The text is presented for informational purposes only. We strongly urge you not to self-medicate. When the first symptoms appear, consult a doctor. We recommend reading: “Why you can’t self-medicate?”
Vitiligo is a skin disease in which the dermis loses its natural pigmentation due to the destruction of melanin in the body. As a result of this process, pigment disappears in some areas of the skin and white spots form.
In medical practice, vitiligo is also called leukoderma. From Latin, this name of the disease is translated as “white skin.” According to statistics, 1% of the total population of the planet suffers from “white skin” syndrome. The disease does not depend on population, place of residence or race. Purely visually, such spots are more noticeable in dark-skinned people for obvious reasons. The onset of the disease most often occurs at the age of 10-30 years - in half of the registered cases of the disease, patients discovered problems during this period.
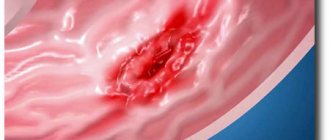
Vitiligo - white spots on the skin
Vitiligo is a type of skin disease when the dermis loses its natural pigmentation due to the destruction of melanin. As a result of this process, some areas of the skin lose color, which creates the effect of white spots or variegation. The disease has been known since ancient times, and in Rus' among the common people it was called “dog,” which is most likely due to the appearance of the patient.
In medical practice, in addition to the name “vitiligo,” you can find another definition of this skin pathology, which sounds like leukoderma. If you turn to Latin, you can understand the origin of this word; translated it means white skin.
As for statistics, according to some data, up to 1% of the world's population suffers from vitiligo. The disease is not population specific, but the spots are more noticeable in dark-skinned people. The disease most often manifests itself between the ages of 10 and 30; this period accounts for up to 50% of all cases of pathology.
Diagnosis of the disease
During diagnostic procedures, specialists must take into account the appearance of the spots on the skin, which are very specific to vitiligo and are not similar to the manifestations of other diseases.
To obtain additional information about the course of the disease, the specialist refers the patient to a series of tests. Sometimes it is important to know at what period vitiligo began to appear, how long it lasts, whether there is a tendency for the pathology to grow, and whether the patient has a hereditary predisposition to such a disease.
When diagnosing vitiligo, it is important to understand whether only one factor caused the onset of the disease, or whether a combination of specific conditions in the body led to such consequences. This will play a role in prescribing treatment and in preventing relapse of the disease in the future.
Symptoms of vitiligo
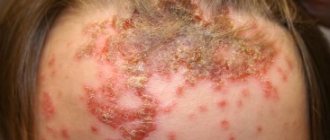
The main symptom of the disease is the appearance on areas of the skin of spots that have a milky white color and clearly defined boundaries. Parts of the body most susceptible to vitiligo include the face (the area around the mouth, ears, eyes, nose), arms and legs (their backs, fingertips, elbows, feet, knees), the groin area and the anal area. Spots may appear on the scalp, including the beard and mustache area in males.
There are several types of spots; the following types of depigmentation can be noted:
- At the point where the skin susceptible to the pathological process transitions into healthy skin, a pigmented contour is observed, the spots themselves have three colors.
- Spots of four colors, which are limited to a border with pronounced pigmentation.
- Spots are inflamed areas that are limited by a slightly raised shaft.
- Spots that have a bluish color.
In addition, the disease may be accompanied by the following symptoms:
- Nest-shaped baldness;
- Choreoretinitis, in which the back of the eye and retina become inflamed;
- Graying or lightening of hair in areas affected by vitiligo;
- Scleroderma;
- Psoriasis;
- Lichen planus;
- Chronic gastrointestinal diseases;
- In the affected areas, sweating processes are disrupted, the skin stops responding to cold and other irritants, muscle-hair and vasomotor reflexes disappear;
- Vitiligo is often accompanied by various types of dermatitis;
- Decreased liver functionality to resist toxins.
As for other subjective symptoms, the patient does not experience them and for the most part suffers only from a cosmetic defect. Therefore, people with this type of skin disease should avoid contact with the sun, as the spots stand out more on tanned skin.
Depending on the localization of the pathological process, it is customary to distinguish a localized clinical form of vitiligo, when pathological foci are located in a certain area of the skin:
- Mucous leukoderma, when the mucous membranes are included in the affected area;
- Segmental leukoderma, when the lesions are located in an area of the skin that is supplied by a single nerve (cranial or spinal);
- Focal leukoderma, when the spots occur singly and are localized in one or two skin areas.
Separately, we can distinguish a generalized form of vitiligo, which manifests itself in the fact that skin changes are quite extensive:
- Acrofacial leukoderma, when the face and limbs are included in the pathological process;
- Vulgar leukoderma, when foci of the disease are located throughout the body;
- Total or universal leukoderma is characterized by the fact that large areas of skin are affected, up to 80%;
- Mixed leukodkermia, when there is a combination of acrofascial and vulgar forms of the disease, or segmental, vulgar and acrofascial forms.
Forecast
Some depigmentation usually remains for life. Occasionally, individual lesions can spontaneously repigment, but after some time they lose pigment again. The prognosis is more favorable when treating newly emerging spots.
See also Skin dyschromia.
Bibliography:
Rakhmanov V. A. Skin pigmentation disorders, Multivolume. Guide to derm.-ven., ed. S. T. Pavlova, vol. 3, p. 368, M., 1964; Tadzhibaev T. T. Vitiligo, Tashkent, 1971; Watzig V. Vitiligo mit entziindlichem Randwall, Derm. Mschr., Bd 160, S. 409, 1974, Bibliogr.
L. N. Mashkilleyson, Yu. K. Skripkin.
Causes of vitiligo
People are not born with vitiligo; this skin pathology begins to form under the influence of a number of external and internal factors. Moreover, it is extremely rare that the disease manifests itself at an early age, namely before 10 years. A connection was established with the onset of vitiligo and periods of increased solar activity in summer and spring.
Among the reasons that provoke the development of the disease are:
- Autoimmune disorders
in the body are factors that provoke the development of the disease. In this case, the functioning of the immune system malfunctions and the antibodies produced to destroy foreign agents begin to attack healthy tissue. Such conclusions about the relationship between vitiligo and autoimmune processes were made based on the fact that people with skin lesions often have concomitant rheumatoid arthritis, thyroid disease, systemic lupus, etc.
- The connection between vitiligo and genetics
has been proven experimentally. Scientist R. Spitz, working at the University of Colorado, has established a family predisposition to the development of this skin pathology. In addition, it has been scientifically proven that if a person has brown eyes, then the risk of developing the disease is higher than that of those with gray and blue eyes.
- Endocrine gland.
The onset of the disease can be triggered by serious disruptions in the functioning of the endocrine gland, as well as fluctuations in hormone levels. This group of causes will be combined into neuroendocrine ones. In addition, disturbances in the functioning of the pancreas, ovaries, pituitary gland and adrenal glands can have an impact.
- Skin trophic disorders
, which are caused by various injuries (burns, including sunburn, scars and microtraumas). Vitiligo begins to form in previously damaged areas, as an inflammatory reaction that has an autoimmune component is triggered in these places. In this case, the cells that produce melanin are destroyed. Moreover, the more often a person exposes the skin to sunlight, the faster the depigmentation process develops. That is, trophic disorders are another reason for the formation of vitiligo.
- Taking certain medications
may trigger the onset of a pathological process.
- Liver diseases that lead to stagnation of bile and changes in the parenchyma of the organ, which has a direct impact on the development of vitiligo.
- Gastrointestinal diseases
, such as dysbiosis, malabsorption syndrome. Violation of the absorption process of enzymes leads to the fact that the skin does not receive the necessary nutrients (zinc, copper, manganese, magnesium) for the normal formation of melanin.
- Exposure to various chemicals
on the skin. These may be low-quality cosmetics, phenol and reagents containing it, formaldehyde, etc.
Doctors rightly believe that vitiligo is the body’s most powerful signal about trouble in general. After all, the disease often starts after viral infections, after intoxication, after physical trauma, especially after head injury.
Thyroid gland as a cause of vitiligo
The fact that disturbances in the functioning of the thyroid gland cause the development of vitiligo is evidenced by figures. Thus, problems with this organ are observed on average in 10.4% of patients with this skin pathology.
Among the diseases associated with thyroid disorders in vitiligo are:
- Goiter 1st and 2nd degree
, without changes in thyroid function, occurs very often, the number of patients reaches 86%. At the same time, an increase in TSH, AT TG and AG TPO hormones is observed, against the background of a decrease.
- 12% of patients with vitiligo have hyperthyroidism.
With this pathological process, there is an increased production of hormones with all the ensuing consequences: weight loss, anxiety, nervousness, increased blood pressure, etc.
- Hypothyroidism
with vitiligo it occurs much less frequently, in only 2% of patients. In this case, symptoms such as low blood pressure, lethargy, fatigue, and passivity are observed.
As can be seen from the above statistics, the connection between vitiligo and thyroid dysfunction is obvious.
Stages of vitiligo
It is customary to distinguish several stages of the disease. Among them are:
- Progressive stage of the disease.
This stage is spoken of when within three months there is a significant increase in the size of the spot, the growth of old depigmented areas begins, or more and more new formations appear. Vitiligo can progress slowly, with new lesions appearing next to the first spot over several months. Slow progression is considered to be the natural progression of the disease. However, there is also fulminant vitiligo. In this case, the patient experiences an increase in the number of spots throughout the body over the course of several weeks.
- Initial stage
, in which a single spot forms on the skin. Depending on the nature of the disease, this stage will subsequently move into a progressive, stable or repigmentation stage.
- Stationary stage
, which is characterized by the fact that the patient has one spot on the skin that is in a stable condition. It does not grow over a long period of time, new formations do not appear.
- Repigmentation stage
. Most often, this stage is observed with the spontaneous formation of a spot caused by therapeutic measures, for example, taking certain medications. Unfortunately, independent and complete repigmentation in this form of skin disease is extremely rare.
Surgical intervention
In 20% of cases, conservative treatment of vitiligo does not give the desired result, then surgery is considered. Surgical treatment consists of transplanting one's own healthy melanocytes onto lesions devoid of pigment. After surgery, new melanocytes are formed in the deep layers of the epidermis. The process of restoring pigmentation takes several months.
Indications for surgical treatment of vitiligo
- The lesions are located on open areas of the body (face, neck, décolleté, arms). They are a significant cosmetic defect and violate the psychological status of the patient.
- Lack of results from local and systemic therapy for 12 months.
- The disease is in remission. Over the course of 1-2 years, new spots do not appear, and existing ones do not grow.
There are several methods of surgical treatment of vitiligo.
- Epidermal transplantation. The affected areas of skin are excised. In their place, an autograft prepared by the PUVA method is placed (a flap of epidermis from a healthy area of the body).
- Minitransplants. Areas of healthy skin less than 1 mm in size are transplanted into depigmented lesions.
- Transplantation of cultured or uncultured melanocytes. Individual cells that produce pigment are implanted into the skin.
Side effects of surgical treatment may include:
- The appearance of scars;
- Uneven pigmentation;
- Rejection of transplanted areas of the epidermis;
Contraindications:
- Tendency to the appearance of scars;
- Intolerance to ultraviolet radiation and laser therapy.
Why is vitiligo dangerous?
It is generally accepted that this disease does not pose a direct threat to human life or health. However, vitiligo itself is most often a consequence of some disorder in the body, which should not be ignored.
Therefore, if a person has vitiligo, you should pay attention to:
- Functioning of the thyroid gland.
- Taking medications, they may not be suitable and require immediate replacement.
- For the presence of other skin diseases, in particular psoriasis, baldness, etc.
- For malfunctions of the immune system and for factors that provoke these disorders. In addition, there is evidence of a connection between vitiligo and diabetes.
- Frequent stress or mental instability.
- Lack of nutrients in the body.
- Vitiligo is often observed with pneumonia and progressive myopia.
Therefore, if, in addition to vitiligo, a person is bothered by any other accompanying symptoms, this must be reported to the doctor. In addition, patients often require psychological help, since such a pronounced cosmetic defect can lead to psychological trauma, depression, the development of an inferiority complex regarding one’s own appearance, etc.
Is vitiligo transmitted?
Is vitiligo inherited?
The question of whether the disease is inherited has been repeatedly studied by various scientists. There is no consensus, but most studies indicate that there is a certain combination of genes that is responsible for the manifestation of vitiligo in members of the same family. Therefore, it is generally accepted that the risk of hereditary transmission varies from 15 to 40%.
But in this case, spots do not necessarily form, but only under the influence of risk factors. Therefore, a child of parents who suffer from vitiligo can live his entire life without experiencing the symptoms of this disease. However, children with a family history are at increased risk.
Scientists have studied certain haplotypes that are most often found in patients with vitiligo. But their frequency of occurrence is constantly changing and depends on the specific population being examined. Therefore, special attention should still be paid to the factors that precede depigmentation.
Is vitiligo transmitted from mother to child?
Naturally, mothers with vitiligo wonder whether there is a risk of transmitting the skin pathology to the child. In this case, it is important not to be confused: the person who is born does not have the disease itself, but a predisposition to its development.
Therefore, if the mother or other family members have vitiligo, the child should be exposed to trigger factors as little as possible. These include psychological and physical injuries, exposure to ultraviolet rays, burns, etc.
If the disease affects a woman during pregnancy, it does not affect its course and does not pose a threat to the fetus. However, during pregnancy, hormonal levels are disrupted, which can lead to the rapid spread of the disease. Signs of vitiligo are extremely rarely observed in newborn children, and even if the disease is inherited, as a rule, it first manifests itself after 9 years. Therefore, if an infant has white spots on the skin, it would be more advisable to suspect psoriasis, pityriasis alba or pityriasis versicolor, as well as allergies. But unlike vitiligo, these formations will peel off.
Is vitiligo transmitted from person to person?
Since the disease is quite common and in your immediate environment you can often meet a person suffering from vitiligo, the question of transmission of the disease by airborne droplets or other means is quite natural.
The answer to this question is clearly negative. This disease is not infectious and a person suffering from it does not pose a danger to others in terms of infection. Therefore, you can fearlessly communicate with people who have spots of the same origin on their skin.
Is there a danger
Manifestations of vitiligo are only painless white spots on the skin of the body; rarely, a change in the color of the iris of the eyes or a decrease in visual acuity is possible. Other consequences of this disease are not known to medicine, but most likely they do not exist, because vitiligo is just an indicator of some processes within the body, and not the cause of the disease.
The danger for the development of vitiligo can be hidden in different everyday situations. For example, to start skin discoloration, it is often enough for a person to come into contact with chemicals, for example, phenols contained in hair dye, household chemicals and other similar products.
Methods of treating the disease can also be dangerous on an individual basis. For example, during pregnancy, women with vitiligo should not use ultraviolet irradiation to awaken melanin in the skin.
Also, if vitiligo is diagnosed, stress at work should be avoided. As a preventive measure, you should not choose work that involves rubbing some areas of the skin on an ongoing basis, as this may provoke disease in the future.
It is important to find out exactly how a skin disease reacts to ultraviolet radiation. In some cases of vitiligo, a person cannot leave the house without sunscreen cosmetics even in winter; in others, one can even be specifically exposed to radiation without using protection. However, this issue must be clarified before the skin is completely damaged. As for the risk of developing skin cancer with vitiligo, most experts are inclined to believe that there is none.
How and with what to treat vitiligo?
If one or more white spots appear on the skin, then you need to go to an appointment with a dermatologist. He will examine the skin using a specialized lamp and determine the nature of depigmentation. If necessary, material will be collected to clarify the diagnosis. These procedures are important because it is necessary to be able to distinguish vitiligo from other skin diseases.
As for therapy, despite the medical cases of complete and spontaneous healing from vitiligo, there is a high risk that the disease will progress without appropriate treatment. Due to the fact that pathology is often accompanied by concomitant diseases, it is important to correctly use drugs from various groups.
Treatment with glucocorticoids (drugs aimed at suppressing autoimmune processes and allergic reactions) is indicated for:
- Localized form of the disease
. In this case, it is advisable to use ointments. To begin with, drugs with average activity are prescribed. Among them are hydrocortisone butyrate, Esperson, Alcomethasone, Fluorocort, Triacort and others. The course must last at least 3 months. If no effect is observed, then ointments with higher activity are indicated. Among them are Elokom, Cutivate, Sinalar, Dermovate, Beloderm and others. These products cannot be used without interruption for more than 8 weeks. The course will need to be repeated after 1 to 4 months.
- Generalized
form of the disease.
However, in this case, the use of drugs in tablet form is indicated. Since when taking glucocorticoids orally there is a high risk of developing diabetes mellitus and Cushing's syndrome, it is necessary to use pulse therapy in parallel, and take the drugs themselves intermittently. Among this group of drugs used to treat the generalized form of vitiligo, Triamcinolone, Dexamethasone, Prednisolone, Methylprednisolone can be distinguished.
Since ultraviolet lamps are often used to treat vitiligo, doctors prescribe photosensitizing drugs to patients. They increase the sensitivity of melanocytes to ultraviolet radiation.
Among plant furocoumarins we can distinguish:
- Containing bergapten and xanthoxin Beroxan;
- Containing one xanthoxin Puvalene, Oksoralen, Lamadin, Methoxalen;
- Containing imperatonin and xanthoxin Meladinin;
- Containing xanthoxin, bergapten and isopimpinellin Ammifurin;
- Psoberan isolated from figs;
- Psoralen, isolated from psoralea.
In addition, there are such products as Elidel and Protopic. They are most often prescribed for the treatment of psoriasis and various dermatitis. But in some cases they are effective in the fight against vitiligo. They are used externally and have an anti-inflammatory effect, suppressing T-lymphocytes and inhibiting the body's immune response. Their action is in some way similar to the effect that can be achieved using glucocorticoids.
Elidel and Protopic can be used in both adults and children. However, the concentration of the active substance in ointments will vary (for children - 0.03%, for adults 0.1%). Treatment should be a course and, depending on the stage and form of the disease, can last from three to six months. The advantage of these agents is that they are not absorbed into the blood, having a local effect.
Systemic therapy is aimed at eliminating hormonal imbalances, lifting patients out of depression, and eliminating mental and other diseases of the nervous system, which are often triggers in the development of vitiligo. It is important that the patient replenishes the deficiency of microelements and vitamins. Therefore, he is indicated for the use of complexes containing ascorbic acid and copper. Your doctor may also prescribe antioxidants and immunomodulators.
Medicine does not stand still and methods for treating vitiligo are constantly being improved. New ways to combat the disease include:
- Treatment using laser or laser therapy.
In this case, the affected areas of the skin are exposed to radiation having a certain wavelength. This method is similar to phototherapy. The greatest effect can be achieved in the treatment of local forms of the disease (for patients with segmental, focal and vulgar forms), when the patient has suffered from vitiligo for no more than five years. There is no need to spend a long time under the laser; the initial procedures only take a few seconds.
- Skin whitening helps make spots less noticeable.
At the same time, its tone is evened out. For this purpose, various injections are used, the most popular are Eloquin, Monobenzone and Hydroquinone. But before deciding on such procedures, it is worth learning more about the presence of contraindications, since each of these drugs is very aggressive and has certain side effects. In addition, the drugs are expensive and will need to be administered regularly.
- Surgical intervention (melanocytic transplantation).
If vitiligo does not affect large areas of the skin, then you can resort to surgery and autologous transplantation. But this method is fraught with complications in the form of rejection and suppuration of the transplanted area. In addition, no doctor can guarantee a stable and long-lasting effect.
- Transfer of own pigment cells
(melanocytes) of a person from undamaged areas of the skin to the problem area.
- Using Melagenin Plus
– an alcoholic extract isolated from human placenta. The drug is most effective if the patient suffers from a localized form of the disease.
Sceness drug .
In the future, a drug developed in Austria called Sceness may be used to treat vitiligo. It is currently used for the treatment of erythropoietic protoporphyria.
In addition, scientists are not abandoning attempts to develop a vaccine that can eliminate the autoimmune reaction that leads to the development of the disease.
In addition, increasing evidence indicates that combination treatment, when surgical treatment is complemented by several non-surgical methods, is most effective.
Also, in rare cases, the doctor is able to detect a connection between vitiligo and an external or internal factor. By eliminating them, you can stop the pathological process. In particular, by ridding the patient of helminthic infestation or stopping contact with a certain chemical.
As for recommendations regarding the patient’s diet, he needs to include foods fortified with copper in his diet. Among these: seafood, apples, tomatoes, cabbage. In addition, it is worth including rice, oats and corn in your diet, as they contain zinc.
There are no specific preventive measures to prevent the development of the disease. However, persons with a complicated medical history are recommended to stay in the sun as little as possible and promptly treat diseases that provoke this skin pathology.
[Video] Dr. Berg - 3 natural remedies for vitiligo:
Ultraviolet lamp for the treatment of vitiligo (UVB therapy)
At this point in time, ultraviolet lamps are increasingly used in the treatment of vitiligo. This method is very effective and is based on exposing the affected areas of the skin to ultraviolet radiation. It is a mistake to use the term PUVA to refer to all types of ultraviolet exposure, because they have some differences.
Thus, when irradiating the skin with type A waves using medicines of both plant and synthetic origin (psoralens), there are a number of serious contraindications and complications. These include the risk of developing cataracts and skin carcinoma. In addition, this procedure cannot be performed by pregnant women, elderly people over 60 years of age, children, patients with cancer and pathologies of the kidneys, liver, heart and blood vessels. Side effects that often occur during the procedure are erythema, nausea and a burning sensation.
Therefore, recently, more and more often, patients with vitiligo are prescribed ultraviolet irradiation, which has a narrower spectrum of action, when the wavelength is 310 nm. In this case, the patient experiences fewer side effects, and the risk of developing malignant skin tumors is reduced.
Narrow-wave therapy does not necessarily require the use of photosensitizers, and its effectiveness is higher than irradiation with type A waves. There are much fewer contraindications to such a procedure, these are: cataracts and the absence of a lens, the presence of melanoma, autoimmune diseases.
The risk of side effects when using narrow-wave therapy is significantly reduced. As a rule, the patient complains of mild itching and dry skin. Burns can only occur if the dosage has been exceeded.
As for the procedure, the exposure time of the lamp to areas with thin skin (in particular, the facial area) should not be more than 2 minutes. Feet, hands and elbows can be irradiated for 5 minutes. You should not expect an instant effect; after the first procedure you will not be able to get rid of vitiligo. Sessions are most often held three times a week. In this case, the doctor can recommend up to 200 procedures, which a patient with vitiligo must be prepared for. To achieve the effect, a course of action will be required. If the skin turns red after irradiation, then it is necessary to apply any cream used for burns. During irradiation, it is important to use special glasses that will protect the lens and retina of the eye.
What vitamins should I take for vitiligo?
Conducted scientific studies prove that taking certain vitamins (for example, E, C, alpha-lipoic acid) affects the course of the disease and can enhance the therapeutic effect. Therefore, doctors often prescribe certain medications to patients with this skin disease. Among the most popular are thiamine, ascorbic acid, pantothenic acid and riboflavin.
The role of folic acid
In Sweden, studies were conducted on the effect of folic acid and vitamin B12 on vitiligo. The study involved 100 patients with vitiligo, all of whom took 5 mg of folic acid twice a day and 1 mg of vitamin B12 once a day. A prerequisite was daily exposure of the skin to ultraviolet rays. Exactly 3 months later the results were summed up. More than half of all participants achieved positive results, and several patients were completely cured by 100%.
On this topic:
10 most effective folk remedies in the treatment of vitiligo
Prevention
Since the cause of vitiligo has not been established, the prevention of this disease is not sufficiently justified. However, it has been noted that regular stays at seaside resorts have a beneficial effect on patients with vitiligo, therefore, if there are cases of vitiligo in the family, you should organize an annual (and if possible, more often) family vacation to the sea. To consolidate the preventive effect, you can take sunbathing for 10 minutes a day throughout the warm period of the year.
You should avoid overloading the body with substances from impaired metabolism: treat chronic diseases of the digestive system, eat a balanced diet.
Some drugs used for vitiligo
Melagenin
Melangenin is used as a topical treatment for vitiligo. It is able to restore skin pigmentation by enhancing its ability to absorb ultraviolet rays.
Currently, the drug Melagenin Plus is actively used, which acts in the same way as melagenin, but its effect is enhanced by the calcium chloride and alcohol extract of human placenta included in the composition. This allows cells to multiply more actively and synthesize melanin with higher bioavailability.
The product is used even in the most severe cases of vitiligo. At the same time, reviews indicate that the depigmentation process does not return, and normal skin is not damaged.
The drug should not be used while pregnant or breastfeeding. It can be used independently, without additional exposure to an infrared lamp.
Ammifurin
The drug Ammifurin is a photosensitizing drug that is prescribed to patients with vitiligo when exposed to ultraviolet rays. Available in the form of tablets and solution for external use, it stimulates the production of melanin.
If used in the form of a solution, the product should be applied before the start of irradiation, one hour before the procedure. If oral use is indicated, then you should take the tablets after meals and drink milk, but 2 hours before ultraviolet irradiation.
The drug is prohibited for use during pregnancy and breastfeeding, in the presence of hypersensitivity to the active substance, stomach ulcers, pancreatitis, cirrhosis, hepatitis, diabetes, cachexia, nephritis, tuberculosis, cataracts, nevi, tumors, high blood pressure and thyrotoxicosis.
It is important to use glasses with dark lenses to protect your eyes while taking the drug in sunny hours. As for effectiveness, the best results in the treatment of vitiligo were recorded in young people, with a short duration of the disease, as well as in brunettes and patients prone to tanning.
The product should not be used independently, without strict medical supervision.
Vitasan
Vitasan is available in the form of a cream and consists exclusively of natural ingredients. It is able to have a complex effect: regulates immune processes, has a sensitizing effect, and stimulates the production of melanocytes.
The product contains the following components:
- St. John's wort extract, which enhances the sensitization effect and increases the sensitivity of the skin to ultraviolet radiation;
- Walnut extract, which saturates the skin with vitamins and microelements necessary for vitiligo - copper, zinc, ascorbic acid, etc.;
- Sequence extract, which enhances the reaction of formation of the pigment necessary for vitiligo;
- Calendula extract containing vitamins PP, C and B;
- Fir oil, which is capable of dilating blood vessels, stimulating blood supply, cell division and growth, and the development of local immunity;
- Cedar nut oil, which contains vitamin E.
For those suffering from vitiligo, it is necessary to apply the product twice, rubbing in thoroughly. To achieve maximum effect, you should use the cream in advance, before the onset of periods of maximum solar activity, that is, in winter.
Among the contraindications, one can highlight only individual intolerance to the components that make up the cream. If side effects occur in the form of itching, redness and burning, you should wash off the product and consult a doctor.
It is important to use the cream not as a single treatment, but as part of complex therapy.
Last news
Scientists have created a genetically modified protein that treats vitiligo in mice. Previous studies have shown that HSP70i, a stress-inducible heat shock protein (its synthesis is activated when the temperature rises), plays a key role in the disease vitiligo.
- HSP70i consists of 641 amino acids. Researchers at Loyola University New Orleans replaced one of these amino acids, creating a genetically modified version of HSP70i. The new modified protein displaces its normal predecessor and stops the development of the autoimmune reaction.
- Scientists injected the modified HSP70i into experimental mice suffering from vitiligo and having a salt-and-pepper coloration. After some time, the mice's fur returned to its normal black color. Similar effects were obtained in experiments on human skin cell cultures.
Experimenters hope that human studies will confirm the effectiveness of the new method and finally make it possible to find a cure for vitiligo. True, the experiments were carried out back in 2013, and nothing more was heard about them. Perhaps the experiments stopped due to the unsafety of genetically modified developments.
How to cover up vitiligo spots?
The desire to hide white spots on the face and body is a completely natural desire of people suffering from vitiligo. Therefore, while treatment is being carried out, you can use the following methods:
- Use of cosmetics
. This is the most affordable and easiest way to make stains less noticeable. At the same time, you need to apply foundation and other mattifying products correctly. First, the skin must be evened out to its natural color, and only then begin to mattify. In addition, you can use permanent tattooing, which will be more durable and will not be erased upon contact with clothing or water.
- Using self-tanning
. If you perform this procedure in a salon, the color will be more even and will last longer. In addition, it can be problematic to choose a shade and apply it to the body on your own. Unlike cosmetics, self-tanning is convenient to use on your arms and legs, as it does not stain your clothes.
- Using green walnut peel.
To do this, you need to grind it using a blender and leave for 2 hours. After this, the mixture should turn brown. The juice from the peel should be squeezed out and applied to the stains using a cotton pad, which will help color them. One of the advantages of this product is that it does not leave marks on clothes.
- A method such as dermabrasion can help disguise vitiligo.
. In this case, the skin is treated layer by layer, and the depth of penetration depends on the form of the disease, the age of the spots, etc.
However, when using these products, it is important not to forget about the rules of caring for affected skin. You should not injure it again or expose it to allergens. It is important not to wear clothes and shoes that are too tight, and not to allow stains to rub; if there is a need to use a razor, then you should be as careful as possible. Jewelry should not leave visible marks on the neck or fingers. It is necessary to limit time spent both in the sun and in the cold. After all, tanning most often provokes the formation of new spots.
Vitiligo is not a death sentence, and treatment is successful in most cases. It is important not to despair if one of the methods turns out to be ineffective; it is possible that another method will help in the fight against the disease. Even when it is not possible to get rid of vitiligo completely, it is quite possible to make the spots less noticeable using modern methods of therapy.
Author of the article:
Kuzmina Vera Valerievna |
Endocrinologist, nutritionist Education: Diploma of the Russian State Medical University named after. N.I. Pirogov, specialty “General Medicine” (2004). Residency at the Moscow State Medical and Dental University, diploma in Endocrinology (2006). Our authors