion with other tissues;
- dense consistency.
When the cause is a tumor process in the lymph node, the clinical picture is less pronounced. Patients experience moderate pain and slight redness of the skin. The nodes are not soldered to and are hard to the touch.
Why do the inguinal lymph nodes become inflamed?
The infection can penetrate the skin or mucous membranes if they are damaged, but more often it is transferred to the node from another inflammatory focus. With injuries, the disease develops quickly, with other pathologies it develops more slowly. Causes of lymphadenitis in the groin:
- malignant tumors, especially of the genital organs;
- viral infections – measles, rubella, chickenpox, herpes;
- inflammatory processes caused by tuberculosis bacillus, streptococcus, staphylococcus;
- osteomyelitis of the lower extremities;
- groin injuries – from impacts, falls;
- trophic ulcers, erysipelas;
- sexually transmitted diseases – syphilis, chlamydia, ureaplasmosis;
- inflammatory processes in the organs of the reproductive system;
- dermatological diseases of the groin area - boils, carbuncles;
- cat scratches.
Articles on the topic
- Groin pain in men - diagnosis by location and type, therapy
- Tuberculosis of the lymph nodes in children and adults - causative agent, symptoms and treatment methods
- The first signs of HIV in men - when and how they appear, stages, clinical picture, emergency treatment
Inguinal lymphadenitis in women
A common cause of the disease is thrush - a fungal infection of the vagina. Its symptoms: curdled discharge, unpleasant odor, itching. Tumors and cysts cause lymphadenitis in women more often than in men. In addition, the disease is caused by:
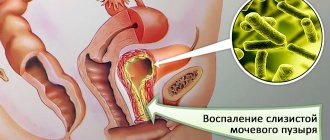
- infectious inflammation of the genitourinary system: colpitis, vulvitis, bartholinitis, cystitis;
- genital herpes;
- Hodgkin's lymphoma is a cancer of the circulatory system;
- venereal diseases from unprotected sexual intercourse - caused by chlamydia, ureaplasma;
- weakened immunity during pregnancy.
In men
The most common causes of lymphadenitis are urethritis, inflammation of the foreskin, sexually transmitted infections: syphilis, gonorrhea. Less commonly, cancer metastases and furunculosis appear in the groin area in men. In athletes, the disease occurs due to injuries to the legs and reproductive organs.
In children
Lymphadenitis develops in a newborn after contracting an infection in the womb or due to skin injuries in the first weeks of life. In infants and older children the disease is caused by:
- weak immunity;
- congenital pathologies of lymph outflow;
- tuberculosis;
- Infectious mononucleosis;
- rubella.
Possible complications
If left untreated, purulent lymphadenitis will sooner or later lead to blood poisoning and tissue death (necrosis). The chronic form does not cause significant discomfort, but can be a sign of a serious illness, tuberculosis or cancer, which, if not addressed in time, can lead to a tragic outcome.
Lymphadenitis in children can signal bone damage, which requires timely diagnosis and long-term therapy.
Treatment of lymphadenitis
For help, contact a gynecologist, surgeon, or venereologist. Therapy is prepared by a doctor based on the results of tests and examinations. Enlarged lymph nodes in the groin in men and women need to be protected from hypothermia, but they should not be warmed up. The patient is advised to rest completely and avoid physical activity. The disease is treated locally and systemically, tactics depend on its cause and form:
- At the early stage of lymphadenitis without an abscess, apply compresses with antiseptic ointments (Levomekol).
- Boils and carbuncles are treated locally with anti-inflammatory ointments and compresses.
- For lymphadenitis against the background of infectious diseases, medications and physical therapy are indicated: electrophoresis, galvanization.
- In case of purulent lymphadenitis in the groin area, an abscess is drained - the pathological exudate is pulled out through a needle and the cavity is treated with an antiseptic.
- Malignant tumors that have metastasized to the lymph are treated with chemotherapy or radiation therapy. Surgery is rarely performed.
- In case of necrosis of the inflamed nodes, surgery to remove them is indicated. It is performed in the absence of alternative exits, since it disrupts the outflow of lymph.
Antibiotics for inflammation of the lymph nodes in the groin
These medications are prescribed for the purulent form of the disease, phlegmon, to kill microbes that have entered the lymph and blood. In case of severe lymphadenitis, the drugs are used in injections, in other cases - in tablets. For treatment, broad-spectrum agents are used, which are selected according to the type of infection and the patient’s age:
- penicillins (Amoxicillin, Ampicillin) - more effective than others for lymphadenitis, but have many contraindications;
- cephalosporins (Cefazolin, Ceftriaxone) – for genitourinary infections;
- macrolides (Erythromycin) – for intolerance to penicillin drugs.
Comprehensive diagnostics
When a patient comes to a medical facility with complaints indicating inguinal lymphadenitis, the first step is a visual examination and palpation of the lymph nodes. Along with a physical examination, an anamnesis is collected: the doctor finds out the details of intimate life, finds out whether there are chronic diseases, and whether medications are being taken. These diagnostic measures are required, but they are not sufficient to make a diagnosis.
Protrusion of the peritoneum into the inguinal canal area is often confused with an enlarged lymph node when palpating the corresponding area. In addition, the signs of the diseases are very similar to each other. A comprehensive examination, which includes:
- general analysis of urine and blood;
- blood biochemistry;
- LN biopsy;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs;
- immunological tests;
- screening for STDs using PCR (polymerase chain reaction);
- bacterial inoculation of the contents of the node.
Only on the basis of the data obtained, the doctor prescribes the necessary therapy. Observation and treatment are carried out by: dermatovenerologist, infectious disease specialist, oncohematologist, surgeon, urologist, gynecologist. Obviously, the choice of specialist depends on the specifics of the underlying disease.
Important! For an initial examination, you should go to a general practitioner, who will give you a referral to a specialist doctor.
How to treat an inflamed lymph node at home
Folk remedies are used only after consulting a doctor as a method of maintenance therapy. When suppurating they are prohibited. Compresses should be cool; heat should not be applied to inflammation. Proven recipes:
- Dilute echinacea tincture with warm water in a ratio of 1:2. Soak a bandage folded three times with the product and apply to the area of lymphadenitis. Secure with a bandage and leave overnight. Do this until the pain disappears.
- Take a collection of yarrow, mistletoe and St. John's wort. Pour 1 tbsp. l. with a heaping glass of boiling water, heat for 5 minutes over medium heat. When the broth has cooled, soak gauze in it and apply it to the sore spot in the evening. Repeat once a day for 1-2 weeks.
Prevention
To protect against lymphadenitis, strengthen your immune system with vitamins and proper nutrition. Adults should monitor the health of their genital organs and see a gynecologist or urologist every six months. In addition, it is necessary to exclude risk factors:
- Use condoms during sexual intercourse.
- Treat diseases of the genitourinary system in a timely manner.
- Be careful when playing sports and avoid injuries to the groin area.
- Treat microtraumas on the skin with antiseptics.