Uterine fibroids are a chronic disease of the uterine body, manifested by the growth of one or several tumor-like nodes in its muscular layers. As a result, the size of the uterus increases and its shape becomes deformed. This leads to unpleasant symptoms - pathological bleeding, frequent urination, pain in the lower abdomen and pelvic region, and reproductive disorders. But this does not always happen - the signs of uterine fibroids in women depend on the number of nodes, as well as their size. In more than half of the cases, myomatous nodes are small in size and do not manifest themselves in any way.
The disease is very common. According to statistics, by the age of 45, up to 70-80% of women suffer from fibroids.
Treatment tactics depend on the stage of the tumor, the speed of its growth, and the age of the patient. Includes conservative and surgical methods. An asymptomatic course requires only regular monitoring by a gynecologist.
What are uterine fibroids: an explanation in accessible language
Myoma is a benign neoplasm localized in the muscular structure of the uterine wall. It is worth noting that this tumor is hormone-dependent, and in most cases is formed when a woman has certain hormonal abnormalities.
Myoma is a common disease that is most often diagnosed in women after 35–40 years of age. It is worth noting that today the disease has become significantly “rejuvenated” and can be detected during reproductive age. Having heard a frightening diagnosis from a doctor, many patients begin to panic, but is it really so dangerous? Let's look at what uterine fibroids are in women, and also talk about all the important nuances associated with this problem.
Ultrasound with Doppler and alternative diagnostics - MRI
Proliferating fibroids are ideally diagnosed using Doppler ultrasound. This examination is also necessary if there is a suspicion of malignant degeneration of a myomatous node (cancer) or endometrial tumor and ovarian tumor. Using color Doppler ultrasound, it is possible to assess blood flow and establish vascular resistance, the presence of intense neovascularization and other signs indicating the quality of tumors.
An alternative examination is magnetic resonance therapy. MRI gives fairly clear results in diagnosing these tumors, but such a study is dangerous, since it is associated with little-studied magnetic scanning, so it is not prescribed unnecessarily.
How is tumor size determined?
When pathology occurs, the muscle cells of an organ in a certain area are exposed to harmful factors and begin to actively divide. In this connection, a myomatous node is formed, the further growth of which provokes an enlargement of the uterus.
The parameters of the lesion can vary from several mm. up to several cm. To find out the parameters of fibroids, the patient is initially sent for an ultrasound and MRI of the pelvis. To calculate the size of the tumor, the doctor uses a table that lists the size of the uterus during different periods of pregnancy, so doctors also indicate the size of fibroids in weeks of pregnancy.
The ICD 10 code for uterine fibroids is D25.
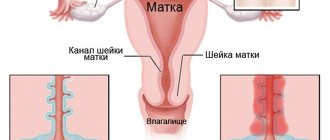
Types of fibroids
Depending on the location of the myomatous node, there are 3 types of tumor:
| Type of fibroids | Localization |
| Submucosal | Formed on the surface of the uterine membrane in the internal cavity. |
| Subserosal | It is localized on the outside of the uterine wall, under the serous layer, which protects the body of the organ from adjacent systems. |
| Intramural | Located in the thickness of the muscle layer. |
| Interligamentous | Pedunculated fibroids often present a diagnostic problem due to significantly difficult differentiation with ovarian neoplasms |
| Cervical | The myomatous node is located in the cervix; first of all, attention is drawn to the enlargement due to the node and deformation of the cervix |
| Parasitic | Subserous fibroids that receive nutrition from neighboring organs with which they have intimate fusion |
With age, the risk of pathology increases. By the age of 30, various disorders in a woman’s body can push uterine cells to divide. It takes about 5 years for an easily diagnosed fibroid to form.
Classification of myomatous formations
The body of the uterus consists of a muscular layer and a mucous membrane that lines its inside.
Myomatous formations are localized in muscle connective tissue. The source of their growth growth is one defective cell, which undergoes certain changes and begins to divide at a faster rate than neighboring ones.
As a result, a myomatous node appears - a local accumulation of chaotically intertwined smooth muscle fibers. On average, its dimensions range from a few millimeters to several centimeters. However, sometimes very large tumors occur. Some reach a weight of several kilograms.
Myomatous cells practically do not degenerate into malignant ones. This happens in less than 1% of cases.
Attention! Even the rapid growth of fibroids is not a sign of its malignancy
Fibroids of the uterine body can be located in different layers. Based on these characteristics, nodes are divided into the following types:
- Submucosal or submucosal - grows into the uterine cavity. It can protrude inward completely, half or less.
- Intramural or intermuscular - located inside the wall of the organ.
- Subserous or subperitoneal - protrudes outside (into the peritoneum).
Among these types there is fibroid, which grows on a stalk.
Causes
The most important aspect of the etiology of uterine fibroids—the initiator of tumor growth—remains unknown, although theories of its occurrence exist. One of them confirms that an increase in the level of estrogen and progesterone leads to an increase in mitotic activity, which can contribute to the formation of fibroid nodes. Another hypothesis suggests the presence of congenital genetically determined pathology of the myometrium in women with uterine fibroids, expressed in an increase in the number of estrogen receptors in the myometrium. The presence of a genetic predisposition to uterine fibroids indirectly indicates the ethnic and family nature of the disease.
In addition, the risk of uterine fibroids is higher in nulliparous women, who may have a large number of anovulatory cycles, as well as obesity. According to one hypothesis, estrogens play a fundamental role in the pathogenesis of uterine fibroids. However, it is impossible to talk about the fundamental importance of estrogens independently of progesterone, since the content of progesterone in the blood, like estrogens, changes cyclically during reproductive age, and is also significantly increased during pregnancy and decreased after menopause.
Thus, clinical and laboratory studies suggest that both estrogens and progesterone may be important stimulators of fibroid growth
Risk factors associated with the development of fibroids
- Early menarche.
- No history of childbirth.
- Age (late reproductive period).
- Obesity.
- African American race.
- Taking tamoxifen.
- High parity.
- Menopause.
- Smoking.
- Taking COCs.
- Hormonal therapy.
- Nutritional factors.
- Foreign estrogens.
- Geographical factor.
Symptoms and signs of uterine fibroids
At the initial stage of fibroid formation, pathology rarely manifests itself. Alarming symptoms and signs appear mainly when the tumor reaches a large scale, due to which intra-abdominal pressure increases several times. The disease can be recognized by several manifestations of the disease, the main ones include:
- instability of the menstrual cycle;
- long (more than 7 days), heavy menstruation;
- frequent bleeding;
- the presence of pain during sexual intercourse;
- defecation disorder;
- increased urination;
- the impossibility of conceiving a child without diagnosing any abnormalities in the woman’s health;
- pain in the lower abdomen, feeling of tightness;
- an increase in abdominal circumference unrelated to weight gain;
- feeling of pain in the pelvis, pain in the lower back, pain during sexual intercourse;
- spasms in the lower extremities.
Important! Only a doctor can identify the disease at an early stage, which is why the recommendation to regularly visit a gynecologist is not empty words. If the formation is not sufficiently visualized, the doctor prescribes an ultrasound examination (ultrasound). The information content of this procedure for diagnosing pathology is 95%.
Advanced fibroids can lead to dysfunction in various body systems.
Brief explanations of this thesis are given in the table.
| Name of organs (body systems) susceptible to the negative effects of uterine fibroids | Brief explanations of the occurrence of pathology |
| Gastrointestinal tract | Compression of the intestines (including the rectum) causes:
|
| Blood system | The tumor, causing prolonged bleeding, causes iron deficiency anemia. Signs of the disease often include:
|
| urinary system | The blood supply to the bladder and kidneys is disrupted due to compression, this can lead to:
|
| Fertile function (child-bearing function) | The tumor, growing into the uterine cavity, creates an obstacle to full gestation of the fetus. In some cases, it provokes the occurrence of infertility. |
During menopause, there is a high risk of degeneration of a benign tumor into a malignant tumor if uterine fibroids do not regress in the first 1 to 2 years of postmenopause. This circumstance, supported by the above facts, confirms the importance of prevention and timely treatment of pathology.
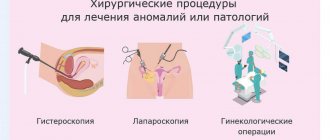
Surgeries to remove fibroids: types and prices
After the doctor has decided on the need for surgical intervention, a set of data is analyzed to select a procedure. Depending on the patient’s age, her health and the size of the tumor, the tumor can be removed in different ways.
Doctor's advice
Uterine fibroids are diagnosed in 77% of women of reproductive age, while various symptoms associated with this disease are recorded in only 25% of cases. Thus, with asymptomatic fibroids, with the exception of large tumors, there is no reason to prescribe medications
Olga Zorina Pregnancy and childbirth, Gynecologist, Gynecologist-endocrinologist
Below is a table of the main types of surgical interventions for the operation with descriptions and prices:
| Type of transaction | Dimensions of the tumor in mm. | Description | Average price for surgery to remove fibroids in Moscow |
| Laparoscopy | 8 — 10 | Small incisions (approximately 15 mm) are made in the abdominal cavity, a laparoscope is inserted into the uterus, the fibroids are removed, and the uterus is preserved. The procedure does not leave scars. Recovery after surgery takes several days. | 86 thousand rubles. |
| Hysterectomy | 60 – 100+ | Abdominal surgery to remove the uterus. Used in the following cases:
| 110 thousand rubles |
| Hysteroscopy | 50 — 60 | Surgical intervention is performed using intravaginal equipment. | 70 thousand rubles. |
| Abdominal surgery | 60 — 100 | Laparotomy is performed through an incision in the abdominal cavity, the uterus is preserved. The recovery period is 14 days. | 125 thousand rubles. |
| Uterine artery embolization | up to 60 | Injection of a special substance to prevent the growth of fibroids. | 185 thousand rubles. |
Uterine artery embolization is considered a popular and safe service, the price of which is from 120 thousand rubles.
At the same time, it is worth considering that the final price for tumor removal depends on its parameters and location, as well as on the general well-being of the patient.
Treatment with Mirena coil
The Mirena intrauterine device for uterine leiomyoma is a hormonal IUD of the latest generation and is used for contraception and treatment. Thanks to the main active ingredient - levonorgestrel, the endometrium is thinned, the blood supply to the tumor is reduced, as a result of which many symptoms of uterine leiomyoma disappear.
The use of Mirena for uterine leiomyoma allows you to achieve the following results:
- cessation of intermenstrual bleeding;
- reduction in the volume of menstrual flow;
- elimination of painful sensations in the lower abdomen characteristic of leiomyoma;
- reducing pressure on nearby organs (with subserous leiomyoma);
- improvement of general well-being.
However, the main advantage of the Mirena spiral is that its use helps to reduce the myomatous node itself. Thanks to the normalization of hormonal balance, the tumor loses its stimulus for development. In addition, Mirena helps prevent the development of endometriosis, hyperplastic processes of the endometrium, often accompanying leiomyoma.
When size matters: indications for surgery
To describe a tumor, a gradation is used based on the size of the tumor:
- small fibroids correspond to a diameter of up to 20 mm;
- the range of the average neoplasm is 20-60 mm;
- large tumor extends beyond 60 mm.
Indication for surgery is the size of the fibroid more than 12 weeks of pregnancy.
It is worth noting that size is not the only indication for surgery. A list of other reasons for surgical intervention is given in the table.
| Indications for surgery | Brief explanations |
| Changes in the functioning of the intestines and organs of the genitourinary system | The neoplasm puts pressure on the kidneys and (or) bladder, intestines, causing disturbances in the functioning of organs. |
| Severe pain syndrome | In some cases, the tumor provokes pain, which is not relieved after taking medications. |
| Concomitant gynecological diseases | The combination of uterine fibroids and gynecological diseases can aggravate the indicated pathologies. |
| Negative effects on the blood system | Repeated blood tests show that the neoplasm caused anemia. |
| Intensive tumor growth | The annual growth of the tumor exceeds 4-5 weeks of pregnancy. |
| Postmenopausal period | This period is dangerous due to the degeneration of a benign tumor into a malignant one. |
| Growth of fibroids during menopause | — |
| Infertility due to fibroids | — |
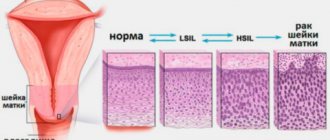
Oncological alertness should be raised by women entering menopause with large tumor sizes, nodes of submucosal localization or with centripetal growth, with recurrent and atypical endometrial hyperplasia, with a combination of uterine fibroids and adenomyosis of II-III degree, in the absence of regression of fibroids existing against the background of prolonged age-related involution of the uterus. This option is especially dangerous, since proliferative processes in myomatous nodes are hormonally independent. Such fibroids are a stage on the path to the appearance of sarcoma.
Olga Zorina
Pregnancy and childbirth, Gynecologist, Gynecologist-endocrinologist
Is it possible to avoid surgery?
Conservative treatment of uterine fibroids is used in modern medicine as:
- alternative to surgery;
- preparation for surgery.
The main treatment methods with explanations for them are shown in the table.
| Treatment methods | Explanations |
| Taking medications that suppress the production of female hormones (estrogens and androgens) | Over 6 months, the tumor decreases by 2 times. Flaws:
|
| FUS ablation | The pathological formation is evaporated by an ultrasonic beam. The exact focus of the beam is adjusted by a specialist using MRI. The obvious advantages of the procedure are:
|
| Carrying out symptomatic and restorative therapy | This method includes:
|
Conservative therapy: Ginesteril
Conservative treatment of fibroids is based on taking medications that correct hormonal imbalances. Based on patient reviews, we can mention the effectiveness of drugs such as Ginestril and boron uterus in the treatment of uterine fibroids.
The use of Ginestril in the treatment of uterine fibroids
Ginestril is a hormonal drug that, according to women, helps to overcome the disease. Thanks to the positive effect of the drug, when taken, it is possible to influence the growth of the tumor, and in case of small-scale tumors, completely get rid of it. In addition, Ginestril is prescribed after surgery to remove myomatous nodes to prevent relapses.
You can be treated with Genistril if the fibroid does not exceed its size for more than 12 weeks. Treatment is carried out for 3 months. The tablets are taken once a day, 1 piece, after the operation the medicine is taken every other day.
Traditional medicine: Borovaya uterus
The herb boron uterus is used in the treatment of all types of myomatous nodes, the size of which is less than 1 cm. According to customer reviews, when using boron uterus, in some cases complete resorption of the tumor or a halt in its development was noted.
A decoction of this herb can be taken orally, as well as douching. The minimum course of treatment is 3 months; during menstruation, taking the drug is suspended and resumed exactly 7 days later.
How to take boron uterus for fibroids, see the table:
| Method of application | How to prepare the solution | Dosage |
| Decoction | For 250 ml. put 1 tbsp of water. l. herbs, after boiling the broth, put the container on low heat for another 5 minutes. Then strain the resulting mixture and pour it into a thermos. | 1/3 tbsp. 3 – 4 rubles/day |
| Tincture | 5 tbsp. l. Borovaya uterus should be filled with 500 ml. vodka. Place the sealed bottle in a dark place and leave for 3 weeks. After which the product must be filtered and consumed orally. | 1 tsp. before meals 3 rubles/day. |
| Douching solution | Add to 1 l. water 5 tbsp. l of herbal mixture and boil for 15 minutes, then remove the boiling water from the stove and let it sit for about 6 hours. | Douching should be done 2 times a day - in the morning and before bedtime. |
Contraindications
Methods for removing myomatous nodes are different. Surgeries with a wide incision are more traumatic and more difficult for patients to tolerate than interventions using minimally invasive and endoscopic methods. For all types of surgical procedures to remove uterine fibroids, there are a number of general contraindications:
- Inflammatory processes of any localization.
- Chronic somatic diseases in the acute stage.
- Hematological diseases characterized by severe pathologies of blood clotting.
Is it possible to get pregnant with uterine fibroids?
Women of reproductive age are especially concerned about the question: is pregnancy possible with uterine fibroids? This type of tumor is not a contraindication for conceiving a child. However, before preparing to plan a baby, you need to consult a gynecologist and reproductive specialist.
Patients with uterine fibroids have every chance of successful conception, but it is still worth taking into account some circumstances - the location of the nodes, their number, the presence/absence of uterine deformation.
In addition, during pregnancy, the disease can provoke miscarriage, early birth, various complications of labor, and in some cases negatively affects the intrauterine development of the fetus. Therefore, pregnant women should approach their situation with special care and constantly be under medical supervision.
During pregnancy
Pregnancy can cause the formation of uterine fibroids, since at the time of gestation a significant change in hormonal levels occurs. But such pathology, as a rule, resolves after the birth of the child and does not affect his health in any way. Symptoms of the disease practically do not appear and do not cause discomfort, and the growth of the pathology stops until childbirth. If a tumor formation progresses in the body of a pregnant girl, the following consequences are possible:
- premature birth (up to 37 weeks), if the myomatous node is located next to the placenta;
- in early pregnancy, fibroids can cause miscarriage;
- incomplete detachment of the placenta, which is accompanied by hemorrhages;
- unnatural position of the embryo caused by deformation of the uterine cavity;
- deterioration of the contractile function of the reproductive organ, which is necessary for natural childbirth.
As a rule, if a woman has fibroids during pregnancy, she is recommended to have a caesarean section (artificial birth) instead of a natural birth. With the help of such an event, not only does the chance of manifestation of all sorts of consequences decrease, but also, during surgery, experienced surgeons are able to remove pathogenic tumor nodes.
However, due to all the complications described above, the woman should calm down, because the myomatous node does not in any way affect the development and health of her baby.
What not to do with uterine fibroids: clinical recommendations
When the diagnosis is confirmed, a woman should adjust her usual lifestyle, follow the doctor’s clinical recommendations and, if possible, eliminate bad habits, these include:
- any stressful situations;
- severe physical loads;
- carry weights (more than 3 kg);
- visit the solarium;
- overheat in a bathhouse/sauna;
- attend some cosmetic and massage procedures (acupuncture, lymphatic drainage, cavitation, massage of the buttocks and abdomen).
A woman should more carefully monitor her mental and physiological state. You should follow the correct rest and work schedule, as well as enrich your daily diet with healthy, fortified foods.
Results: about the most important in three theses
- Knowing that there are no symptoms of the disease in the initial stages, do not neglect regular visits to the gynecologist.
- Exercise and eat right. These measures will help get rid of the main causes of the disease: stagnation of blood in the pelvis and hormonal disorders.
- If you have been diagnosed with a pathology, do not delay treatment. Remember that advanced fibroids have a negative impact on adjacent organs and can transform into a malignant neoplasm.
Do not neglect visits to the gynecologist and be healthy!
For more information about the disease, watch the video:
This article has been verified by Olga Zorina, a current qualified physician, and can be considered a reliable source of information for site users.
Rate how helpful this article was
5 2 people voted, average rating 5
Did you like the article? Save it to your wall so you don’t lose it!
Popular questions
Good afternoon, I am 31 years old, I have fibroids.
Buserelin spray was prescribed for 2 months. If side effects occur, tell me if there are any medications. I’m very afraid because according to reviews it’s a very scary drug. And approximately how long does it take for side effects to appear? Hello! You should follow the recommendations of your doctor. When using this drug, drug-induced menopause occurs. This may be accompanied by vegetative manifestations - fever, hot flashes, mood swings, sleep disturbance and genitourinary syndrome - dryness in the genital tract. The use of climafemin Ginocomfort will help improve your well-being, and the Ginocomfort gel with mallow extract will cope with dryness.
Hello, I am 47 years old, I have multiple uterine fibroids, two fibroids, large and medium (76 mm and 40 mm) had blood flow along the periphery, yesterday I had an ultrasound on the same machine and by the same doctor, it turned out that the large fibroid was not the same size has changed, but there is no blood flow, can this be the case, until yesterday I had an ultrasound scan there 2 times, once every six months and the blood flow was IR 0.5 and IR 0.55 in the periphery, what is this fraught with, could there be necrosis due to malnutrition ? and can it shrink in size without blood flow?
Hello! A decrease in blood circulation in the nodes of uterine fibroids indicates the process of completing the growth of the formation. This requires ultrasound control after 3 months. In the absence of pain, fever, or ultrasound changes in the node described as necrosis, it is impossible to assume this process.
Good day. We discovered a 45mm fibroid (Submucosal) and there is bleeding after menstruation. It's been 2 weeks already. The doctor talks about the operation. I'm waiting for the commission. What operation is done in this case? They scared me that it was possible to remove the uterus. I'm 38 and still want to give birth.
Hello! You should tell your doctor about your reproductive plans. This will resolve the issue in favor of organ-sparing surgery - conservative myomectomy. The method - hysteroscopic or strip surgery - is decided collectively, taking into account technical capabilities, medical practice, type of submucosal node, its location, etc.
Is it possible to place Klinon-D suppositories after conization of the cervix?
Hello! If your doctor recommends their use, then use them.
For an accurate diagnosis, contact a specialist