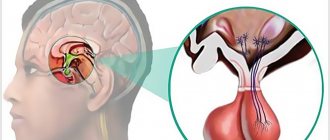
What is an ovarian dermoid cyst, how is it different from others, and how to get rid of it? A dermoid cyst is a non-malignant formation that develops in utero and is formed from fragments of embryonic tissues of the embryo.
The structure looks like a mobile capsule with a dense whitish shell, connected to the ovary by a long stalk. The capsule is filled with thick jelly-like contents with elements of various body tissues: fat, bones, nerve fibers, hair, teeth and cartilage, glandular organs formed during the development of the embryo.
Other medical terms (names) used to refer to this type of neoplasm are mature teratoma, dermoid or teratodermoid ovarian cyst.
It should be noted that a dermoid cyst is often considered a germinal tumor because, unlike cystic structures that are formed due to the accumulation of fluids, it is formed as a result of mitosis (cell division).
Structure Features:
- The size of the dermoid reaches 120 – 150 mm.
- The development of a mature teratoma is quite slow, so the pathology may not manifest itself for years.
- Among diagnosed cystic ovarian structures, this pathology accounts for 15–20%.
- Diagnosed at any age, starting from newborns. It is most often found in growing girls at the stage of puberty, in women of childbearing age and those in menopause.
- Malignancy (cancerous degeneration) of cells is possible (1 – 3%).
Symptoms of a dermoid cyst
The symptoms of a dermoid cyst, regardless of its location, are characterized by an implicit nature and practically do not manifest themselves, since they develop slowly. Clinical manifestations occur when the size of the tumor exceeds 5-10 cm and begins to put pressure on nearby organs, the growth becomes inflamed, and suppuration occurs. In some cases, symptoms visually manifest as a cosmetic defect (hair cyst on the eye, neoplasm on the head). In most cases, the growth is discovered accidentally or during an exacerbation.
Manifestations depend on the location of the formation:
- Symptoms of a large ovarian dermoid cyst put pressure on neighboring organs, which causes constant aching pain in the lower abdomen, tension in the peritoneum, and enlargement of the abdomen. There is a disturbance in the functioning of the intestines (constipation, diarrhea), a disorder of urinary processes (frequent urge, pain in the lower abdomen during urination). A complicated neoplasm with suppuration provokes severe pain in the woman’s ovarian area and an increase in temperature. The danger of ovarian dermoid formations lies in the possibility of their malignancy, therefore these formations require mandatory surgical intervention;
- Large growths in the pararectal area compress the rectum, resulting in pain and difficulty during bowel movements. Due to pressure on the lumen of the rectum, the feces become flat and take on a ribbon-like shape;
- Large dermoids in the middle sections of the chest cavity (mediastinum) begin to put pressure on the trachea, lungs, and pericardium. The result is difficulty breathing, regularly occurring tachycardia, cough, and bluish skin.
Localization
A dermoid cyst often appears on one of the ovaries - and more often a benign sac is diagnosed on the right one, since the left one has a several times lower blood supply, and the fertilization productivity of the right one is much higher.
The formation of the gland plays a role - the right side appears much earlier, including in children. Left-sided dermoid cysts are diagnosed in rare cases; the frequency of bilateral cysts is 5-6 percent of the total number of cases.
Germinal ovarian cyst
A similar tumor can appear on other vital organs - often a teratoma appears on the head, forming from skin cells.
Causes of dermoid cysts
The neoplasm owes its formation to disturbances that occur during embryonic development. The main causes of dermoid cysts include:
- Hormonal factor. The development of a neoplasm can be triggered by hormonal changes during puberty and menopause;
- Consequences of trauma or contusion of the peritoneum.
Ovarian dermoid cyst - teratoma is a dense hollow formation, the contents of which consist of keratinized elements, particles of hair, bones, sebaceous and fatty inclusions. The main cause of the tumor is embryonic anomalies. The development of formation to visible sizes occurs at stages of age-related hormonal changes: menopause, puberty.
In most cases, a dermoid cyst of the right ovary is formed. This occurs due to the more active functioning of the right organ. Hormonal imbalances affect the right-sided ovary more strongly. A dermoid cyst of the left ovary is rare, and the teratoma formed on the organ does not reach large sizes. Usually the largest volume of the tumor is 6 cm.
Ovarian teratomas must be removed, since one of the consequences of this type of tumor is infertility.
A dermoid cyst on the eyebrow is a congenital pathology. This neoplasm is manifested by external deformation of facial tissues and is detected at an early age. The development of education is asymptomatic, but manifests itself visually. The structure of the growth is dense with clear boundaries, painless and mobile. Pain syndrome occurs with the development of inflammation. When the tumor suppurates, the surrounding skin becomes painful, the temperature rises, and attacks of headache, nausea and weakness may occur.
The formation must be removed surgically, since a hollow node can deform bone tissue and have a negative effect on the nasopharynx and brain.
A dermoid cyst of the eye is a benign cavity formation, in most cases of a congenital nature. The growth is localized in the area of the upper eyelid, in the cornea, on the apple, and sclera. The development of the formation is asymptomatic, but its increasing volumes can affect the reduction in the size of the eye and provoke disturbances in visual perception that cannot be corrected with lenses or glasses.
The formation is a dense capsule filled with contents from particles of the epidermis and hair follicles. Hair is often visible on the surface of the growth, which is why this formation is called a “hairy cyst.”
A dermoid cyst on the head is a hollow growth containing elements of hair, dermis, and keratinized particles. Not characterized by clear localization. It can form on the lips, eyelids, eyeballs, back of the head and any area of the scalp, bridge of the nose, ears, nasolabial folds, oral cavity, nasopharynx. At the initial stage of development, it is asymptomatic, and its development is clearly visualized.
Treatment is possible exclusively through surgery. Removal of a tumor is not performed in children under 5 years of age, since general anesthesia is used during the operation. The exception is cases when the neoplasm threatens the health and life of the child.
Preoperative preparation
An important stage of surgical intervention is preoperative preparation. In most cases, the cyst removal procedure is planned, so there is enough time for preparation. It includes:
- A complete examination, which consists of a blood and urine test, a biochemical study, determination of sugar levels, blood group and Rh factor, coagulation patterns, testing for dangerous infections (syphilis, hepatitis, HIV). In addition, the woman takes a vaginal smear.
- Consultation with a therapist, gastroenterologist and dentist. Doctors may order additional examinations if necessary.
- Ultrasonography. It is necessary to carry out before surgery to identify the exact size of the tumor and its location.
- Conversation with the patient. It is the doctor’s responsibility to talk about the purposes of the upcoming operation, how it will take place and how it may be dangerous. The woman should be fully informed about possible complications and the scope of manipulation. After all the details are clarified, the patient signs a written agreement.
- Preparing the body. Anticoagulant drugs are discontinued a few days before surgery, and laxatives are prescribed the day before. An enema is given immediately before the operation. Eating is allowed later than 12 hours before surgery. These should be low-fat, easily digestible dishes. Surgery should be scheduled during the first phase of the menstrual cycle to reduce the likelihood of bleeding.
- Prevention of thrombosis. The formation of blood clots is one of the most common complications of surgical procedures. If a woman takes oral contraceptives, they are canceled a month before the planned operation. During the procedure itself, the lower limbs are bandaged with elastic bandages or placed in special compression garments.
Dermoid cyst on ultrasound
This type of examination allows you to accurately assess the condition of the affected organ and provides accurate information about the formation of the tumor. Ultrasound examination allows you to identify the localization of the dermoid, determine the volume, contents of the capsule, and the effect of the neoplasm on neighboring organs. The dermoid cyst of the brow ridge, as well as dermoids localized in other areas, are determined in real time (3D, 4D projections). Ultrasound is a necessary research method for differentiating perineal dermoid cyst and mesenchymoma.
Dermoid in a child
In a child, this formation is almost always detected:
- in the sacrococcygeal area;
- on the face;
- or on the neck.
On the face, as a rule, the child’s eyes and brow ridges are affected.
In the neck area of a child, the area of the submandibular lymph nodes is usually affected.
In an infant or a newborn in general, teratoma requires special attention. In infancy, the risk of complications is always higher. This may be why children are almost always prescribed surgical treatment when this pathology is detected.
If for an adult local anesthesia is often enough, then in the case of a child general anesthesia is used for obvious reasons.
MRI
Differential diagnosis makes magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) necessary. This type of examination is based on the impact of high frequency magnetic radiation on the area of interest. The objective of the study is to obtain images of the tumor in different planes. The method is one of the most accurate and visualizes soft tissues and organs in detail. MRI allows you to determine the nature of the capsular contents, the location of the formation, and the degree of impact on neighboring organs. It is the most important method of differential diagnosis (differentiating a dermoid cyst of the upper eyelid from a cerebral hernia, mucoceles). Magnetic resonance imaging (unlike CT) does not use x-rays, so this diagnostic method can be prescribed for studying teratomas in children and identifying dermoid cysts during pregnancy.
Doctor's advice
As already mentioned, such neoplasms do not resolve. But an actively dividing structure can develop into a malignant formation.
Therefore, when making a diagnosis according to ICD 10 D10-D36, it is necessary to monitor:
- do ultrasound regularly;
- if necessary, donate blood for tumor markers.
Such a rare pathology as dermoid sinus, given that it is observed mainly in children, is best eliminated immediately. To avoid the risk of serious infection.
Treatment of dermoid cyst
The only way to treat dermoids is surgery. As a rule, operations are carried out upon reaching 5-7 years of age and beyond. Surgical treatment of a dermoid cyst, depending on its location, can be performed under local or general anesthesia. In most cases, excision of the formation takes place without affecting healthy tissue areas; complete elimination of the growth along with nearby tissues occurs to prevent complications.
If the size of the formation is small, the operation lasts no more than 30 minutes. Purulent neoplasms require complex manipulations consisting of several stages (surgical treatment of a dermoid cyst in the ovaries with extensive organ damage, cerebral dermoids).
During surgery, the cystic capsule is opened, its contents are extracted, and the cavity is drained in cases of suppuration. Complete excision is performed to prevent recurrence and complications.
Modern surgical methods have a low degree of trauma to nearby healthy tissues and a short recovery period. The most common methods of surgical intervention include laparoscopy, laser exposure, and endoscopy. Removal of dermoids is one of the safest operations with a favorable outcome.
Diagnostics
Which doctor should I contact?
The appearance of relevant complaints forces you to contact a therapist or pediatrician, who will refer you to specialized specialists: a surgeon, a pediatric surgeon, an oral and maxillofacial surgeon, an ophthalmologist, a gynecologist, an oncologist, and a neurologist.
The specialist who will deal with the case will determine the scope of intervention and necessary diagnostic studies.
Ultrasound
An informative method used in gynecological, surgical, oncological, and therapeutic practice allows one to detect a formation, assess its size, the presence of fluid in it, and the nature of the capsule. Under ultrasound navigation, specialists can puncture the formation and collect fluid and cellular material from it.
CT, MRI
A modern, but not available in all clinics, method that allows you to confirm and clarify the localization of the formation, its connection with certain organs and structures. The character can be assumed: benign or malignant, but histological verification is required.
Analysis for tumor markers
They will allow you to suspect a malignant process. Dermoid cysts in some cases can develop into cancer.
For ovarian cysts, an analysis is performed for:
- CA 125 and HE 4 (most significant);
- CA 19-9, REA, M-CSF (of secondary importance).
Tumor markers are still not specific proteins, so the detection of their elevated levels in the blood does not provide grounds for making a diagnosis. A comprehensive examination with a biopsy of the material (cyst contents or cellular elements of the neoplasm) is necessary.
Histological examination
“Gold standard” in the differential diagnosis of malignant and benign tumors. When examining the structure of cysts and their contents, derivatives of the ectoderm are found - hair, sebaceous and sweat glands.
The shell is made of fibrous connective tissue, including sebaceous glands and hair follicles. The inside is lined with stratified squamous epithelium.
Dermoid cyst removal
One of the most common ways to remove a dermoid cyst, as well as other neoplasms, is laparoscopy. The method of surgical intervention has become widespread and popular due to its low morbidity, effectiveness, and short recovery period. Laparoscopic surgery is effective in eliminating teratomas of any size, even up to 15 cm.
When performing this type of surgical intervention, access to the dermoid is carried out through minimally sized incisions (5-7mm). The edges of the incisions practically do not bleed, due to the use of laser, ultrasound, and electrical instruments. This technology provides effective and quick access to the damaged organ while simultaneously sealing the vessels along the edges of the incision. Postoperative sutures are almost invisible and completely disappear within 3 months.
The most effective method is laparoscopic removal of a dermoid cyst in the ovary. This operation allows, in most cases, to preserve a woman’s reproductive function. Six months after the procedure, the patient is able to conceive.
Laparoscopy is not used for tumors in the brain area.
Features of surgery
The tumor can be eliminated exclusively by surgery; the choice of type of operation depends on many factors: age, location, size of the tumor, the presence of chronic diseases, and the patient’s state of health.
In most cases, surgical intervention is performed upon reaching 5 years of age (not earlier), since from this age the child’s body can tolerate not only local, but also general anesthesia.
When the dermoid is complicated by suppuration, its elimination is carried out after drug therapy, the task of which is to relieve inflammation and pain. Surgical intervention is possible at the stage of stable remission.
For uncomplicated, slowly developing tumors, removal is carried out as planned. The operation is performed using a standard surgical method or laparoscopy is used.
During the operation, the neoplasm is carefully opened, the contents of the capsule and the walls of the cavity are removed. It is important to destroy all fragments of the dermoid to avoid relapses. The surgical operation is carried out within the formation, nearby healthy tissue is not affected. The duration of the operation depends on the location and degree of damage to the cyst and can last from 15 minutes to several hours.
Removal of small dermoids localized in the coccyx or head area does not require general anesthesia. General anesthesia is used in cases where the operation is scheduled for a small child (from 5 years old), since it is difficult for children to comply with the conditions of the operation.
Elimination of the dermoid is the only method of successful treatment of this type of cyst. Surgical intervention is mandatory for the development of a neoplasm, since there is a possibility of inflammation and suppuration of the cyst, disruption of the functioning of organs due to the growth of the formation, and a small but existing possibility of malignancy.
During pregnancy
Dermoid pathology in an expectant mother does not pose a danger to the fetus, but fluctuations in hormones often provoke the progression of the anomaly.
Dermoid pathology in an expectant mother does not pose a danger to the fetus.
Moreover, the pressure of the enlarged uterus on the peritoneal organs leads to torsion of the pedicle and death of the ovarian tissue. Then this anomaly should be operated on immediately.
If a complicated process is not diagnosed, the cyst is excised after 4-6 months (natural birth) or during a cesarean section for other indications.
Prognosis and prevention
Dermoid cysts are congenital in nature; their root cause is abnormal development of the fetus during the embryonic period. Therefore, during pregnancy you should adhere to the rules of a healthy lifestyle necessary for the normal development of the baby. Proper nutrition and taking prescribed vitamin and mineral complexes, adequate physical activity, stabilization of the psycho-emotional background - all this minimizes the possibility of any disturbances in the development of the fetus.
With an existing cyst of small size, strengthening the immune system and general health of the body will help prevent its development, according to rules similar to those for expectant mothers: healthy eating, feasible physical activity, stable emotional state, taking vitamin complexes if necessary.
It is necessary to undergo routine medical examinations. This attitude towards your health will allow you to identify and begin timely treatment of any disease. Detection of a dermoid at an early stage and its excision will not in any way affect the patient’s quality of life, but can prevent possible complications.
Low propensity to malignancy, slow growth, high-quality removal of dermoid formation using modern surgical methods makes the prognosis very favorable.
Complications
A dermoid type cyst grows quite slowly. Consequences in the absence of therapy occur a long time after the onset of the development of the pathological process.
The most serious complication is the degeneration of the tumor into cancer. But the process of cell mutation is observed only in 3% of cases.
Also among the consequences there is a disruption in the performance of the affected organs, which can result in heart failure and diseases of the pelvic organs.
That is why, when a dermoid cyst is diagnosed, you should undergo a timely course of therapy.