Tick-borne encephalitis is a very severe acute viral disease of the nervous system. The brain and central nervous system, peripheral nervous system, and spinal cord are affected. Protection against the disease can only be vaccination. A vaccinated person can also get sick with viral tick-borne encephalitis, but in a mild form and with full recovery of the body.
Due to serious damage to the nervous system, the consequences of the disease can be extremely severe - death, partial or complete paralysis, the development of mental illnesses caused by organic damage to the brain. Age and level of development in this case have no role. Both a child and a mathematics professor can get sick.
When the peripheral nervous system and spinal part of the brain are damaged, muscle atrophy, inability to use limbs, tissue drying, and decreased sensitivity of the skin are observed.
The likelihood of getting sick after a tick bite in the European part of Russia is not too high, this is due to the spread of mandatory medical vaccinations.
Carriers of tick-borne encephalitis
The main carrier of the virus is the European taiga and forest tick, which is a hereditary carrier of the virus. That is, from an infected female the virus is transmitted to the offspring and subsequent generations of the tick. The blood of a person or animal is necessary for ticks to reproduce, which peaks in the spring and summer. This is the time when the risk of a tick bite is greatest. In addition to encephalitis, ticks carry Lyme disease, which is also a rather unpleasant disease with a slow development cycle.
It is not only the tick itself or the infected animal that is dangerous. Feces and other waste products are also dangerous. The fluid inside an encephalitis tick is a potential source of infection. When scratching the skin and getting into the bloodstream, indirect infection is quite possible.
Goats can also carry the virus. In this case, infection occurs through unprocessed goat milk consumed as food. The virus dies when boiled, does not tolerate sunlight, you can drink any boiled milk without fear.
Parasite bite
The parasite's bite is imperceptible to humans, so the victim usually notices the tick after it has firmly attached itself to the skin. The insect looks like a small mole or dot, slightly protruding above the surface of the skin; favorite places for bites are under the armpits, in the groin and on the neck (where the skin is especially thin and delicate).
With an individual reaction to tick saliva, a mild allergic reaction of a local nature is possible - slight redness, inflammation and itching. If the tick falls off on its own, it is almost impossible to determine the fact of the bite, since no traces remain on the person’s skin.
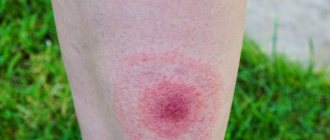
Photo
The photo below shows what the area looks like after a tick bite, with characteristic signs on the human body.
IMPORTANT! According to statistics, 6 ticks out of a hundred are carriers of the virus, and the probability of infection ranges from 2 to 6%. These are small numbers, but we should not forget that parasites carry not only encephalitis, but also borreliosis, Lyme disease and other dangerous diseases.
How long is the incubation period?
The incubation period of the disease ranges from several hours in case of immediate development of the disease, to 14-30 days if the body is ready to resist or was vaccinated against encephalitis in childhood, and at least a small amount of antibodies remains in the blood.
During the incubation period, no painful manifestations are observed. If anti-encephalitis serum is administered during the incubation period, the temperature will rise sharply, and even delirious states are possible. However, the development of the disease can be prevented.
Immediate medical intervention and administration of immunoglobulin before the onset of the disease can reduce the risk of the disease. Immunoglobulin mimics a vaccine to some extent and contains the corresponding antibodies. The severity of the disease depends on how well it can be absorbed by the body. The effectiveness of immunoglobulin depends on the individual characteristics of the body. The medicine is a preparation made from a donor's blood - serum or plasma with already existing antibodies against tick-borne encephalitis.
The body's reaction to the introduction of serum can be painful, so treatment is carried out exclusively in hospitals. A normal reaction to the administration of serum is fever, pain, aching joints, and weakness. In rare cases, clouding and confusion may occur. Strengthening and antiviral drugs are also introduced. The serum is also used for emergency vaccination in case of epidemics.
well-fed tick
During the incubation stage there are no manifestations of diseases. For this reason, many do not seek medical help exactly when it is needed and can really help.
Vaccination schedule
Vaccination against tick-borne encephalitis is an effective measure to prevent this disease.
Vaccine administration method:
- Passive immunization - carried out when a tick bites by administering immunoglobulin to those who have not been vaccinated previously;
- Active immunization - vaccination 1 month before the tick activity season for residents of encephalitis-endemic areas.
Vaccinations can only be done after a therapeutic examination. There is a traditional and emergency vaccination schedule.
Vaccination schedule:
- The first vaccination is carried out at the time prescribed by the doctor.
- The second – 1-3 months after the first.
- The third – after 9-12 months.
If the third vaccination is not given, you can expect protection for one year after vaccination. The completed course guarantees a stable immune response for 3 years.
Emergency vaccination option:
- First vaccination at the invitation of a medical institution.
- The second – 2 weeks after the first.
- The third - after 9-12 months.
An emergency vaccination option is used in the event of an unexpected trip or business trip to endemic areas.
Contraindications to vaccination against encephalitis:
- Allergy to the vaccine and chicken egg white;
- Use of medications;
- Cardiovascular failure;
- Rheumatism;
- Tuberculosis;
- Diabetes;
- History of stroke and heart attack;
- Acute form of somatic and viral diseases;
- Pregnancy and lactation - with caution, only at high risk.
In Russia, they use a culture-purified vaccine against encephalitis, as well as Encevir, Encepur for children and adults, and FSME-immune.
Symptoms of the disease
The first symptoms of the disease are usually chills, fever, and increased temperature. In some cases, this is accompanied by aches in the bones and muscles, and an increase in temperature.
A symptom may be pain in the head; characteristic signs of meningitis are the inability to bend the head. Pain in the lumbar region, in the back. In some cases, epilepsy, convulsions, and strabismus are possible. Few people associate a sudden illness with a walk in the woods or in the park a couple of weeks ago.
A little later, the main symptoms develop - numbness of the skin, extreme weakness, high fever, convulsions, nausea. Sweating and rapid heartbeat are often noted.
After the development of the main stage of the disease, immunoglobulin and antiviral drugs are useless.
Depending on the location of the lesion, the course of the disease may differ. There are 5 main courses of the disease:
- A febrile form in which damage to the nervous system is minor, the prognosis for recovery and full recovery is positive. This form feels similar to a severe flu. Be sure to treat in a hospital to avoid relapses. After treatment, it is advisable to visit a sanatorium for complete recovery.
- Polyradiculoneuritis is a fairly common form, when the febrile form of the disease suddenly gives way to meningitis. The duration of the febrile form is about a week, inflammation of the meninges lasts about 2 weeks, recovery takes several months. The percentage of recovery with full recovery is high, the runs are generally positive. However, in this form, the development of ascending paralysis is possible.
- Meningeal is the most common form. Characterized by inflammation of the membranes of the brain. A characteristic symptom is stiffness of the neck muscles - the inability to tilt the head down and press the chin to the sternum. Symptoms include delirium, strabismus, inability to express one’s thoughts, and a sharp increase in temperature. Increased skin sensitivity and eye sensitivity to light are often noted. In mild forms it is relatively easy to treat and without consequences. After recovery, depression lasts from 2 to 12 months.
- Poliomyelitis form caused by damage to the spinal cord. General weakness gives way to nagging pain in the neck and back. The muscles become inflamed and swollen. Severe muscle pain is possible.
- Meningoencephalitic. The main signs are neurological signs - numbness of the tongue and facial muscles, shaking legs and arms, changes in behavior. This is one of the most dangerous forms, directly affecting brain cells. Changes can last a lifetime.
Unfortunately, it is impossible to predict the development of the disease in advance.
The only real protection against tick-borne encephalitis is vaccinations. Even a vaccination received in childhood seriously increases the incubation period of the disease. This gives you a chance to get medical help before the disease fully develops.
Recovery after illness
Medicine has advanced greatly. Nerve cells are restored, but this will require significant funds. You will also need therapy, massages, muscle stimulation, and restoration of sensitivity. Cases that were considered incurable just half a century ago can be cured. There is no need to despair, but it is still better to prevent the development of the disease with vaccinations and use personal aerosols in the forest. It is also worth taking care of closed clothing and, upon arriving home, carefully inspect each other for the presence of ticks. Contrary to rumors, ticks rarely bite in immediately. They spend quite a long time choosing the most vulnerable place - the armpit, groin area, stomach, scalp.
Diagnostics
The main parameters that experts focus on are the clinical characteristics of encephalitis, laboratory data, and epidemiological information.
- Clinical picture of encephalitis
. When examining a patient, a neurologist objectively assesses signs of damage to the patient’s systems and organs. It takes into account the complaints of a person suffering from encephalitis, the time of onset of the initial symptoms, and the sequence of their appearance.
- Laboratory data.
To establish a diagnosis, a blood and cerebrospinal fluid test is used using polymerase chain reaction (PCR). An additional method is to determine the antibody titer using serological methods and blood serum testing. This analysis is taken at intervals of two weeks. The level of antibodies in the sample and the dynamics of their changes depending on the time period that has passed since the onset of the disease are assessed.
- Epidemiological information.
To narrow the circle of people presumably suffering from encephalitis, information about the patient’s place of residence, the season during which the infection occurred, what foods the patient consumed, and his professional activities are analyzed.
What to do if you are bitten by a tick
If you are bitten, immediately, regardless of whether you have been vaccinated or not, place the insect removed from the skin into a glass jar with a lid and take it for examination. It's free. Look up the examination address for your area on the Internet.
When removing a tick, try not to tear off its head or crush its abdomen - this is fraught with unpleasant inflammation. But even if it’s torn off, bring what’s left for examination. For tissue analysis, the tick's head and its state of health are not a prerequisite.
What does a patient look like?
There are no external manifestations of tick-borne encephalitis - in the first phase it is impossible to distinguish it from other diseases without clinical studies. In people who have been bitten, the face turns red, sometimes there are pinpoint hemorrhages on the whites of the eyes and mucous membranes, and tearing. In severe cases, intoxication and weakness are so severe that the person is unable to lift his head from the pillow. In the vast majority of cases, there is no rash throughout the body - a similar sign is observed only in allergy sufferers, young children and people with weakened immune systems.
Below are photos of people after being bitten by an encephalitis tick.
Changes in appearance and behavior when a person is bitten by an infected tick appear in the second stage, when the virus attacks the nervous system. Tick-borne encephalitis can be recognized by the following manifestations:
- motor agitation, hallucinations, delusions;
- dysfunction of facial muscles (the face looks distorted, one eye does not close, speech is impaired, the voice becomes nasal);
- epileptic seizures;
- change and constant lacrimation due to irritation of the mucous membrane, strabismus, impaired movement of the eyeballs;
- minor muscle twitching, usually occurring after physical exertion, sometimes even minor;
- a specific pose with a bent back and head hanging down on the chest (the reason is weakness of the muscles of the neck, chest, arms);
- weakness of the lower extremities, muscle atrophy (observed very rarely).
Even in the presence of characteristic symptoms, an accurate diagnosis can be made only after a comprehensive examination of the patient. Signs of tick-borne encephalitis resemble manifestations of other diseases associated with damage to the nervous system, tumor processes and other pathologies.
REFERENCE! A patient with tick-borne encephalitis does not pose a danger to others at any stage, since in the human body the virus passes through the final stage of development and is unable to be transmitted further.
Prevention
Prevention of tick-borne encephalitis is pre-administered vaccinations. Only through vaccination and the presence of antibodies in the blood can one resist a viral infection.
Antibiotics can remove or reduce inflammation, fortifying drugs and bed rest will help restore health, but in reality, humanity has nothing against any virus - from influenza to encephalitis or smallpox - except vaccinations.
Ticks themselves are a problem. The toxins that ticks inject during a bite and release later are quite harmful and lead to weakening of the body. Small animals and young animals can die from multiple tick bites. Not from the volume of blood drunk - it is insignificant, but from the harmful effects of insect toxins.
When outdoors, be sure to use sprays that repel and kill ticks.
Initial signs in children and adults
The danger of tick-borne encephalitis lies in the fact that there are no specific signs in the first stages. An attached tick can easily be confused with a mole or wart, and after it falls off, a small red spot remains, on which a drop of blood may appear.
On the second day, redness, as a rule, increases, mild itching and rash may occur, but in an adult healthy person after a bite the signs are mild. If the wound becomes infected, slight suppuration may occur.
Elderly people, children and allergy sufferers suffer the most from tick bites. In such cases, severe allergic reactions, including Quincke's edema, are possible.
The first symptoms usually develop after a few days. They resemble ARVI or a severe cold, but occur without respiratory symptoms (cough, runny nose, sore throat). Sometimes the first phase of tick-borne encephalitis is confused with severe poisoning, especially in cases where it is accompanied by severe vomiting. The main differences are that patients do not have diarrhea, which is characteristic of such conditions. Sorbents like activated carbon also do not have an effect, since the pathogen is not in the digestive tract, but in the blood.
If you do not consult a doctor after the first symptoms appear, the disease will progress to the second stage, which is characterized by more severe symptoms and often leads to serious complications.
Is it possible to kill ticks?
In Soviet times, forests and parks were necessarily treated with special chemicals that killed ticks. This is quite an expensive pleasure, but in principle it is possible in our time. To do this, you need to contact our service and agree on the implementation of work to prevent insect activity.
Trees, grass and shrubs are treated with special chemicals that specifically target ticks. To achieve maximum processing efficiency, the area must be large, at least a hectare.
Read more about acaricidal anti-tick treatment - HERE!
What are the consequences after illness?
Tick-borne encephalitis can cause serious complications, including death.
With the Western subtype of the disease, the mortality rate is 2-3%, with the Far Eastern variety - about 20%. With irreversible damage to the nervous system, the patient may remain partially or completely disabled. People who have had to deal with complications of tick-borne encephalitis experience paralysis, muscle weakness, epileptic seizures, and persistent speech impairments.
It is impossible to restore impaired body functions, so the person and his loved ones will have to adapt to their condition and completely change their lifestyle.
Sources
- Boucher A., Herrmann JL, Morand P., Buzelé R., Crabol Y., Stahl JP, Mailles A. Epidemiology of infectious encephalitis causes in 2021. //Med. Mal. Infect. -2017. -Vol.v47. -No. 3. - p. 221-235.
- Bröker M., Kollaritsch H. After a tick bite in a tick-borne encephalitis virus endemic area: current positions about post-exposure treatment. // Vaccine. -2008. - Vol. 26. - No. 7. - p.v863-868.
- Crijnen YS., de Vries JM., Schreurs MWJ., Titulaer MJ. Clinical symptoms of patients with autoimmune encephalitis: a guide to timely recognition and treatment. //Ned. Tijdschr Geneeskd. -2019. - Vol. 163.
- Non-profit partnership “National Scientific Society of Infectious Diseases”. Clinical recommendations. Tick-borne viral encephalitis in adults. -2014.
- CDC. Vaccines and Immunizations
Feverish form
The course of tick-borne encephalitis of the febrile form is usually characterized by a condition inherent in fever. The duration of this form is no more than 10 days. Very often it has a wave character: the first rise in temperature is replaced by a state of subsidence of the initial symptoms, after which a recurrence of the disease is possible with characteristic new attacks that continue for several days.
After 8-10 days, the patient’s body temperature returns to normal, and his general health becomes much better. However, symptoms such as general weakness, palpitations, poor appetite, and sweating may be present in the patient for a whole month, even after the person has already recovered.
Treatment
All sick people must be hospitalized in a hospital (infectious diseases or neurological department)! They are shown strict bed rest. Patients should be kept in intensive care wards or under the constant supervision of medical personnel due to the unpredictability of the pathology. If complications develop, patients are transferred to the intensive care unit.
Drug treatment
- etiotropic therapy (directly aimed at destroying the pathogen) - specific donor immunoglobulin, homologous donor polyglobulin, leukocyte donor interferon, reaferon, laferon, intron-A, neovir, etc.;
- infusion therapy - solutions of glucose, Ringer, Trisol, Sterofundin;
- antipyretic drugs - paracetamol, infulgan. It is forbidden to use acetylsalicylic acid due to possible complications on the liver;
- glucocorticosteroids (methylprednisolone, prednisolone) - drugs in this group prevent damage to the brain and spinal cord, reduce their swelling;
- anticonvulsant therapy – sodium hydroxybutyrate, magnesium sulfate, sibazon;
- decongestants – mannitol, furosemide, l-lysine escinate;
- neurotrophics – complex B vitamins (neurorubin, milgamma);
- substances that improve microcirculation in the brain - thiotriazoline, trental, dipyridamole, actovegin;
- hyperbaric oxygenation.
During the recovery period, exercise therapy procedures, therapeutic massage, and classes with a rehabilitator are indicated.